
MIT's Breakthrough Injectable Gel Offers New Hope for Nerve Regeneration and Repair
Researchers at MIT have developed a groundbreaking injectable gel that has the potential to regenerate damaged nerves, offering a promising solution for patients suffering from nerve injuries caused by accidents, surgeries, or various diseases. This innovative treatment represents a significant leap forward in the field of medical research, as nerve regeneration has long been one of the most difficult challenges in medicine. The development of this injectable gel offers a new hope for millions of people around the world who have experienced nerve damage and the loss of vital sensory and motor functions.
The injectable gel works by creating a favorable environment for nerve cells to regenerate and reconnect. Traditionally, nerve injuries have been difficult to treat because nerve cells have a limited capacity to heal themselves, especially in the case of severe damage or injury. The gel's formulation mimics the extracellular matrix, the natural scaffold that supports nerve growth, helping to guide the regeneration of nerve cells and promoting re-establishment of their connections. Early studies on the gel's effectiveness have shown remarkable results, with treated nerves regaining both sensory and motor function. In some cases, patients who were previously unable to feel sensations or move affected limbs are seeing a return of these abilities, significantly improving their quality of life.
What sets this injectable gel apart from traditional treatments is its ability to achieve these results with minimal invasiveness. Unlike conventional therapies, which often only partially restore function or involve complex surgeries, this gel can be injected directly into the affected area, reducing the need for invasive procedures and the associated risks. The gel provides a less invasive, more accessible solution, potentially transforming the way we approach nerve injuries. This approach could lead to faster recovery times, fewer complications, and better long-term outcomes for patients.
This breakthrough has the potential to treat a wide range of neurological injuries. Although spinal cord injuries and peripheral nerve damage have been some of the most difficult challenges in neurobiology, the gel could be adapted to treat these conditions as well as other forms of nerve damage. From people who have suffered traumatic injuries in car accidents to patients recovering from surgeries like limb amputations, the possibilities for this technology are vast. The ability to restore function to damaged nerves could significantly improve the lives of people living with neurological disorders, providing them with the chance to regain independence and better manage their daily activities.
Furthermore, the innovation behind this injectable gel is a testament to the power of bioengineering and advanced medical research. By combining cutting-edge techniques from materials science, biotechnology, and neurobiology, the researchers at MIT have been able to develop a solution that holds the potential to address one of medicine’s oldest and most persistent challenges. The collaborative efforts of researchers in these fields have made this breakthrough possible, demonstrating how interdisciplinary research can result in transformative medical solutions.
As with any new medical treatment, further development and clinical trials are necessary before it can be widely adopted for human use. The promising results observed in early-stage studies are encouraging, but additional testing is needed to determine the long-term safety and effectiveness of the gel. If further trials confirm its potential, this injectable gel could be used to treat a wide range of patients, offering an affordable, minimally invasive, and highly effective solution for nerve injuries.
Ultimately, the MIT injectable gel could redefine the future of nerve repair and offer a new lease on life for those affected by nerve damage. With continued research and clinical testing, this treatment could provide a life-changing solution for countless individuals, helping to restore not only their physical abilities but also their independence and quality of life.
News in the same category


The Final Supermoon of 2025: What You Need to Know About the Cold Moon on December 4

UK Scientists Develop Groundbreaking Graphene-Based Filter to Convert Seawater into Drinking Water

Study Raises Concerns About Long-Term Risks of Current Uterine Closure Methods After Cesarean Deliveries
Microplastic Exposure Found to Worsen Artery Plaque Buildup in Male Mice, Study Reveals
Biological Mechanism Behind Men's Increased Susceptibility to Periodontitis Revealed in New Research

When Potatoes Took to the Skies: Boeing’s Unusual Experiment to Improve In-Flight Wi-Fi
Stanford Study Shows “Cyclic Sighing” Breathing Technique Significantly Reduces Stress and Anxiety
Breakthrough Polymer Cream Could One Day Replace Insulin Injections, Study Suggests

Norwegian Startup Develops Liquid Natural Clay to Transform Deserts Into Fertile Farmland

Tsinghua University Scientists Engineer Industrial Fungus Into a High-Protein Meat Alternative

New Zealand Adds Feral Cats to Predator Free 2050 Target in Major Biodiversity Push

Christian Bale Launches $22 Million Foster Village in California to Keep Siblings Together

Patient Wins $500,000 After Recording Anesthesiologist Mocking Him During Colonoscopy

