
High Olive Oil Intake Linked to Significantly Lower Risk of HER2-Negative Breast Cancer
🌿 The Mediterranean Advantage: Olive Oil's Potent Role in Breast Cancer Prevention
The quest for effective strategies to reduce cancer risk has long emphasized the power of dietary choices. Among the most studied and validated dietary patterns is the Mediterranean diet, where Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) stands as a cornerstone. Emerging research is now isolating the specific impact of this golden liquid, with findings providing a compelling link between its consumption and a significantly lowered risk of certain breast cancer subtypes.
The visual highlights a crucial finding: Women who consumed more than 3 tablespoons (about 40–45 grams) of olive oil per day showed a significantly lower risk of certain breast cancer subtypes, with the strongest reduction observed for HER2-negative tumors (about 46% lower risk).
Olive Oil's Anti-Cancer Components
Olive oil is not merely a source of fat; it is a complex mixture of biologically active compounds, primarily monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) and various polyphenols.
-
Oleic Acid (MUFA): This is the main fatty acid in olive oil. It is believed to modulate cell membrane properties and influence gene expression related to cancer cell growth.
-
Polyphenols (e.g., Hydroxytyrosol, Oleuropein): These compounds are potent antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents. They are the key distinction, particularly in extra virgin olive oil, which retains higher levels than refined oils.
The Mechanism of Prevention
The protective effect of high olive oil consumption, especially against HER2-negative tumors, is likely driven by its multi-targeted action against several hallmarks of cancer :
-
Anti-Inflammatory Action: Chronic low-grade inflammation is a major driver of cancer development. The polyphenols in EVOO, like oleocanthal (which mimics the action of ibuprofen), effectively dampen this inflammatory environment, thus inhibiting tumor initiation and promotion.
-
Antioxidant Power: Polyphenols scavenge free radicals, reducing oxidative stress that can damage cellular DNA, a common precursor to malignancy.
-
Hormonal Modulation: The MUFAs and polyphenols may favorably influence estrogen metabolism and signaling pathways, which is particularly relevant in hormone-sensitive breast cancer subtypes.
-
Apoptosis Induction: Certain olive oil components have been shown in laboratory studies to selectively induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells without harming healthy cells.
Focus on HER2-Negative Subtypes
The finding emphasizes the strongest protective effect against HER2-negative tumors, which account for a large proportion of breast cancers. These tumors lack the amplification of the HER2 gene, making them a diverse group that includes the aggressive Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) subtype (Estrogen Receptor-negative, Progesterone Receptor-negative, and HER2-negative).
-
The 46% lower risk associated with high olive oil consumption suggests a particularly effective role for the oil's compounds in targeting the non-hormonal, inflammatory, and signaling pathways that drive these tumors.
-
Given that TNBC has fewer targeted treatment options than other subtypes, this dietary protective measure holds significant clinical importance.
Dietary Recommendation and Clinical Relevance
The threshold identified in the research—more than 3 tablespoons (40–45 grams) per day—is substantial and characteristic of traditional Mediterranean dietary habits, where olive oil is used not just for cooking but as a generous dressing for salads and vegetables.
This research reinforces the recommendations from health organizations to adopt a Mediterranean-style diet. It suggests that substituting less healthy fats (like saturated fats or refined seed oils) with high-quality Extra Virgin Olive Oil provides measurable, cancer-protective benefits, especially for women seeking to mitigate their risk of certain breast cancer subtypes. The purity and high polyphenol content of EVOO are crucial for achieving these benefits.
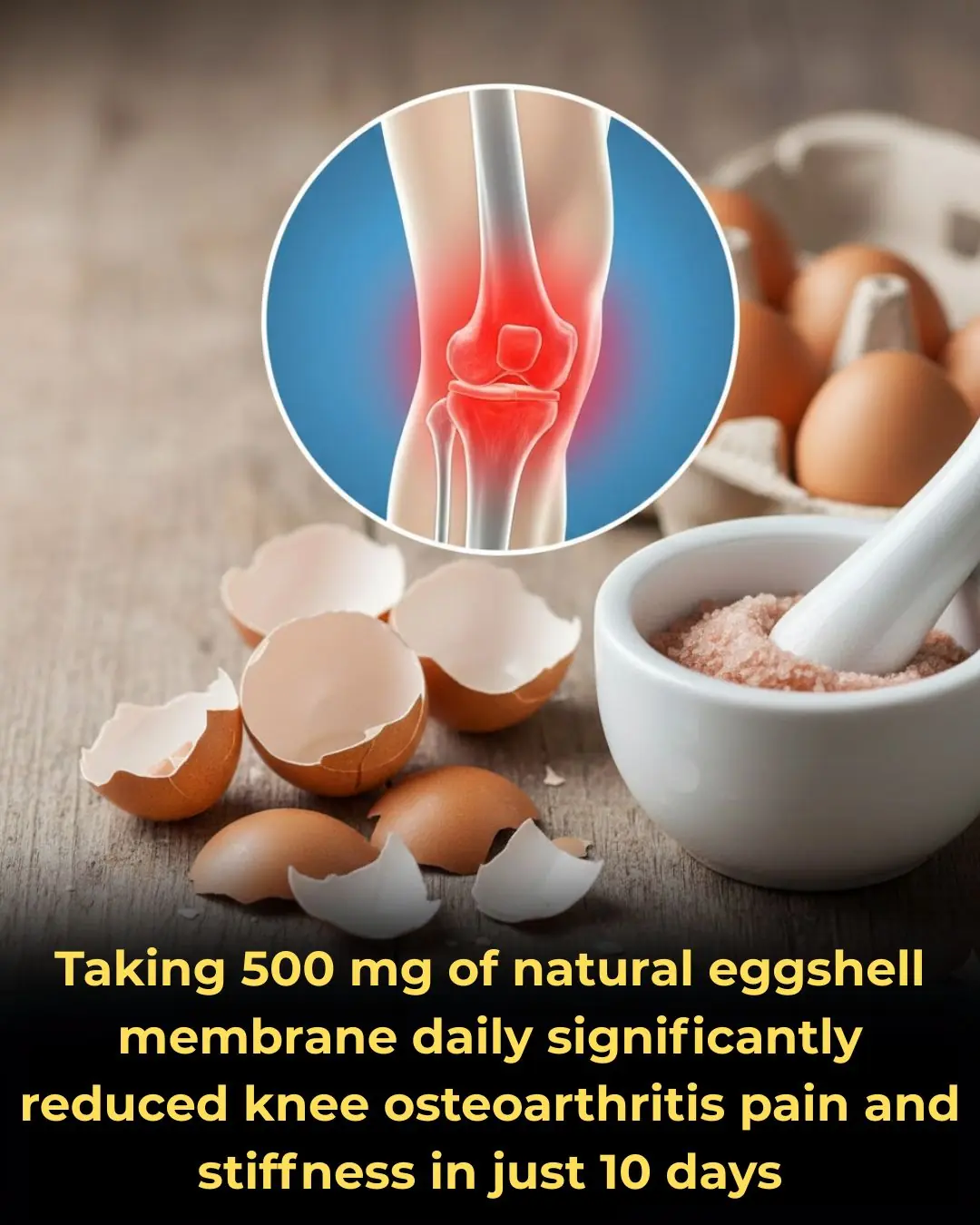
