The Key to Everlasting Memories? Scientists discovered the "glue" that makes memories stick!
Memories are the essence of who we are. They shape our personalities, guide our decisions, and connect us to the people we love. But what makes some memories last a lifetime while others fade away? For years, scientists have been trying to unlock the mysteries of memory—how it is formed, stored, and recalled. Now, in a groundbreaking discovery, researchers believe they have identified the “glue” that makes memories stick: a protein that helps stabilize neural connections in the brain.
The protein is called PKM-zeta (Protein Kinase M-zeta), and it plays a critical role in the process of memory consolidation—the transformation of short-term memories into long-term ones. When we learn something new, our brain forms connections between neurons, known as synapses. These connections strengthen with repetition and become the basis for memory. However, for a long time, scientists were puzzled as to how these connections remained stable for years, or even decades. The answer, it seems, lies in PKM-zeta.
In experiments conducted at leading neuroscience labs, researchers found that increased levels of PKM-zeta in certain parts of the brain led to stronger, more permanent memories. When the protein was blocked, even well-established memories began to fade. In contrast, when PKM-zeta was enhanced, it appeared to “lock” the memory in place. One scientist described it as “the molecular Velcro of the brain,” holding together the pieces of experience that would otherwise drift apart.
The implications of this discovery are enormous. Understanding how PKM-zeta functions could lead to new treatments for memory-related conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, dementia, and even post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Imagine being able to enhance positive memories while gently erasing traumatic ones. With further research, that could become a reality.
Moreover, this knowledge could be used in the field of education. If scientists can find safe ways to stimulate PKM-zeta during learning, students might be able to retain information more effectively and for longer periods of time. This could revolutionize how we approach everything from studying for exams to learning new languages or skills.
Of course, as with any discovery, ethical questions arise. Should we have the power to selectively erase or enhance memories? What happens to our identity if we can alter the past we remember? These are deep philosophical questions that society must consider as science advances.
For now, the focus is on understanding how this memory “glue” works and how it can be used to help people. Researchers caution that we are still in the early stages of turning this discovery into practical treatments, but the progress is promising. Already, animal studies have shown that manipulating PKM-zeta can drastically alter behavior and memory retention. The next step is translating those results into human applications.
Memory is not just a technical process; it’s deeply emotional. A scent, a song, or a photograph can instantly bring us back to a moment long gone. With the discovery of the molecular glue behind memory, scientists are one step closer to unraveling one of the brain’s greatest mysteries.
In conclusion, the discovery of PKM-zeta as the protein responsible for memory stabilization is a monumental step in neuroscience. It not only deepens our understanding of how the brain works but opens up exciting possibilities for the future. Whether it’s preserving precious memories or treating memory loss, the "glue" that makes memories stick could one day change countless lives.
News in the same category


