Never realized this

Tanker trucks are specialized vehicles designed to transport liquid or gaseous materials such as fuel, water, chemicals, and food-grade liquids. These vehicles feature a large cylindrical tank mounted securely on a heavy-duty chassis, engineered to safely contain and deliver potentially hazardous cargo. Every component of a tanker truck serves a specific safety or functional purpose—and one of the most noticeable yet often misunderstood features is the extra chain hanging from the back of the vehicle.
Although it may appear simple or even unnecessary, this chain plays a critical role in ensuring safety during the transportation of flammable substances.
The Purpose of the Extra Chain on Tanker Trucks
The primary function of the chain is grounding. As a tanker truck moves, static electricity can build up due to friction between the liquid cargo and the inner walls of the tank, as well as from the truck’s motion across the road. When transporting flammable liquids such as gasoline or diesel, this static charge can become extremely dangerous.
If static electricity is allowed to accumulate, it may discharge in the form of a spark. Even a small spark can ignite flammable vapors, potentially causing fires or explosions. The grounding chain drags along the ground, creating a conductive path that safely dissipates static electricity into the earth. This significantly reduces the risk of ignition and helps protect the driver, the vehicle, and the surrounding environment.
Historical Background: How the Grounding Chain Became Standard
In the early days of fuel transportation, the dangers of static electricity were not fully understood. As a result, accidents involving fires and explosions were more common and often catastrophic. Investigations into these incidents revealed that static discharge was frequently the cause.
As awareness grew, safety practices and regulations evolved. The grounding chain emerged as a simple, reliable, and cost-effective solution to the problem of static buildup. Over time, it became a standard feature on tanker trucks worldwide and remains an essential safety measure today.
Safety Regulations and Industry Standards
Transporting hazardous materials is subject to strict safety regulations. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) and similar authorities in other countries have established detailed guidelines governing tanker truck design and operation. These regulations address tank construction, pressure control, grounding requirements, and static electricity management.
The grounding chain is often a mandated safety feature, and its presence and condition are checked during routine vehicle inspections. Compliance with these regulations is crucial to prevent accidents and to ensure the safety of transport workers and the general public.
The Science Behind Static Electricity in Fuel Transport
Static electricity occurs when two surfaces come into contact and then separate, causing an imbalance of electrical charges. Inside a tanker truck, the movement and splashing of liquid fuel generate friction, which can create static charge—especially during loading, unloading, or transport over long distances.
Flammable liquids produce vapors that can ignite easily. The grounding chain provides a continuous route for excess electrical charge to flow harmlessly into the ground, preventing the buildup of dangerous energy and reducing the likelihood of sparks.
Modern Alternatives and Complementary Grounding Methods
While grounding chains remain widely used, modern tanker trucks may also employ additional grounding technologies. These include:
-
Static grounding reels with retractable cables attached during loading and unloading
-
Anti-static fuel additives that reduce charge buildup
-
Advanced tank materials and coatings designed to minimize friction
These systems are often used alongside grounding chains, providing multiple layers of protection rather than replacing the chain entirely.
Common Misconceptions About the Extra Chain
Many people assume the chain is leftover equipment or serves no real purpose. Others believe it helps stabilize the truck or improves braking—neither of which is true. Another misconception is that modern technology has made the chain obsolete.
In reality, the chain remains a vital safety feature because of its simplicity, reliability, and effectiveness. It requires no power source, works continuously, and provides a dependable method of grounding under a wide range of conditions.
The Role of the Chain in Accident Prevention
By continuously grounding the tanker truck, the chain plays a crucial role in preventing fires and explosions caused by static discharge. It ensures that static electricity does not reach dangerous levels, dramatically reducing the risk of ignition during transport.
This simple feature has helped prevent countless accidents and continues to be a cornerstone of fuel transport safety.
Maintenance and Inspection of Grounding Chains
Like all safety equipment, grounding chains require regular inspection and maintenance. Over time, chains can wear down, corrode, or break, reducing their effectiveness. Routine inspections ensure the chain remains intact, conductive, and in consistent contact with the ground.
Damaged or excessively worn chains must be replaced promptly to maintain proper grounding and compliance with safety regulations.
Conclusion: A Small Chain with a Big Impact
The extra chain hanging from the back of a tanker truck may seem insignificant, but it serves a vital safety function. By safely dissipating static electricity into the ground, it helps prevent fires and explosions during the transport of flammable liquids.
Despite advances in technology, the grounding chain remains an essential component of tanker truck design. Its effectiveness, simplicity, and proven reliability make it a critical safeguard in hazardous material transportation. Understanding its purpose—and ensuring it is properly maintained—is key to protecting lives, property, and the environment.
News in the same category


