
The Hidden Truth About Tinnitus: Why That Ringing in Your Ears Shouldn’t Be Ignored
That constant ringing, buzzing, or hissing in your ears may seem harmless, but experts warn it can signal deeper health issues.
Tinnitus is more than just an annoyance—it’s often a clue to underlying problems that deserve immediate attention.
What Exactly Is Tinnitus?
Tinnitus is not a disease on its own but a symptom of another condition. It manifests as a persistent sound in the ears with no external source. People often describe it as ringing, humming, whistling, or even whooshing noises. While it may come and go for some, others experience it continuously, making daily life frustrating, distracting, and emotionally draining.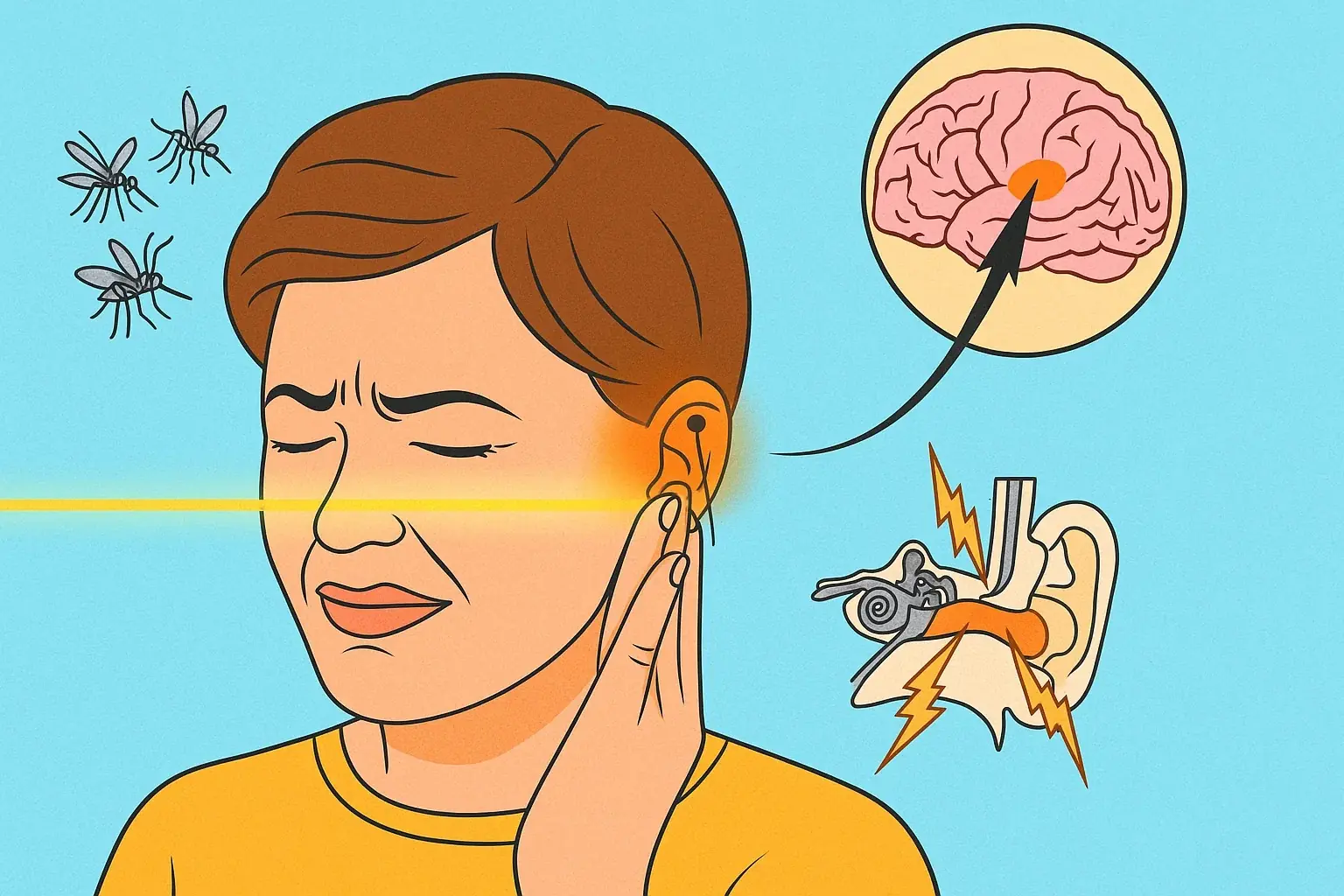
This condition can interfere with concentration, sleep, and overall quality of life. In severe cases, it can lead to heightened stress, irritability, or even anxiety. Understanding what triggers tinnitus is essential to finding relief.
Common Causes of Tinnitus
- Ear Damage
The human ear is a delicate organ, consisting of three main parts:
- Outer ear – the visible auricle and the ear canal.
- Middle ear – home to the eardrum and three tiny bones (ossicles) that transmit sound vibrations.
- Inner ear – which contains the cochlea and auditory nerve, responsible for sending signals to the brain.
Damage to the middle or inner ear can interrupt sound transmission or distort how the brain interprets signals, leading to tinnitus. In some cases, growths or tumors pressing on the auditory nerve may cause ongoing ringing or buzzing.
- Prolonged Noise Exposure
Extended exposure to loud environments is one of the leading contributors to tinnitus. Individuals most at risk include:
- Factory and construction workers operating heavy machinery such as hydraulic hammers.
- Musicians, concertgoers, and nightclub staff frequently exposed to loud music.
- People who use headphones at high volumes for long periods.
Over time, repeated noise trauma damages tiny hair cells inside the cochlea, which cannot regenerate, resulting in permanent hearing changes and tinnitus.
- Medication-Related Triggers
Certain drugs are known to produce or worsen tinnitus as a side effect. These include:
- Specific antibiotics
- High doses of aspirin
- Certain diuretics and antidepressants
Doctors often refer to these as ototoxic medications, meaning they can negatively affect hearing or balance. Patients who experience ringing after starting new medication should consult a healthcare provider promptly.
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders
The TMJ joint, which connects the jawbone to the skull, may also play a role in tinnitus. Misalignment of the jaw, teeth grinding (bruxism), or chronic inflammation can put stress on the ear structures, leading to ringing or buzzing sensations. Addressing TMJ problems through dental care, therapy, or physical exercises can often reduce tinnitus symptoms.
Final Thoughts
Tinnitus is a complex condition with many potential triggers—ranging from ear damage and noise exposure to medication side effects and TMJ disorders. While some cases may be temporary, persistent or worsening symptoms should never be ignored.
Seeking professional evaluation is crucial, as identifying the root cause can lead to targeted treatments, lifestyle adjustments, or therapies that provide lasting relief. Remember, tinnitus is more than a nuisance—it’s a signal from your body that something deserves closer attention.
News in the same category