A Common Drug Used in Tylenol, Excedrin, and More Was Just Linked to ADHD

Pulsatile Tinnitus: Why You Hear Your Heartbeat While Lying Down

Doctor's Warning To People Whose Fingers And Toes Change Color And Feel Numb In The Cold
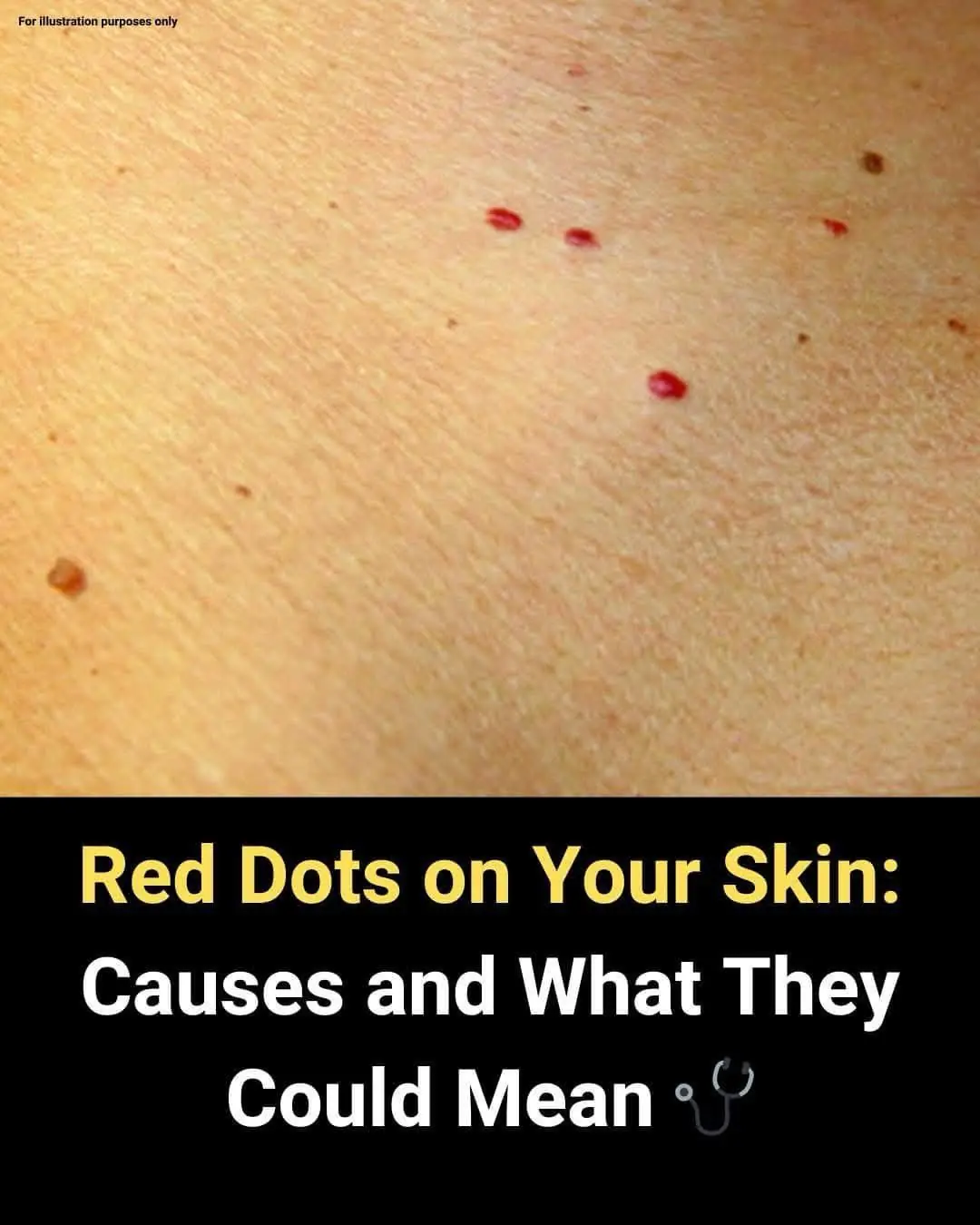
Red Spots on Skin: 13 Common Causes