Young Filipino Boy’s $3 Savings Turn into Heartwarming Korean Barbecue Surprise for Grandfather

32-Year-Old Carabao Rescued from Slaughter Thanks to Community Fundraising in the Philippines

A Simple Wedding Choice Sparks Big Conversations About Love and Costs

Groundbreaking Antibody Discovery Could Revolutionize HIV Treatment and Prevention
News Post
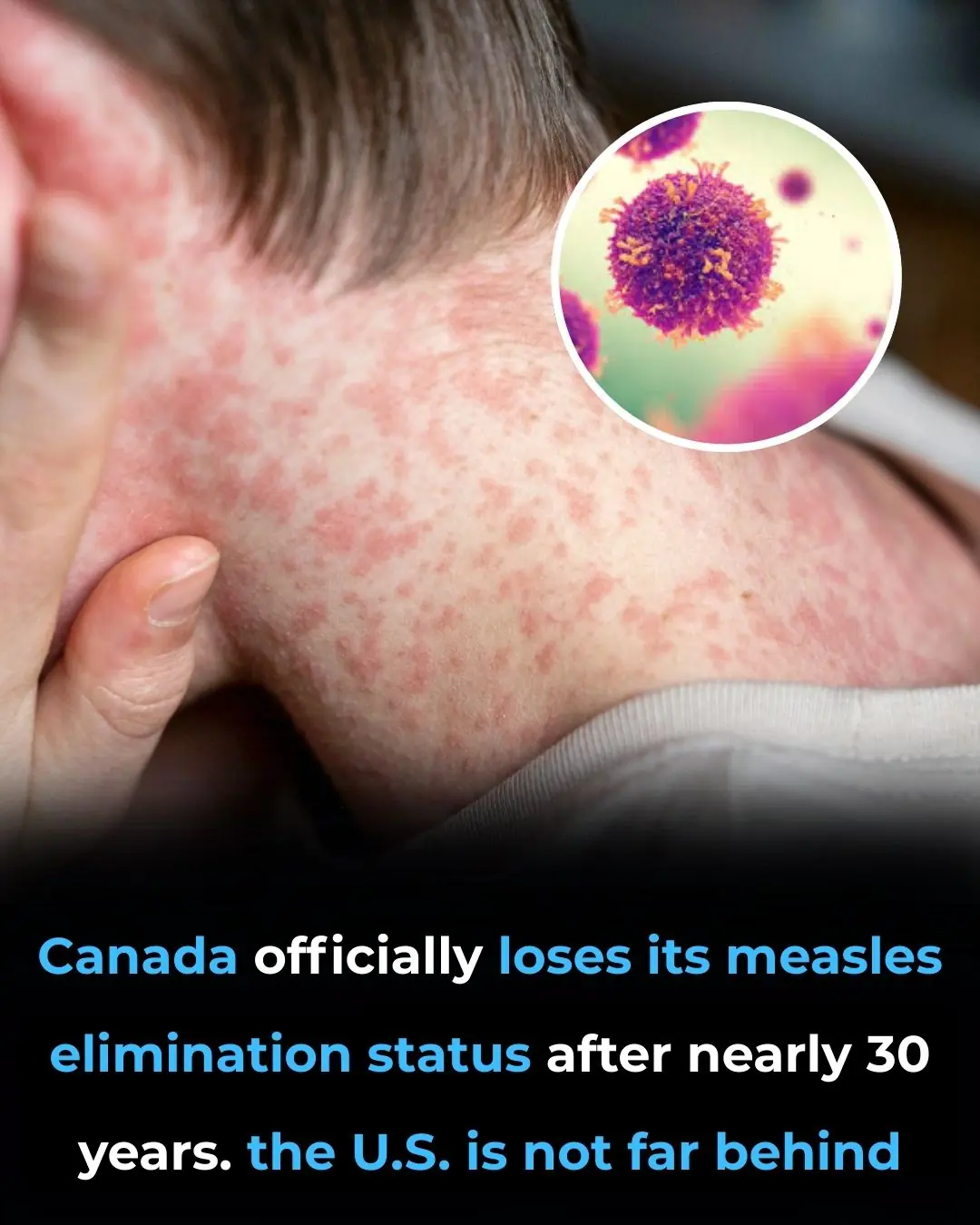
Canada Loses Measles-Free Status After Nearly 30 Years as the U.S. Faces Growing Risk
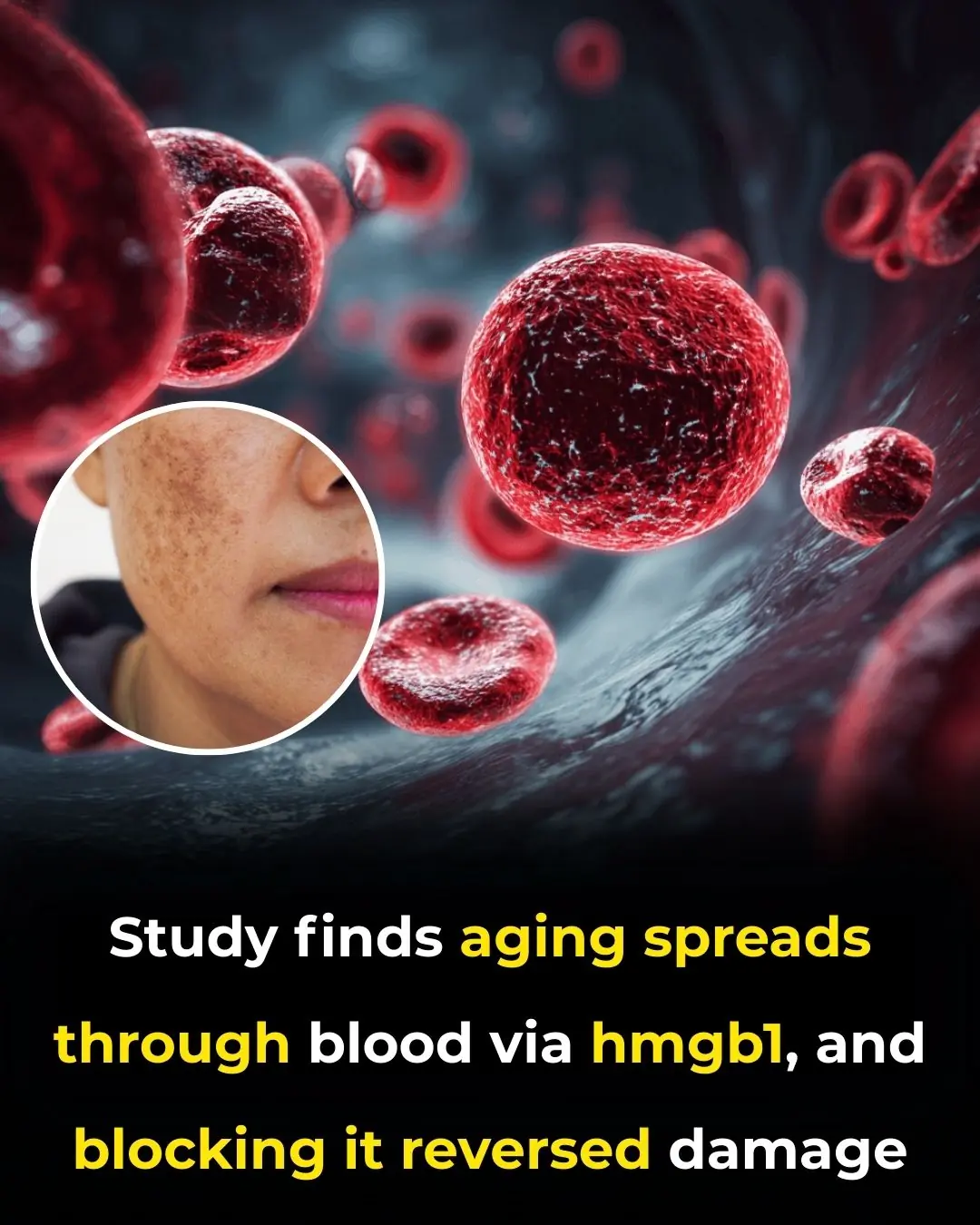
How a Blood Protein May Be the Key to Slowing Aging

