Growing Organs from Your Own Cells
Growing Organs from Your Own Cells
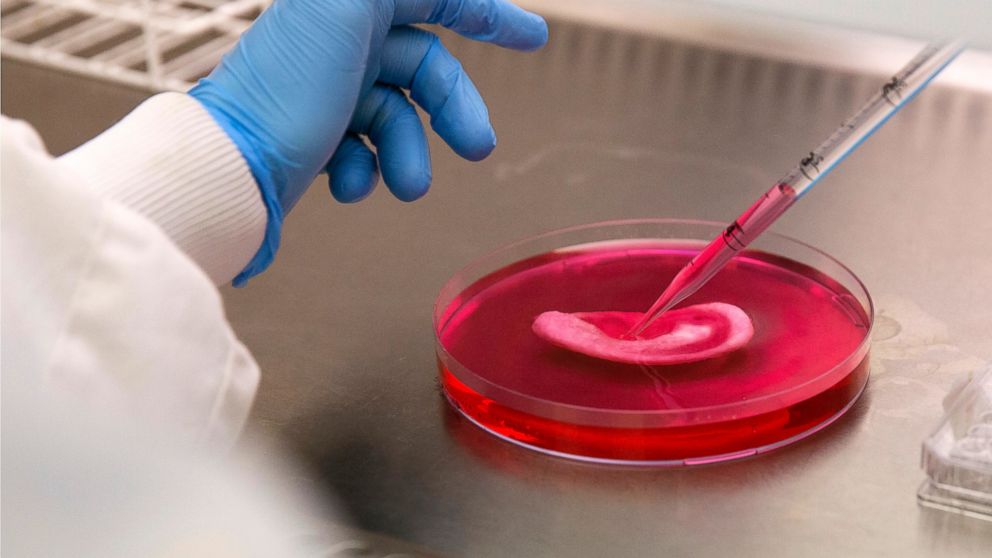
The Future of Medicine: The Promise of Growing Organs from Your Own Cells
In recent years, the world of medicine has seen incredible breakthroughs, and one of the most exciting developments is the ability to grow complex tissues and organs from a person’s own cells. Renowned theoretical physicist Michio Kaku has predicted that in the near future, medical science will evolve to the point where organ failure becomes a thing of the past. “Already from your own cells, scientists can grow skin, cartilage, noses, blood vessels, bladders, and windpipes. In the future, scientists will grow more complex organs, like livers and kidneys. The phrase ‘organ failure’ will disappear,” Kaku says. This vision of the future is not far from reality, and it opens up new possibilities for the treatment of organ diseases and the advancement of personalized medicine.
The Power of Regenerative Medicine
The idea of growing organs from one’s own cells may seem like science fiction, but it is grounded in a field of study known as regenerative medicine. Regenerative medicine involves the use of stem cells and tissue engineering to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs. Scientists have already made significant progress in creating functional tissues from a patient’s own cells, which greatly reduces the risk of rejection that can occur with donor organs.
For instance, researchers have successfully grown skin for burn victims, cartilage for joint repair, and blood vessels for patients with circulatory issues. Bladders and windpipes have also been successfully grown and transplanted into patients. These advances show that the process of growing organs is not only possible but is already being applied in clinical settings.
Growing More Complex Organs: A Step Toward the Future
While growing simple tissues is already a reality, the challenge now lies in creating more complex organs, such as livers and kidneys. These organs have intricate structures and perform highly specialized functions that are difficult to replicate. However, scientists are making strides in this area. For example, researchers are working on developing liver tissue using stem cells, which could one day lead to fully functional, lab-grown livers for transplant. Similarly, scientists are exploring ways to grow kidneys and even heart tissues, which could alleviate the shortage of organs available for transplant.
One approach to growing complex organs involves using 3D bioprinting technology, which allows scientists to “print” tissues layer by layer using living cells. This technology has the potential to create organs with highly organized structures that mimic the complexity of human organs. With this technology, it’s possible that in the future, we could grow entire organs such as livers, kidneys, or even hearts from a patient’s own cells.
The Benefits of Personalized Organ Growth
One of the most significant advantages of growing organs from a person’s own cells is the reduction of the risk of organ rejection. In traditional organ transplants, patients must take immunosuppressive drugs to prevent their bodies from rejecting the new organ, which can have harmful side effects. However, with lab-grown organs created from a patient’s own cells, the risk of rejection is dramatically reduced, as the organ is genetically identical to the patient’s body.
In addition, personalized organs would eliminate the need for long waiting lists and organ shortages. Every year, thousands of people around the world die waiting for organ transplants. By growing organs on demand, this crisis could be alleviated, offering new hope to patients in need.
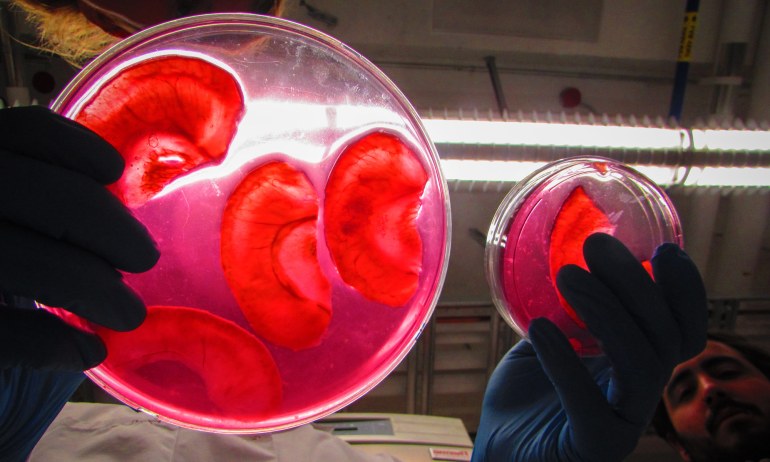
Overcoming Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the potential for organ growth is immense, there are still several hurdles to overcome. One of the biggest challenges is the complexity of replicating the full functionality of organs like the liver or kidney. Organs are not just collections of cells; they have complex vascular systems and intricate tissue structures that must work together to function properly. Scientists are still working to understand how to create these structures and ensure that lab-grown organs can perform all the necessary tasks.
There are also ethical considerations to address. As we move toward growing human organs in labs, questions around the use of stem cells, genetic manipulation, and the potential for organ trafficking must be carefully considered. These ethical issues will require regulation and oversight to ensure that the technology is used responsibly and safely.
Conclusion
Michio Kaku’s vision of a future without organ failure is one that seems increasingly achievable. As scientists continue to refine techniques for growing organs from a patient’s own cells, the possibilities for treating organ failure become limitless. The ability to create personalized, lab-grown organs could revolutionize medicine, eliminating the need for organ transplants and offering a future where organ failure is no longer a death sentence. While challenges remain, the promise of regenerative medicine is a beacon of hope for patients and families affected by organ failure, and it is a testament to the remarkable advances of modern science.
News in the same category