Vaping vs. Smoking: New Study Says Vapes May Be More Harmful

Study Explains How the First Born Child Is Often the Most Intelligent

What 20 Seconds of Hugging Can Do for You
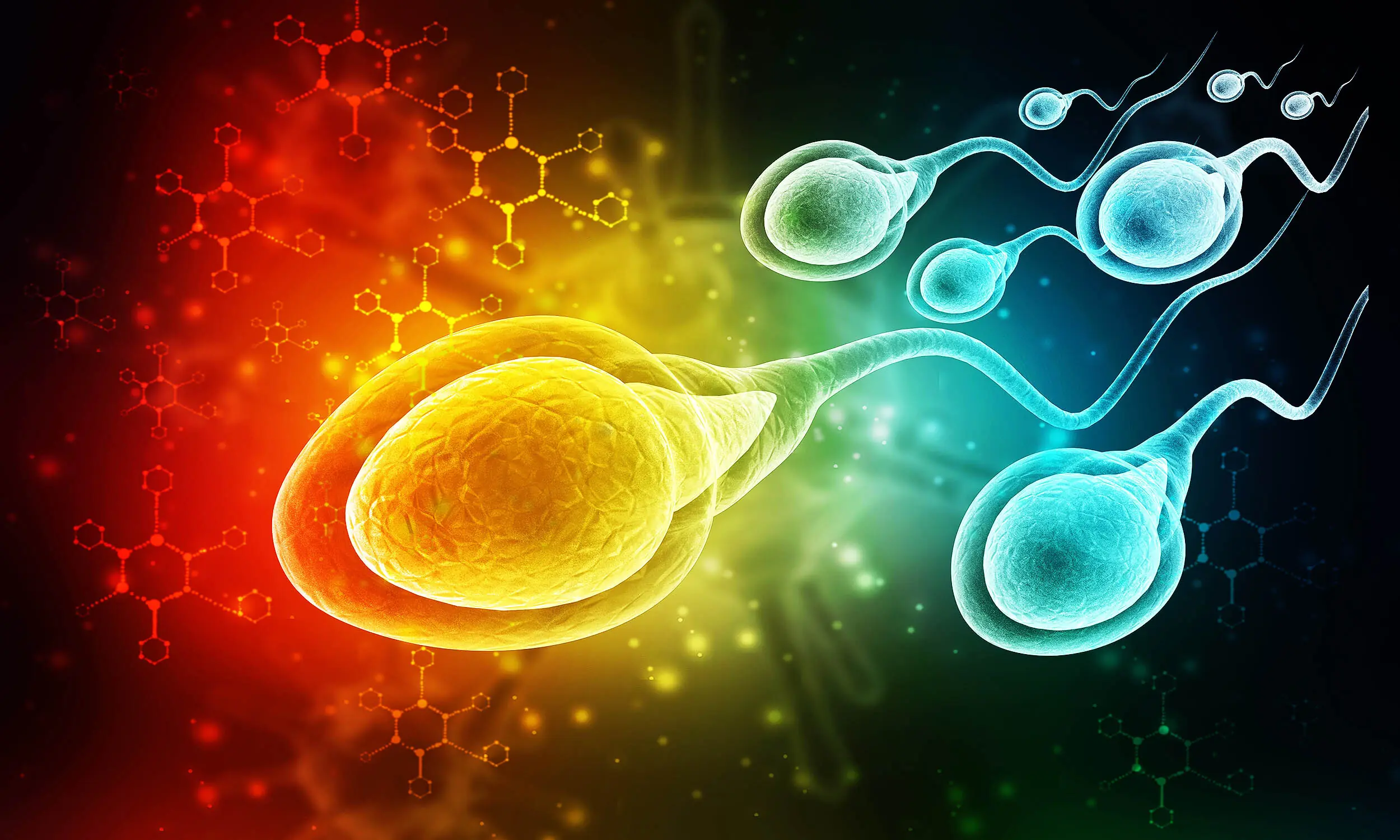
New Study Found Microplastics In Every Single Human Semen Sample