8 Teas to Drink for a Healthier Body and Mind

DIY Turmeric & Ginger Shots to Fight Inflammation, Boost Immunity & Soothe Your Gut

Coconut water: Is It Good for You, Nutrition, Benefits, Side Effects (Science Based)

Clean Arteries: 10 Foods to Eat Daily
10 Warning Signs of Parasites in Your Body

Diet and Uric Acid: Foods to Avoid for Gout Prevention

8 Foods That Help Eliminate Cancer Cells
Natural Remedies to Address Skin Tags, Warts, and Blackheads

The Deficiency of These Vitamins Contributes to Panic Attacks

25-Year-Old Groom Dies from Acute Liver Failure After Eating Chicken – Doctors Warn of One Critical Danger!
Doctors caution people with pre-existing liver conditions, weakened immune systems, or chronic illnesses to exercise extra care when handling poultry and other high-risk.
What Your Legs Can’t Say, Your Vagina Can — The Truth About the Female Body Most People Don’t Know
9 Areas Where Itching Could Signal Malignant Tumors — #7 Happens Most Often

The World’s Deadliest Food Kills 200 People Every Year — Yet 500 Million Still Eat It
Despite its deadly reputation, millions of people continue to eat this every day without issue.

Doctor Warns on TikTok: The Hidden Dangers of Kissing the Dying
Boosting Fertility: The Surprising Power of Lifestyle on Semen Quality and Reproductive Health
In many cases, the most effective solutions are already within reach—on your plate, in your daily habits, and in the way you manage your mental well-being.
3 Dangerous Habits of Husbands That Secretly Put Their Wives at Higher Risk of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer doesn’t just come from genetics or lifestyle — sometimes, it’s fueled by a husband’s hidden habits. These three common behaviors may seem harmless, but they silently put wives at serious risk if not stopped in time.

How many eggs should you eat a week?
News Post

Parasite Cleanses: Do They Really Improve Your Gut Health — and Are They Safe?

8 Teas to Drink for a Healthier Body and Mind

DIY Turmeric & Ginger Shots to Fight Inflammation, Boost Immunity & Soothe Your Gut

Coconut water: Is It Good for You, Nutrition, Benefits, Side Effects (Science Based)

Clean Arteries: 10 Foods to Eat Daily

10 Warning Signs of Parasites in Your Body

Diet and Uric Acid: Foods to Avoid for Gout Prevention

Hiker Encounters Massive Snake Camouflaged Along South Carolina Creek

8 Foods That Help Eliminate Cancer Cells

David Quammen, the COVID Predictor Warns of New Pandemic Threats

Natural Remedies to Address Skin Tags, Warts, and Blackheads

Tips for Selecting Fresh Pork at the Market

The Deficiency of These Vitamins Contributes to Panic Attacks

Researchers Find Higher Intelligence Is Correlated With Left-Wing Beliefs and Seems to Be Genetic

Urgent Health Warning Issued After Pigs With ‘Neon Blue’ Flesh Are Discovered in One Specific Part of the Us

25-Year-Old Groom Dies from Acute Liver Failure After Eating Chicken – Doctors Warn of One Critical Danger!
Doctors caution people with pre-existing liver conditions, weakened immune systems, or chronic illnesses to exercise extra care when handling poultry and other high-risk.

What Your Legs Can’t Say, Your Vagina Can — The Truth About the Female Body Most People Don’t Know

9 Areas Where Itching Could Signal Malignant Tumors — #7 Happens Most Often

The World’s Deadliest Food Kills 200 People Every Year — Yet 500 Million Still Eat It
Despite its deadly reputation, millions of people continue to eat this every day without issue.