I keep wondering why this happens to me

7 easiest ways to distinguish real milk from fake milk that consumers should know by heart

How to Restore a Worn Non-Stick Pan Instead of Throwing It Away

I keep noticing thin black lines forming above my door frames, and they seem to get darker every winter. What can I do to fix?

No one told me
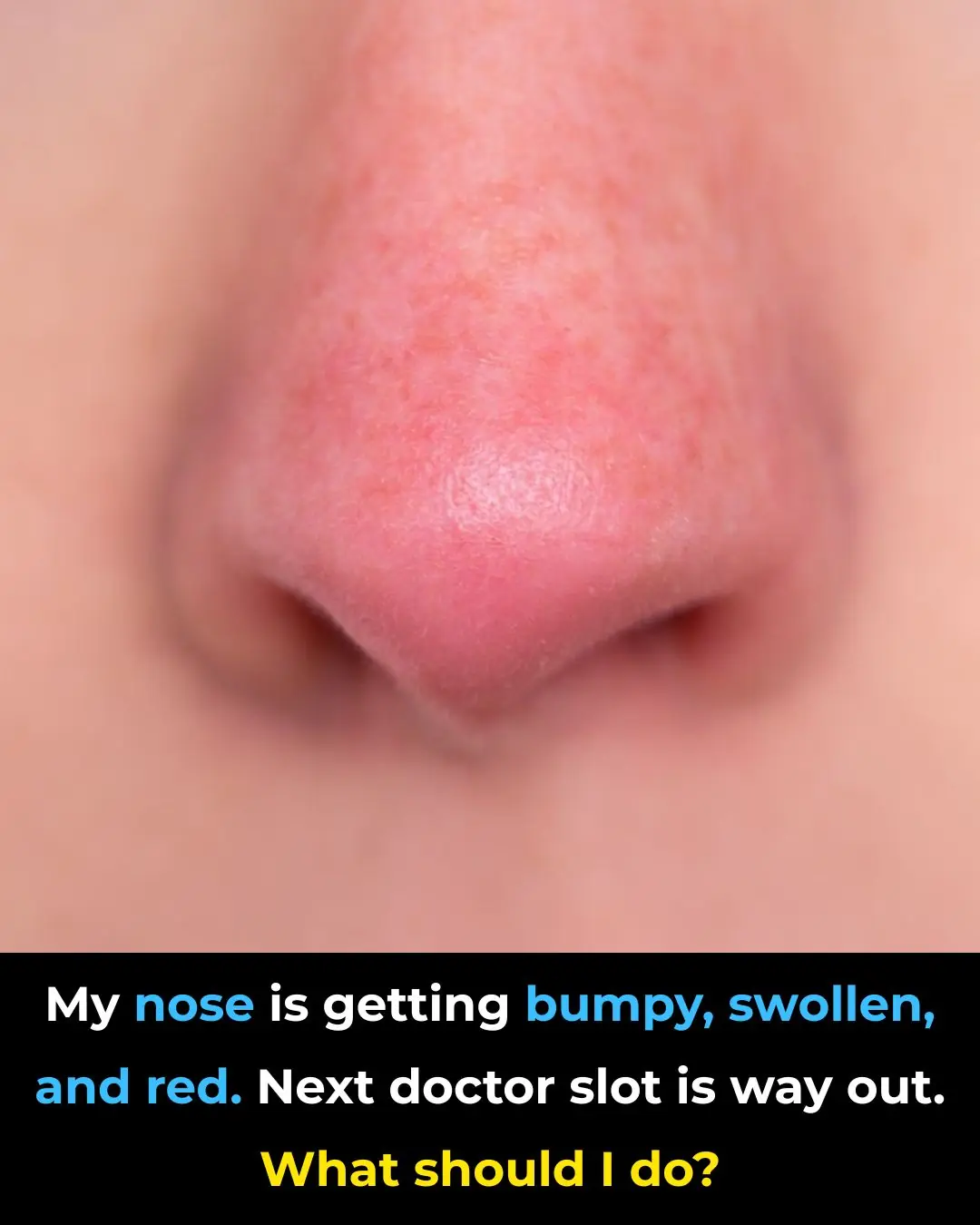
My nose is getting bumpy, swollen, and red. Next doctor slot is way out. What should I do?