Unlock the Health Benefits of the Castor Bean Plant: A Natural Remedy for Wellness
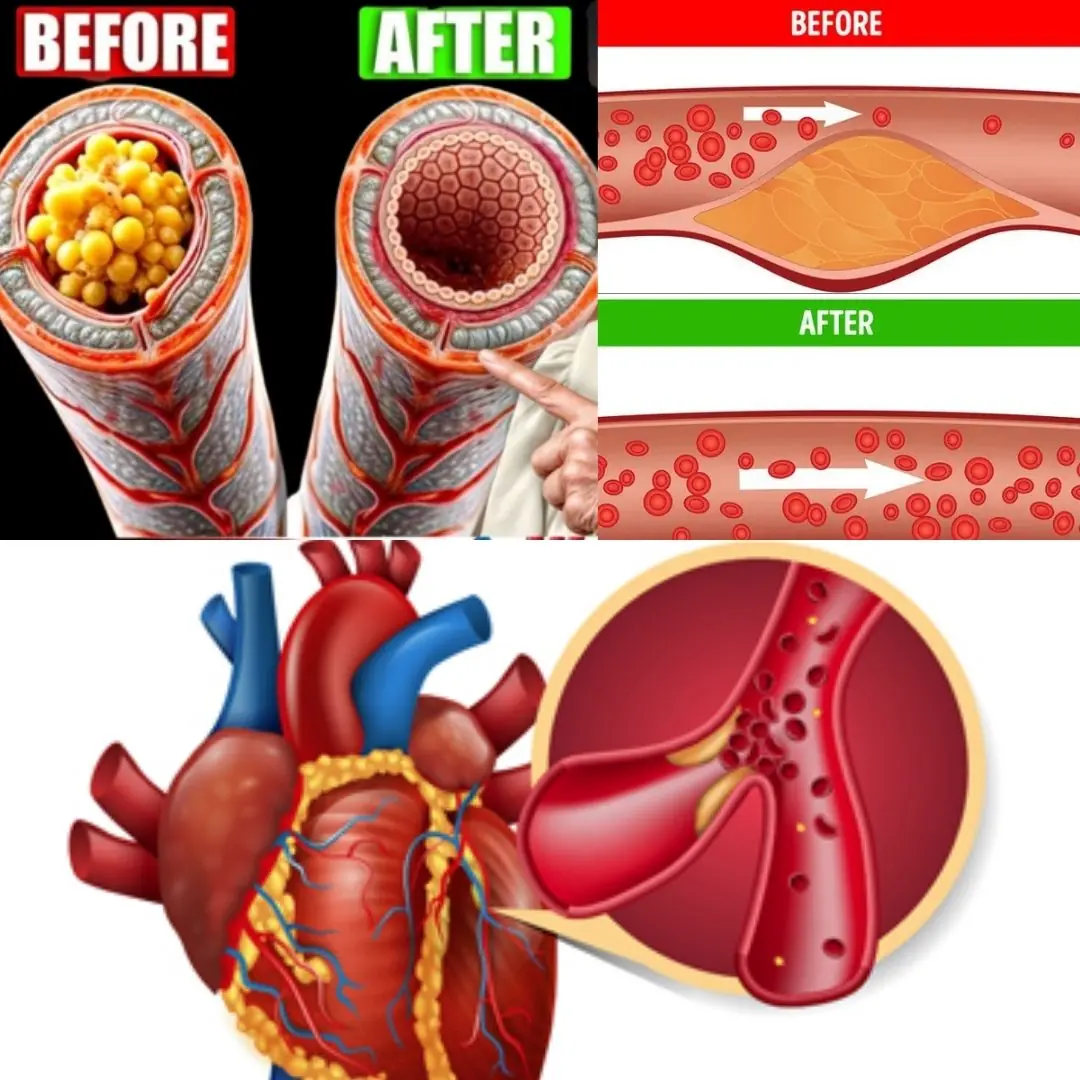
10 Vegetables That Are Good for Your Heart

