
A Hidden Consequence of Tick Bites You Should Know About
A Tick Bite That Changes Everything: The Rise of Alpha-gal Syndrome
A specific species of tick is increasingly being linked to a rare but potentially life-threatening condition known as Alpha-gal syndrome, an unusual allergy in which a single bite can permanently change how the human body reacts to food. Unlike typical food allergies that develop early in life, this condition can appear suddenly in adulthood, leaving many people confused and undiagnosed for years.
Alpha-gal syndrome occurs after a person is bitten by certain ticks—most notably the lone star tick in the United States. Following the bite, the immune system becomes sensitized to alpha-gal, a sugar molecule found in the meat and byproducts of mammals, including beef, pork, lamb, venison, and sometimes dairy or gelatin. Once sensitized, the body begins treating alpha-gal as a threat, triggering allergic reactions after consumption.
What makes this condition especially alarming and difficult to diagnose is the delayed onset of symptoms. Unlike most food allergies, which cause immediate reactions, Alpha-gal syndrome typically triggers symptoms three to six hours after eating red meat. Affected individuals may experience hives, intense abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, shortness of breath, or swelling of the lips and throat. In severe cases, the reaction can escalate into anaphylaxis, a medical emergency that can be fatal without prompt treatment.
Because of this delay, many patients fail to associate their symptoms with meat consumption. As a result, people often spend years undergoing medical tests and dietary changes before receiving a correct diagnosis. Physicians, too, may overlook the condition due to its atypical presentation and relative rarity compared to other food allergies.
In recent years, reported cases of Alpha-gal syndrome have been increasing worldwide. Scientists attribute this rise largely to climate change and shifting ecosystems, which are expanding tick habitats into new regions. Areas that previously had little to no history of this condition are now seeing a steady increase in patients who suddenly become allergic to foods they have eaten without issue for most of their lives. Warmer temperatures and longer tick seasons are further accelerating this trend.
Currently, there is no cure for Alpha-gal syndrome. The primary treatment involves strict avoidance of red meat and other mammal-derived products, along with carrying emergency medication such as epinephrine for accidental exposure. For some individuals, the allergy may lessen or disappear over time, particularly if they avoid additional tick bites. However, for others, the condition becomes long-term or permanent, requiring lifelong dietary vigilance.
As tick populations continue to spread and awareness of Alpha-gal syndrome grows, health experts stress the importance of prevention, early recognition, and education. Understanding the risks associated with tick bites may help reduce future cases of this unusual but serious allergy.
Sources
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Alpha-gal Syndrome.
-
Mayo Clinic. Red Meat Allergy Caused by Tick Bites.
-
National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID). Alpha-gal Allergy Research Overview.
-
BBC Future. The Tick Bite That Can Make You Allergic to Meat.
-
World Health Organization (WHO). Climate Change and Vector-Borne Diseases.
News in the same category