Drinking a Cola Could Shorten Your Lifespan by This Exact Amount, According to Scientists

Newly Identified COVID-Linked Syndrome That Can Severely Damage Lungs

8 ways to utilize eggshells, both effective and saving money

3 mothers use "cooling fan" to save electricity in a very simple way: Knowing how much it costs

The ant only needs this one thing, the whole colony will disappear and never return.

How to distinguish real honey from fake honey is very simple: Just put it in the refrigerator and you will know.
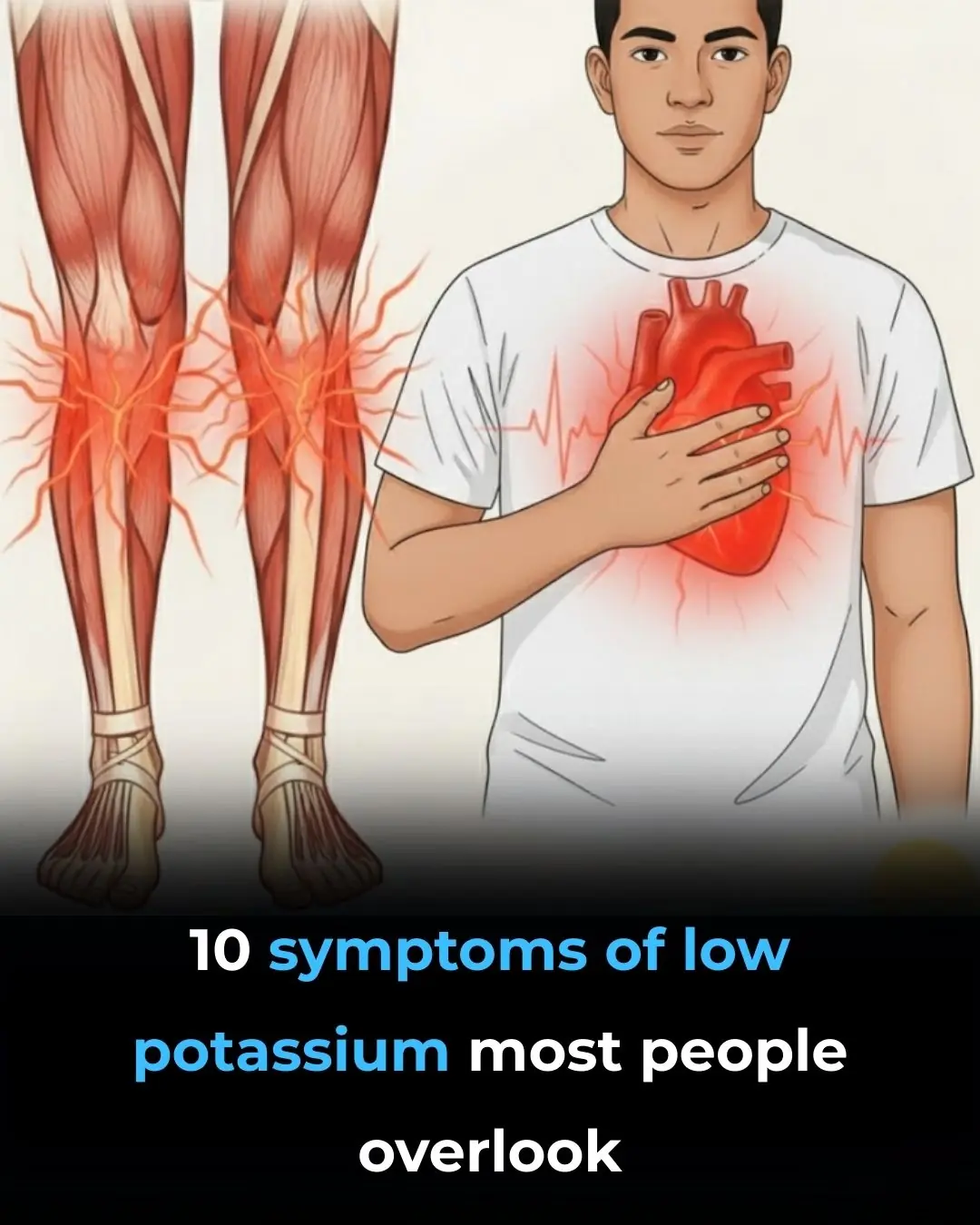
Top 10 Symptoms of LOW Potassium You May Be Ignoring

Stanford Study Reveals Epstein-Barr Virus as the Key Trigger for Lupus

The Final Supermoon of 2025: What You Need to Know About the Cold Moon on December 4

Period Pain Can Match the Intensity of a Heart Attack — And Women Deserve to Be Believed

UK Scientists Develop Groundbreaking Graphene-Based Filter to Convert Seawater into Drinking Water