I-motif DNA structures are formed in the nuclei of human cells
Hyperacute rejection-engineered oncolytic virus for interventional clinical trial in refractory cancer patients
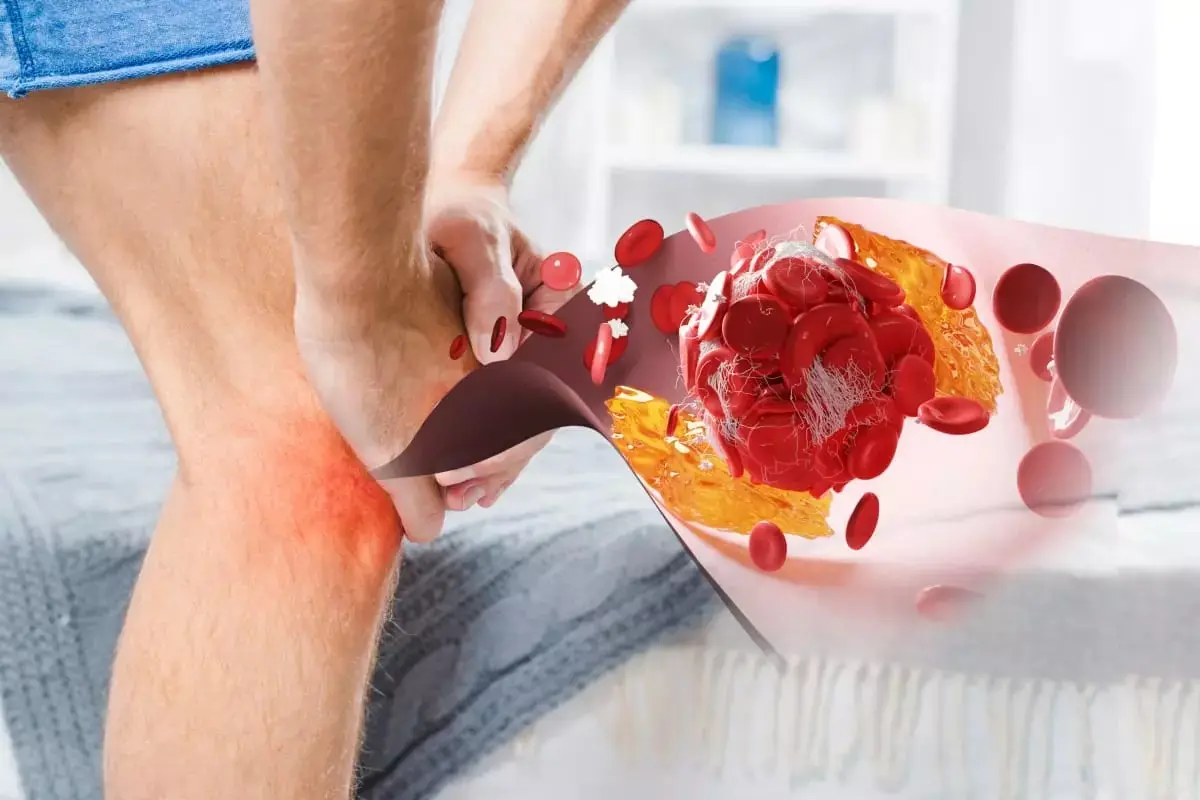
Your Feet Could Be Signaling That Your Arteries Are Clogged

36-Year-Old Teacher Dies From Diabetes Doctors Say Was Triggered By Everyday Foods