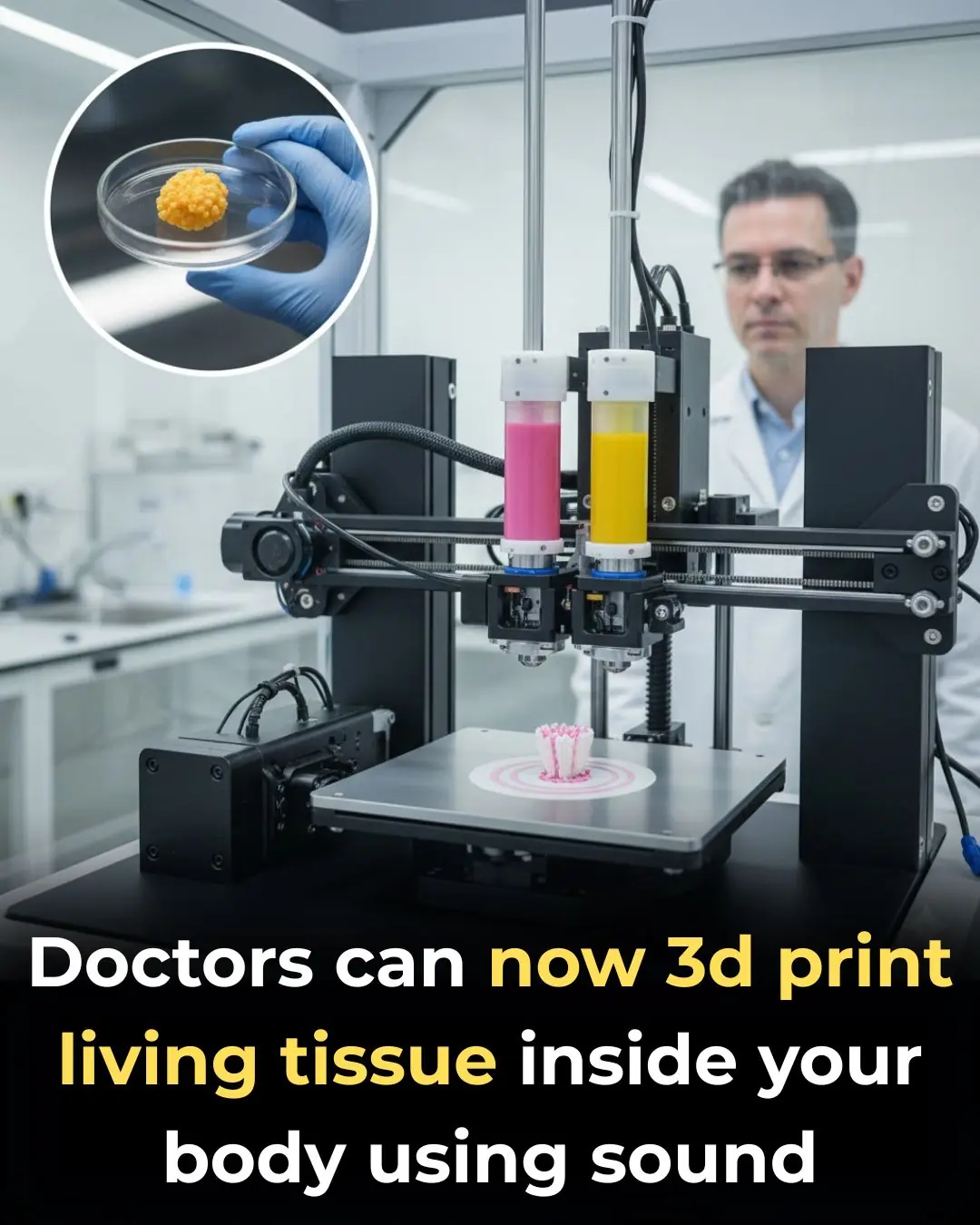
Medicine Breaks New Ground as Ultrasound Builds Tissue Without Surgery