It Takes 1–2 Years for a Woman to Fully Recover From Pregnancy — Not Just 6 Weeks

Study Raises Concerns About Long-Term Risks of Current Uterine Closure Methods After Cesarean Deliveries

Microplastic Exposure Found to Worsen Artery Plaque Buildup in Male Mice, Study Reveals

Biological Mechanism Behind Men's Increased Susceptibility to Periodontitis Revealed in New Research
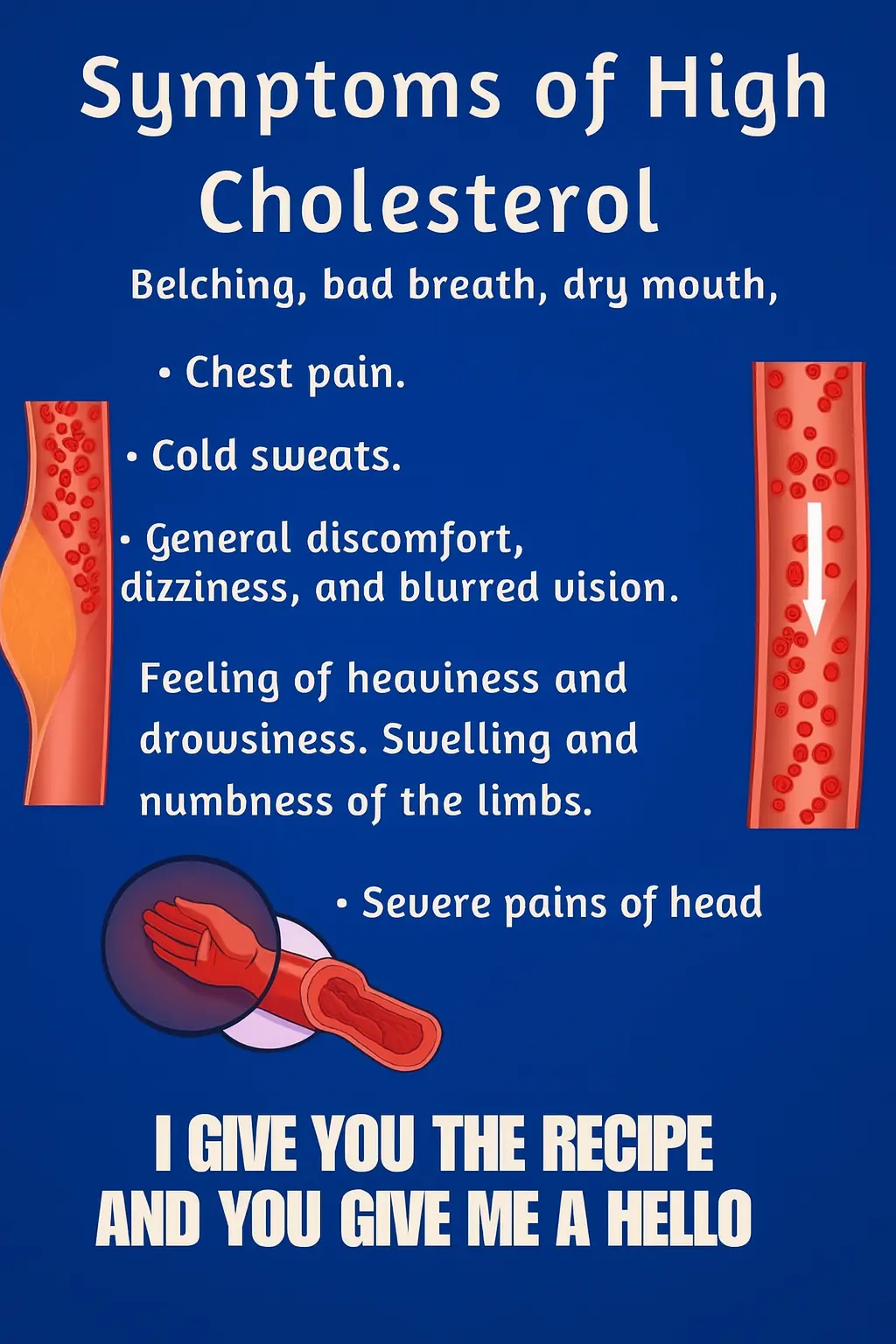
High Cholesterol Symptoms & Natural Recipes to Support a Healthy Lifestyle

The 2-ingredient natural fix for knee pain doctors don’t tell you about!