Cancer Rates Rising in Gen X and Millenials Compared to Older Generations, Study Finds
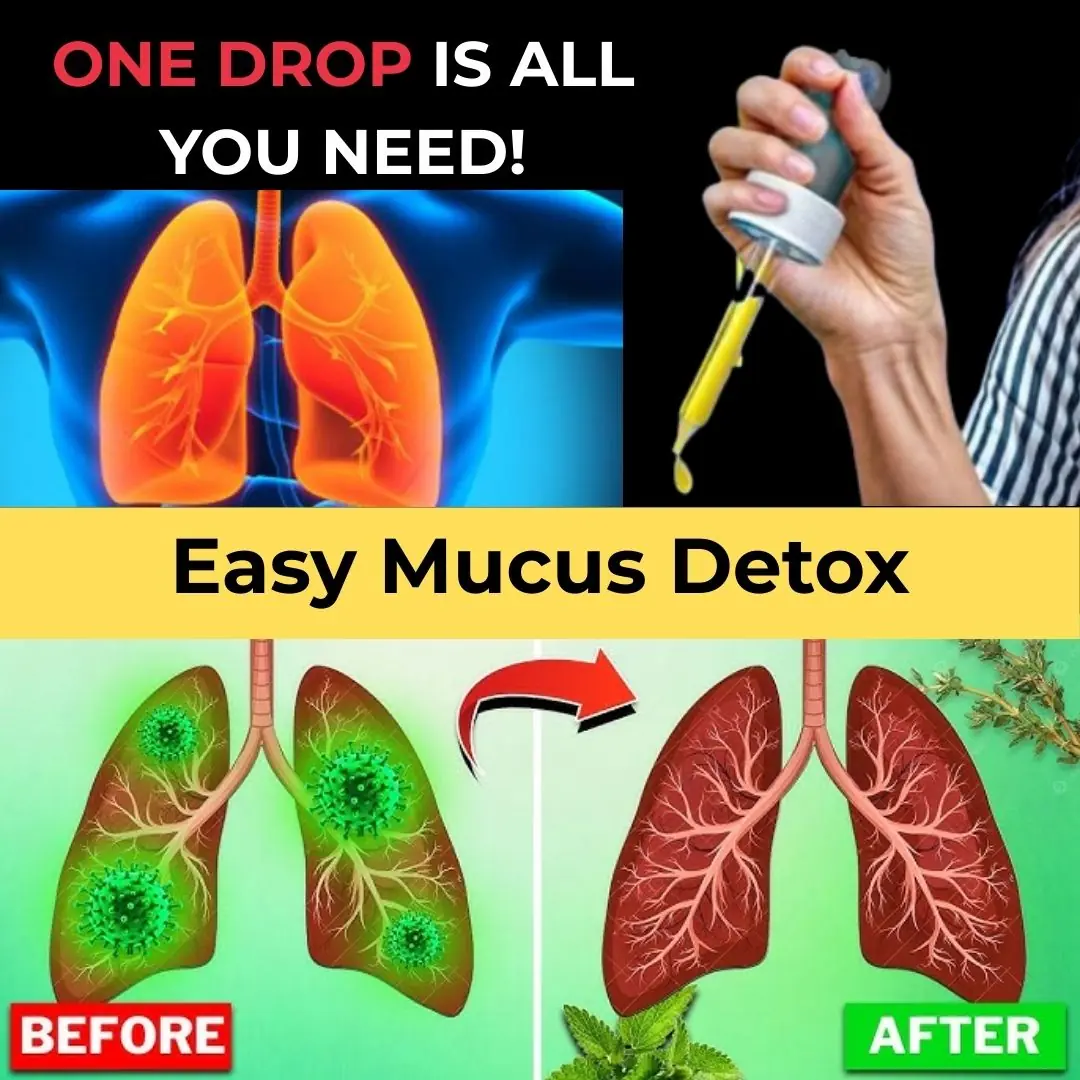
Lungs Full of Mucus? 1 SINGLE Drop Clears Airways & Restores Lung Health! | Barbara O’Neill
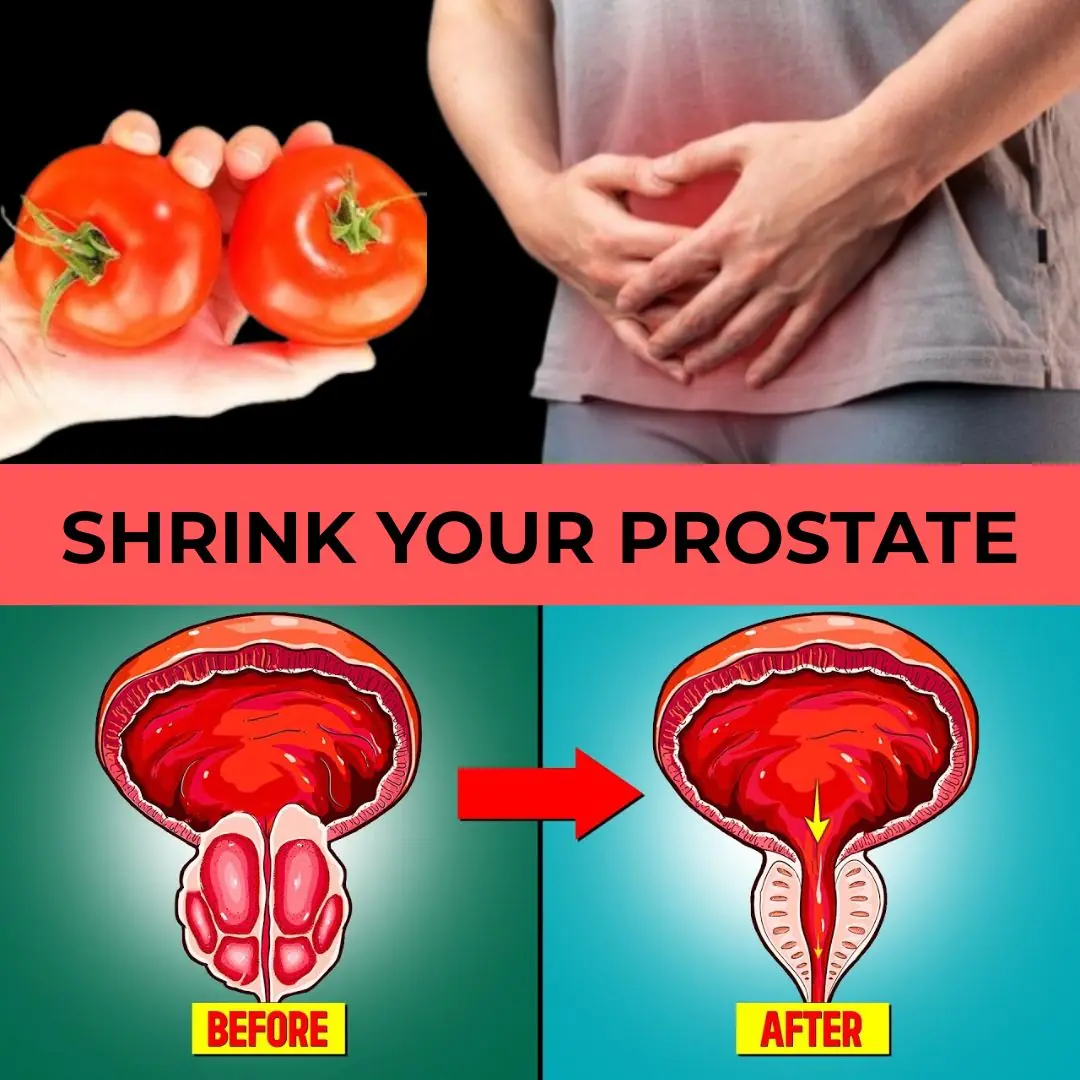
Rejuvenate Your Prostate Naturally: The Incredible Power of Tomato and Garlic Juice