Terminally Ill Man is Warning Others to Not Make The Same Mistake He Made
10 Natural Home Remedies To Help Lower High Blood Pressure
Scientists have discovered a key genetic factor that explains why women’s brains age at a different rate than men’s.
Experts who predicted covid say new virus appearing in US could threaten 'all of mankind'

Why Your Brain ‘Blinds’ You for Two Hours Each Day
11 Reasons Why You Have Red Dots On Your Skin

The Benefits and Potential Dangers of Eating Tilapia Fish

Cancer Doctor Reveals ‘Common Theme’ Seen Regularly In Patients Before Diagnosis

How Often Should You Change Your Underwear?

WHO issues its first-ever reports on tests and treatments for fungal infections

Scientists Have Officially Measured the Speed Limit of Human Thought

How Your Sleeping Position Affects Your Health
Only People With Perfect Color Vision Can Read These Words

What Does It Mean When A Person Who Has Passed Away Appears In Your Dream

Discover the Incredible Health Benefits of Melon Seeds

Are you over 40? LONGEVITY SECRETS You Need to KNOW!
Hidden Benefits of Herbs: This Article Reveals It All!

Over 200 People Are Killed By The “World’s Deadliest Food” Every Year, But Almost 500 Million People Still Eat It
Man Loses Pulse For 45 Minutes, Wakes Up, And Reveals This Spine-Chilling Vision Of Afterlife
News Post

8 cancer-killing foods you didn't consider!

Terminally Ill Man is Warning Others to Not Make The Same Mistake He Made

10 Natural Home Remedies To Help Lower High Blood Pressure

Scientists have discovered a key genetic factor that explains why women’s brains age at a different rate than men’s.

The Hidden Power of Garlic Peels: Benefits for Your Health, Garden, and More

Experts who predicted covid say new virus appearing in US could threaten 'all of mankind'

Why Your Brain ‘Blinds’ You for Two Hours Each Day

Castor Oil: Discover the Transformative Effects After Just 7 Days

11 Reasons Why You Have Red Dots On Your Skin

The Benefits and Potential Dangers of Eating Tilapia Fish

My 32-Year-Old Son Threw a Wild Birthday Party at My House and Nearly Destroyed It

I Was Looking At a Photo of My Late Wife and Me When Something Fell Out of the Frame and Made Me Go Pale

My Husband Moved Back in with His Mom Because My Cough 'Was Annoying' While I Was Sick with Our Baby – So I Taught Him a Lesson

Cancer Doctor Reveals ‘Common Theme’ Seen Regularly In Patients Before Diagnosis

My Husband Threw $50 at Me and Said, 'Make a Lavish Christmas Dinner for My Family — Don't Embarrass Me!'

My Husband’s Best Friend Moved in Weeks Ago, Expecting Me to Clean after Him – Husband Sided with Him, So I Taught

How Often Should You Change Your Underwear?

WHO issues its first-ever reports on tests and treatments for fungal infections

Scientists Have Officially Measured the Speed Limit of Human Thought