🥚 The Power of the Peel: Natural Eggshell Membrane for Rapid Relief of Knee Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a pervasive and debilitating condition, particularly affecting the knees, characterized by chronic pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. A striking finding highlighted in recent nutritional science suggests a powerful solution: Taking 500 mg of natural eggshell membrane daily significantly reduced knee osteoarthritis pain and stiffness in just 10 days.
Eggshell Membrane (ESM) Composition
The eggshell membrane (ESM) is the thin, fibrous matrix between the shell and the egg white. Modern research has unveiled its rich biochemical composition, positioning it as a potent nutraceutical for joint health :
-
Collagen: Provides structural integrity to connective tissues.
-
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs): Including Glucosamine and Chondroitin, essential building blocks for cartilage.
-
Hyaluronic Acid: A crucial component for joint lubrication.
Scientific Basis for Rapid Relief
The key to ESM's success, particularly its remarkably quick action—achieving significant relief in just 10 days—lies in its multi-faceted mechanism, focusing on managing inflammation and supporting the joint matrix.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Action: OA is driven by chronic inflammation. The unique blend of proteins and GAGs in ESM is hypothesized to help down-regulate pro-inflammatory cytokines, quickly reducing pain and swelling. Studies have investigated the speed of ESM's effect in journals such as Clinical Rheumatology.
-
Cartilage Matrix Support: The natural presence of glucosamine, chondroitin, and hyaluronic acid provides essential raw materials for maintaining and potentially repairing the damaged cartilage matrix. Research in the Journal of Medicinal Food supports that ESM components help inhibit the activity of cartilage-degrading enzymes.
-
Synergistic Effect: ESM delivers its components in their natural, biologically available ratios, offering greater therapeutic effect than single-ingredient supplements.
The finding of significant reduction in pain and stiffness in just 10 days is supported by clinical research using standard clinical measures like the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC).
🧄 The Gut Guardian: Roasted Garlic Reverses Leaky Gut in 3 Weeks
The integrity of the intestinal barrier is fundamental to overall health. When this barrier is compromised—a condition often termed "leaky gut"—it can lead to inflammation and systemic issues. A remarkable finding concerning one of the oldest medicinal foods provides a potential solution: Roasted garlic reversed leaky gut caused by chemical colitis in just 3 weeks by restoring tight junction proteins that normally break apart during inflammation.
The Intestinal Barrier and Tight Junctions
The intestinal barrier consists of epithelial cells sealed together by complexes called tight junctions (including Zonulin, Occludin, and Claudins). These junctions act as selective gatekeepers. In inflammatory conditions like colitis, the inflammation causes these tight junction proteins to break down, leading to increased intestinal permeability, or "leaky gut" .
Garlic's Active Role: Restoration and Healing
Garlic (Allium sativum) has long been revered for its anti-inflammatory properties, attributed to its sulfur-containing compounds. The roasting process alters the chemical profile of the compounds, potentially making them more effective in modulating the gut environment.
-
Protein Restoration: Garlic's compounds appear to signal the intestinal cells to re-synthesize or reassemble the tight junction proteins, effectively closing the gaps and restoring the gut's barrier function. The core finding is this restoration of tight junction proteins.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Modulation: The compounds suppress the production of inflammatory mediators that specifically target and degrade the tight junction proteins.
-
Prebiotic Effects: Garlic is a source of prebiotics like inulin, which nourishes beneficial gut bacteria. A healthy microbiome strengthens the barrier by producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs).
News in the same category