Cold air pours in under the garage door and the repair company can’t come until after New Year. What can I do now?

I swear, I didn’t have the faintest clue about this!

Thought this was mold but I guess not. Am gonna check my bathroom again

If you eat cucumbers everyday, this is what happens to your body

Your method isn't quite right. Here's the correct way to maintain a clean home.

Don't put the scallions straight into the refrigerator after buying them; follow this method, and they'll last for a whole month without spoiling.

Found this on my son’s scalp. Have no idea what it is and we can’t get a doc appt soon. Tips?

Cutting lemons seems simple but many people do it wrong

Most people will go their entire life without ever knowing what the little arrow next to the gas gauge actually means

3 types of fruits that are cheap in Vietnamese markets but are considered "pure gold" to protect health
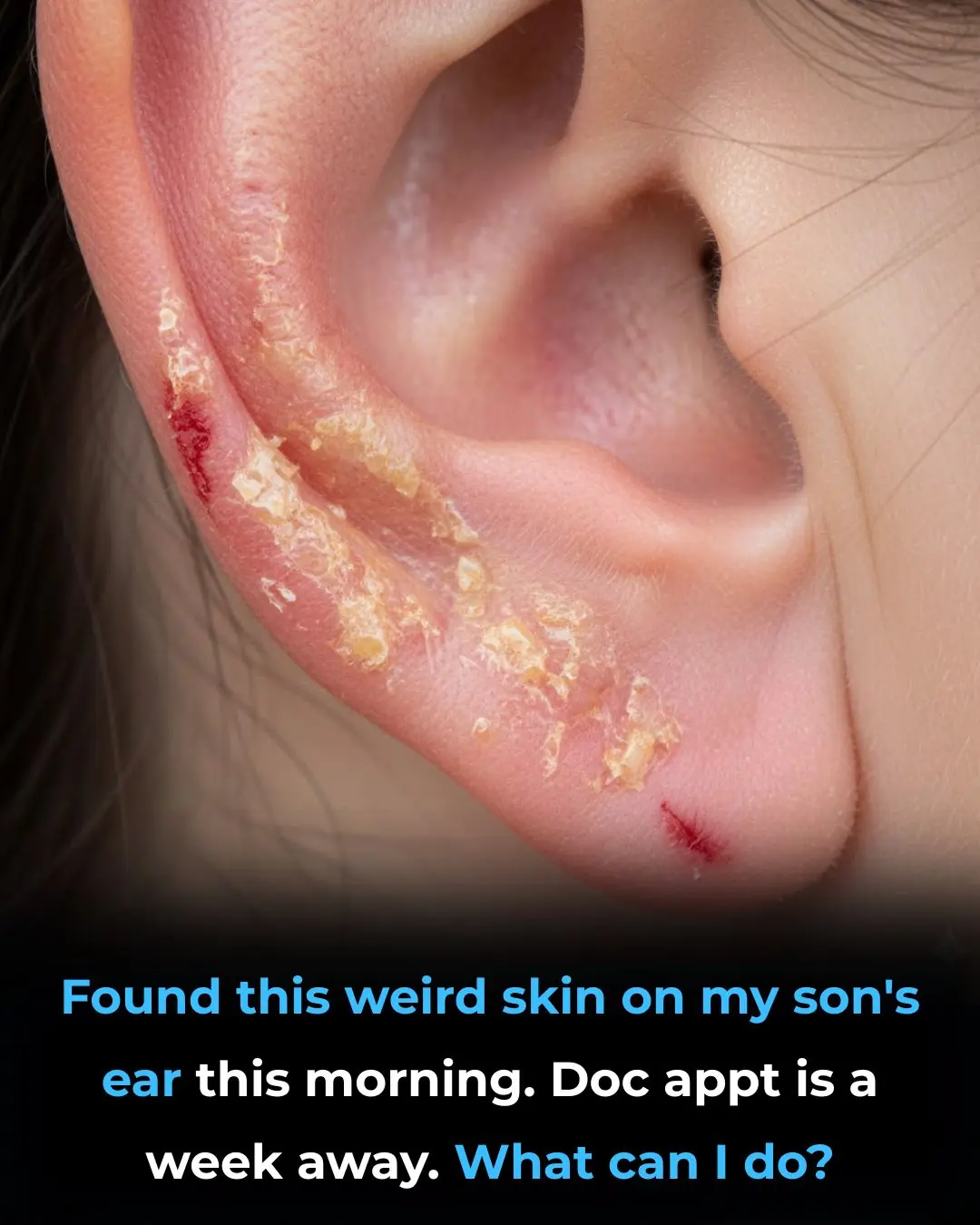
Found this weird skin on my son's ear this morning. Doc appt is a week away. What can I do?

My nana taught me this hack to get rid of dark circles in 5 mins with 0 work. Here’s how it works
News Post

