Skin Cells Can Send Electrical Signals to Help Heal Wounds – A New Discovery in Wound Healing
Skin Cells Can Send Electrical Signals to Help Heal Wounds – A New Discovery in Wound Healing
When you think of cells sending electric signals, nerve cells probably come to mind. But recent research has uncovered something truly surprising: skin cells can also send out electrical pulses after being injured—and while these signals are slower than those in nerves, they may play a key role in how wounds heal.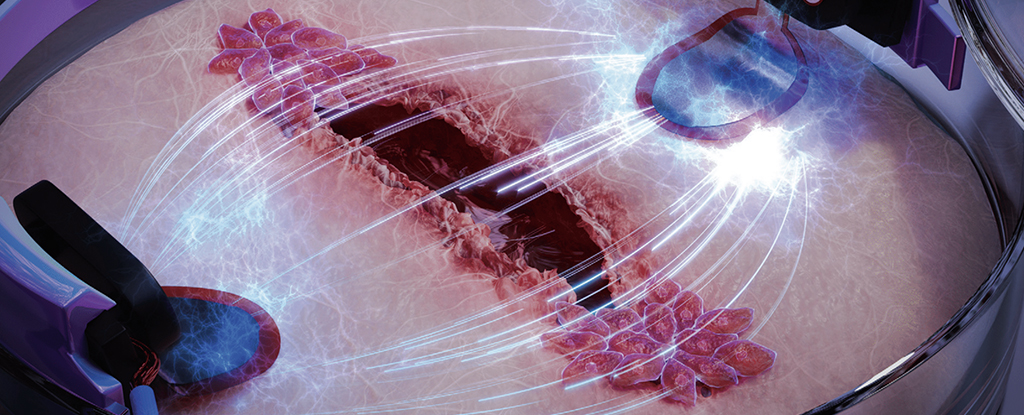
A Shocking Discovery: Skin Cells Can Communicate Electrically
For years, scientists believed that only neurons could send electric signals to communicate across the body. But researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have discovered that epithelial cells—the kind found in skin and internal organs—can also produce electrical pulses when damaged.
The pulses are slow but steady, traveling across 500 micrometers, or about the width of 40 skin cells. These signals may act as a warning system, telling nearby cells that injury has occurred and preparing them for wound healing.
How the Experiment Was Conducted
To study this phenomenon, scientists grew human skin cells and dog kidney cells—both types of epithelial cells—on special chips equipped with electrodes. Using precision lasers, they created controlled damage to some of the cells and then monitored the electrical activity.
What they found was unexpected: tiny voltage spikes triggered by the flow of calcium ions. While similar in voltage to nerve impulses, these electric pulses were much slower, taking 1–2 seconds to register, compared to nerve impulses that occur in milliseconds.
In fact, the pulses were so slow that the researchers nearly missed them. Their monitoring software was initially set to detect only fast nerve-like signals and ignored anything slower than 500 milliseconds. Once that filter was removed, the signals became clear—and consistent.
Electric Pulses That Last for Hours
One of the most fascinating findings was that the injured cells continued to emit electrical signals for over five hours. This suggests that the signals are not just a brief response, but a long-term communication system.
The goal? Likely to coordinate wound healing by signaling surrounding cells to respond—either by removing damaged cells, initiating immune responses, or starting the repair process.
Why This Matters: A New Understanding of Wound Healing
Scientists have long known that wounds alter the electric fields in tissues, but this is the first time epithelial cells themselves have been seen sending electric spikes. It marks a fundamental shift in how we understand the body’s healing process.
While nerve signals handle fast, immediate responses, these slow, sustained electrical pulses may manage the long-term healing process, which takes days or even weeks. It’s a crucial new piece of the puzzle in regenerative medicine.
What’s Next? 3D Tissue and Cross-Cell Communication
The research team plans to extend their study by exploring how these electric signals work in 3D tissue models and how they interact with other cell types. This could lead to breakthroughs in how we treat wounds, from skin injuries to post-surgical healing.
Understanding the electrical side of biology could also open doors for new medical technologies, such as electrical therapies that promote faster, more efficient healing.
Conclusion
This groundbreaking study from the University of Massachusetts Amherst has revealed a new layer of communication in our bodies—one powered by electricity, not just chemicals. As researchers continue to explore this hidden language of cells, it’s becoming clear that bioelectricity plays a bigger role in health and healing than we ever imagined.
So next time you get a scrape or cut, remember—your skin cells might just be talking to each other through tiny electric pulses, setting the stage for your body’s natural repair system to kick into gear.
News in the same category

I spent a couple of nights at my friend’s previous apartment and saw these unusual bumps
Understanding the Link Between Your Blood Type and Health
10 Unusual Signs Your Blood Sugar Is Constantly Too High

Five Simple Drinks That Help Eliminate Uric Acid and Prevent Gout Flare-Ups

Red and Processed Meat Consumption Increases Cancer Risk, Experts Warn

The Hidden Dangers of Eating Leftover Food Stored Overnight

Two Rare Neurologic Disorders Added to US Newborn Screening Panel

Intensive Long-Distance Running and Colon Health: Emerging Evidence of Increased Risk for Advanced Adenomas
After Many Years of Practice, Doctors Noticed Six Common Morning Habits Among Cancer Patients

Six Foods That May Help Prevent Colorectal Cancer — Especially After Age 45
How to treat nerve pain in the foot, toes & legs
Why Your Legs Cramp At Night And How To Stop It From Happening
1 teaspoon a day melts away fatty liver naturally
Revolutionary science is changing how we treat joint damage.

Don't be fooled by their supposed health benefits; these 3 fruits are secretly damaging your liver

Early signs of stroke should not be ignored, regardless of age

Surprising Health Benefits of Eating Ginger Every Day

Bizarre theories about people who have ‘never broken a bone’
The Cardiovascular Benefits of Pomegranate Juice: Scientific Evidence and Mechanisms
News Post

Jesy Nelson's celebrity friends including ex Chris Hughes show support as Little Mix singer reveals twin girls' devastating diagnosis

People with weak kidneys often do these 4 things every day: If you don't stop soon, it can easily damage your kidneys

Get Soft, Pink Lips Naturally: A Simple DIY Scrub for Smoother Lips

Over 60? Waking Up at 2 A.M. Every Night? This One Warm Drink May Help You Sleep Through Till Morning

7 Everyday Foods That Help Maintain Muscle Strength and Stay Active After Age 50

Oregano for Eyes: The Little Leaf That May Protect Your Vision After 40

I spent a couple of nights at my friend’s previous apartment and saw these unusual bumps

The Healing Power of Small Gestures in Hospitals 💧💕

From Coal to Clean: Maryland’s Largest Solar Farm Goes Live 🌞⚡🌿

Understanding the Link Between Your Blood Type and Health

I swear, I didn’t have the faintest clue about this!

Jeff Bezos: “Earth Has No Plan B” — Why Industry May Need to Move Into Space 🌍🚀

Chiefs confirm Patrick Mahomes tore ACL in left knee

Elon Musk Just Became The First Person Ever Worth $600 Billion

From Stage Lights to Ring Lights: Young Thug’s Atlanta Proposal Stuns Fans

Six Georgia Inmates Risk Nothing and Save Sheriff’s Life

Condolences: Angela Yee Shares Her Brother Passed Unexpectedly At 51 After Suffering From An Aneurysm

Rethinking Land Use: Protecting Forests Through Redevelopment

Woman at center of viral 'kiss cam' moment at Coldplay concert breaks silence