Why Your Legs Show Signs of Aging First — and 3 Drinks That Can Help Keep Them Strong
Intensive Gum Disease Treatment Slows Artery Thickening, Benefiting Heart and Brain Health

Tight Junction Proteins and Permeability Improved by Roasted Garlic in Mice with Induced Colitis
Randomized Controlled Trial Confirms NEM® Efficacy and Safety in Reducing Osteoarthritis Pain and Stiffness

Whole Fish Trumps Pills: Study Finds Whole-Food Factors, Not Isolated Omega-3s, Lower Autism Risk

Dark chocolate and tea found to significantly lower blood pressure
How To Clear Your Sinuses

How to lower blood sugar without giving up carbs

Doctor reveals 5 nutrient deficiencies linked to brain fog, dementia and Alzheimer’s

10 powerful plants to eliminate excess mucus and phlegm naturally

Why This Doctor Chooses Not to Prescribe Statins for High Cholesterol — and What He Recommends Instead

5 Foods You Must Avoid If You Have High Blood Pressure

21 Effective Home Remedies for Kidney Stones to Relieve Pain Fast

People with heart problems should avoid these 4 things to reduce stimulation to the heart

12 Bizarre Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency You Need to Know
8 warning signs of colon cancer you should never ignore
The daily drink that helps clear blocked arteries naturally
News Post

A Massive Spider Megacolony Thriving in a Sulfur-Fueled Cave Ecosystem
Rapid Pain and Stiffness Relief in Knee Osteoarthritis

Tamarind: The Tangy Superfruit Your Body Will Thank You For

Why Your Legs Show Signs of Aging First — and 3 Drinks That Can Help Keep Them Strong

Intensive Gum Disease Treatment Slows Artery Thickening, Benefiting Heart and Brain Health

The #1 Food Proven to Support Kidney Cleansing and Protection

Tight Junction Proteins and Permeability Improved by Roasted Garlic in Mice with Induced Colitis

Randomized Controlled Trial Confirms NEM® Efficacy and Safety in Reducing Osteoarthritis Pain and Stiffness

Whole Fish Trumps Pills: Study Finds Whole-Food Factors, Not Isolated Omega-3s, Lower Autism Risk

Dark chocolate and tea found to significantly lower blood pressure

Burglar Uncovers Shocking Crime During Robbery, Turns Himself In and Exposes Serious Offense

The Black Diamond Apple: A Rare Gem from the Mountains of Tibet

The Power of Pine Needles: 30 Benefits and Homemade Uses

Marvin Harvin Becomes One of the First Incarcerated Individuals to Graduate from Yale University, Highlighting the Power of Education in Prison Reform

The Hidden Power of Pistachio Shells: Benefits and Clever Homemade Uses

Warren Buffett’s Ice Cream Quote: A Simple Yet Powerful Lesson on Taxes

Papaya Seeds: A Powerful Remedy for Liver Health and How to Use Them as a Pepper Substitute

30 Amazing Benefits of Lactuca serriola (Wild Lettuce)