Tata Sierra vs Mahindra XUV 7XO: A Mid‑Size SUV Showdown 🚙🔥

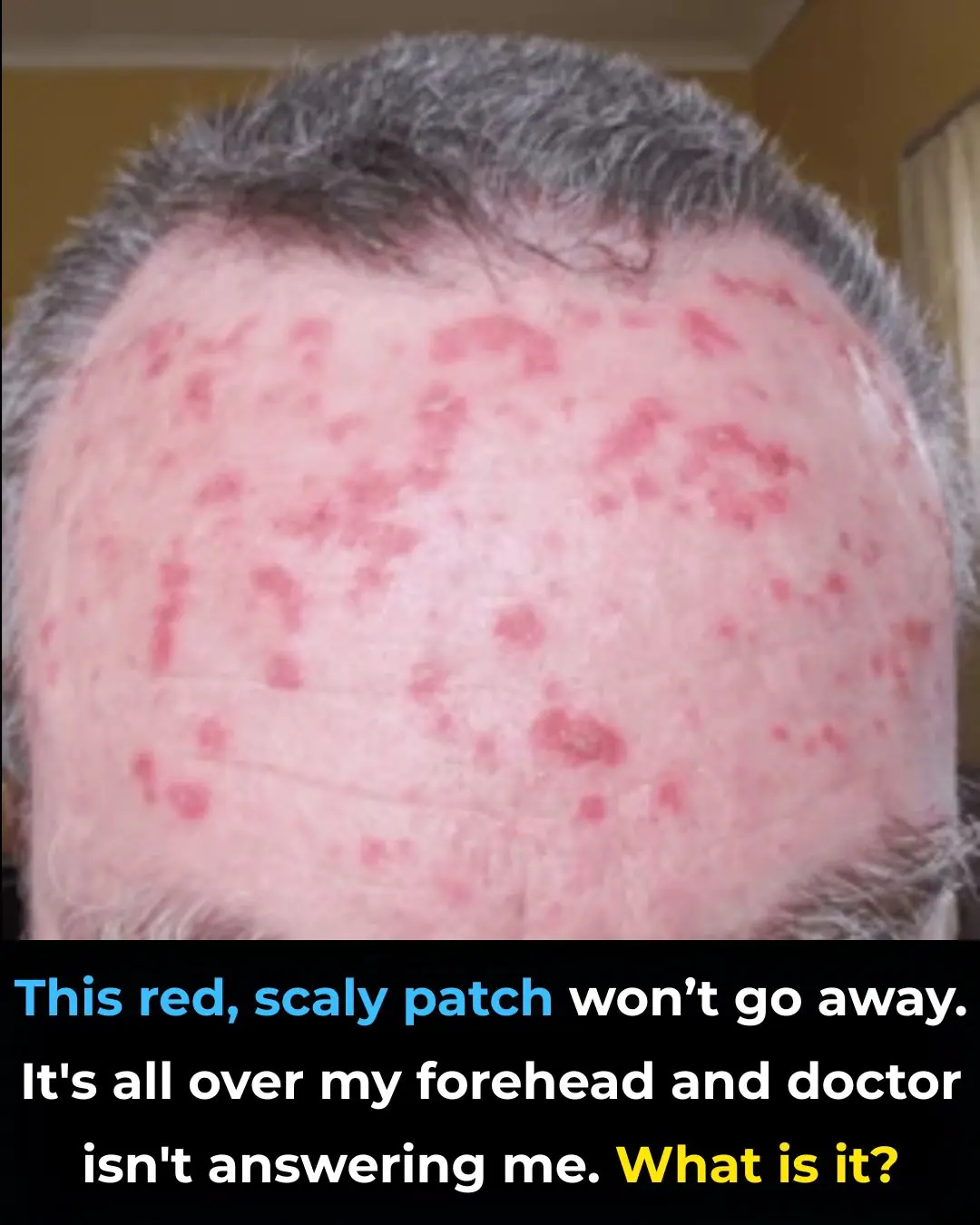
This red, scaly patch won’t go away. It's all over my forehead and doctor isn't answering me. What is it?

I keep wondering why this happens to me

The Impressive Health Benefits of Guava Fruit and Leaves & How to Eat Guava (Evidence Based)