Experts reveal the five foods that seriously affect your eyesight including one many of us eat every day
News Post

Girls Visit Dad's Grave to 'Show' Their New Dresses as He Asked, See 2 Boxes with Their Names

Turns Out I Rented an Apartment to My Husband's Mistress, and Their Next Date There Was One I'll Never Forget

Neighbor Mocks Poor Woman for Filthy Look of Her House, Apologizes after She Sets Foot Inside

My Wife Kicked Me Out of the House Because of the Sudden Confession of My Director

My Son’s New Classmates Turned Him from a Straight-A Student into a Troublemaker — But I Didn’t Give Up on Him

After My Brother's Funeral, His Widow Gave Me a Letter – I Wasn't Ready for What He'd Confessed

Listening to Music Literally Speeds Up Recovery from Surgery, Research Shows

A Common Drug Used in Tylenol, Excedrin, and More Was Just Linked to ADHD

Pulsatile Tinnitus: Why You Hear Your Heartbeat While Lying Down

Doctor's Warning To People Whose Fingers And Toes Change Color And Feel Numb In The Cold

Red Spots on Skin: 13 Common Causes

Vaping vs. Smoking: New Study Says Vapes May Be More Harmful
Businessman Loses All Hope After His Diagnosis, but One Hospital Encounter Changes Everything

My Husband's 'Business Partner' Showed Up at Our Door and Mistook Me for the Cleaning Lady — I Decided to Play Along

My Husband Asked for a Divorce Right After Learning About His Rich Father's Inheritance

Entitled Mom Claimed My Seat at the Cafe — Her Face Turned Red after I Taught Her a Lesson

My Fiancé Told Me His Grandma Wanted to Meet Me Before the Wedding – As I Arrived, a Nurse Pulled Me Aside and Said, 'Don't Believe a Word'
The Healthy Benefits Behind Grapeseed Extract: A Comprehensive Guide