How to Naturally Increase Estrogen Levels

Evidence-Based Health Benefits of Honey (Raw, Pure, Natural) + Turmeric Golden Honey Recipe
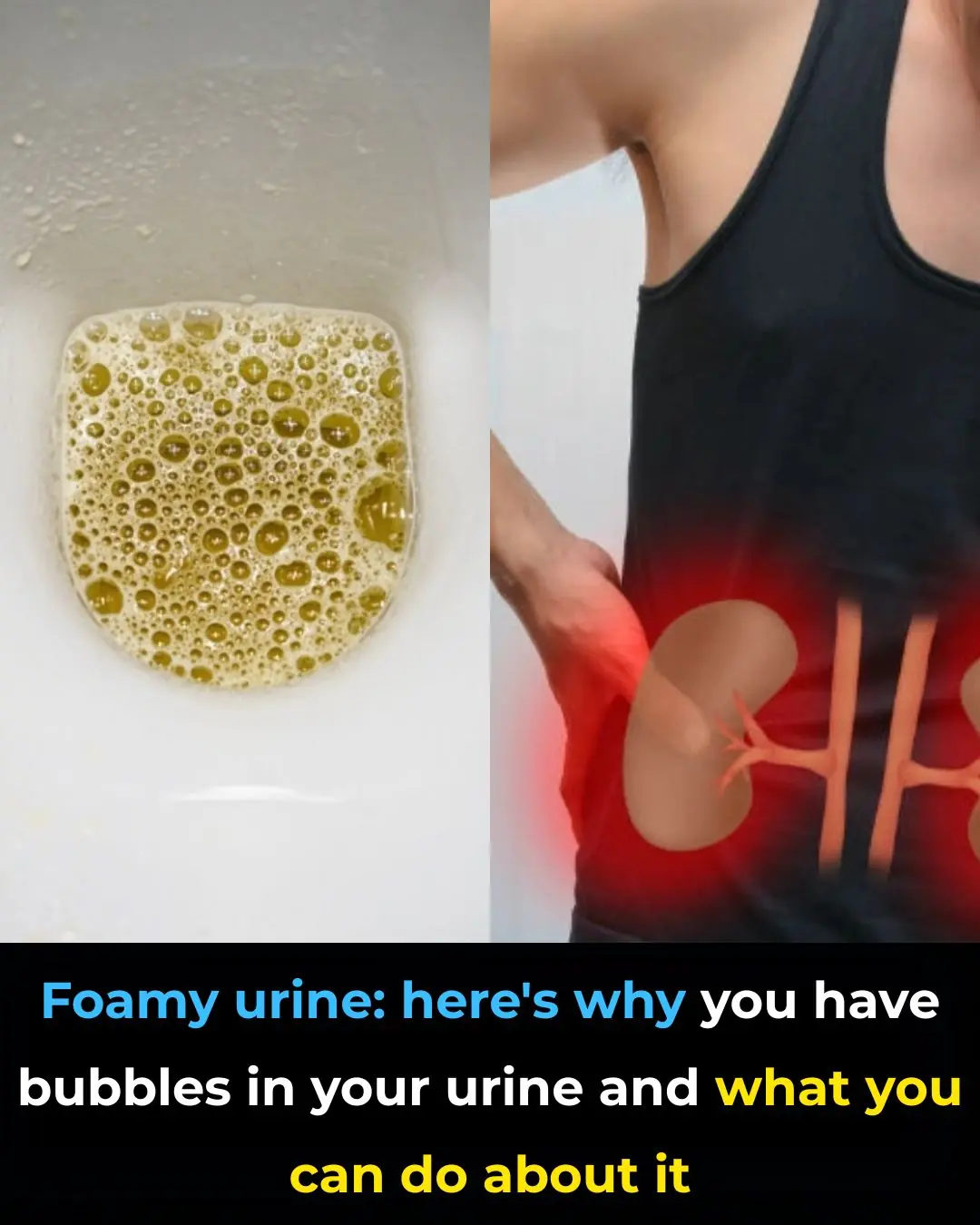
Foamy Urine: Here’s Why You Have Bubbles in Your Urine

Why Almonds Are So Good for You: Health Benefits of Almonds Backed by Science

When Garlic Turns Harmful: Common Mistakes That Can Make a Healthy Food Risky
The Most Affordable Food That Supports Bone Health and Helps Fight Osteoporosis

Onion Water for Hair Growth: What It Can Do, What It Can’t, and What Science Really Says
A Cardiac Surgeon’s Warning: Why Many Elderly Patients Should Be Cautious About This Common Medication

Canada Builds the Future in Wood: Inside Toronto’s Groundbreaking Timber Skyscraper

The Woman Who Refused to Quit: How Jacklyn Bezos Changed Her Life—and Helped Shape the Future of the World

San Francisco Establishes Reparations Fund Framework to Address Historical Racial Inequities

From Prison Food to Fine Dining: How Lobster Became a Luxury in America

No Reset: When a Clinical Mindset Takes Over Your Whole Life

India’s Olympic Ambition vs. Football’s Struggle ⚽🏟️🇮🇳

Brishti Gupta: Turning a Home Kitchen into Global Inspiration 👩🍳❤️🌍