A Heartbreaking Survival Trick: How a Stray Cat Learned to Hide His Pain

Bears Turn Honey Theft Into a Surprising Taste Test in Turkey

Scientists Say Your Butt Shape May Say More About Your Health Than You Think
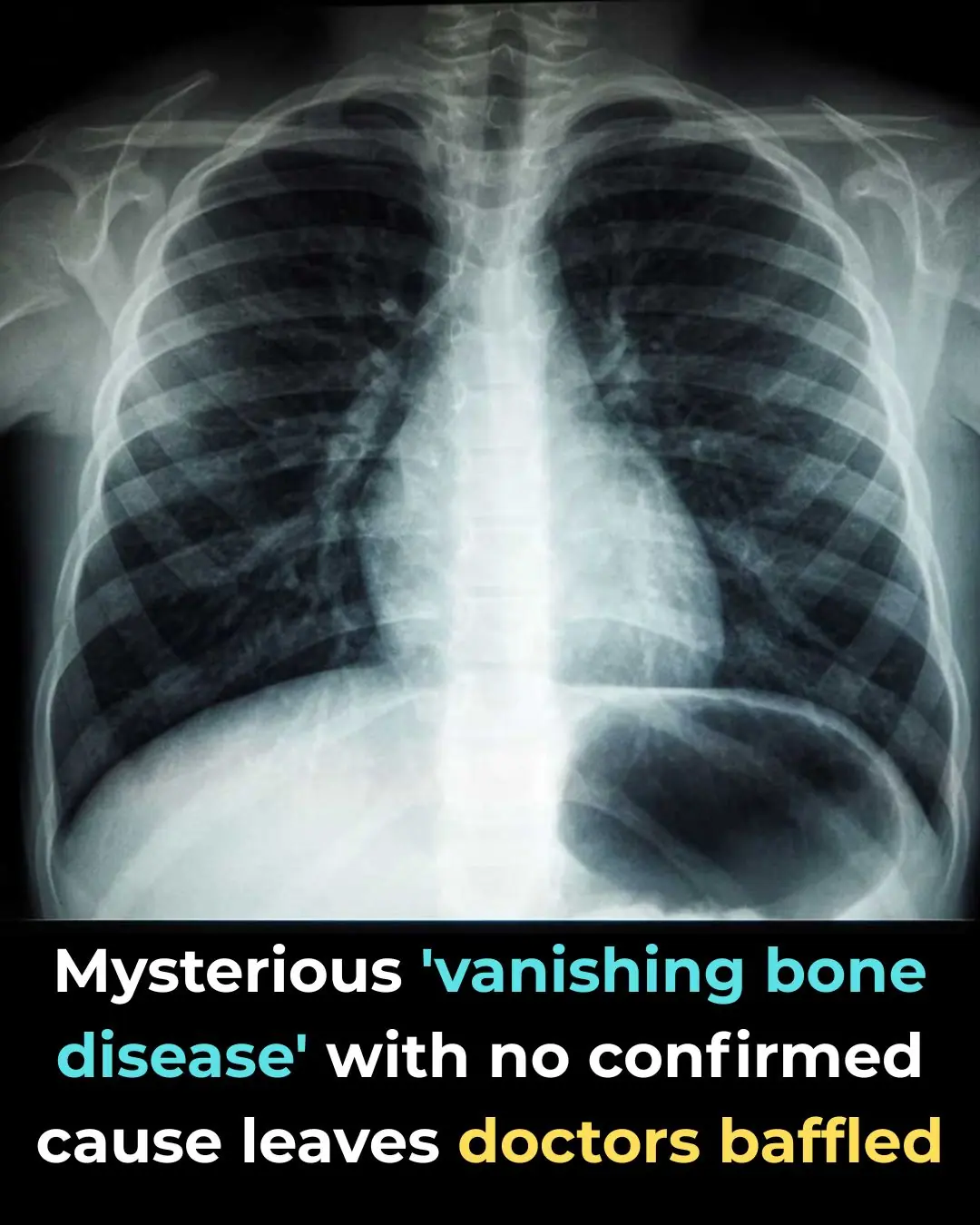
The Rare Condition That Makes Human Bones Slowly Vanish

Smoking, Obesity, and Hypertension: The Leading Risk Factors for Kidney Cancer

Three Friends, One Hive, and a Very Bad Idea

Measles Cases Hit 30-Year High in the US, Raising Urgent Public Health Concerns

Why Skipping Housework on New Year’s Day Might Bring You Good Luck

Millie Bobby Brown’s Reaction to Eleven’s Ending Goes Viral After Stranger Things Finale

Baby Name Expert Predicts the Most Popular Naming Trends for 2026

No Fines, No Enforcement: How Trust Worked During Japan’s Toll System Failure

This “Easy” Puzzle for Kids Is Completely Stumping Adults

Beavers Build a Dam in the Czech Republic, Solving a Years-Long Environmental Problem

Social Media Users Agree on the Most Painful Physical Experience — and It’s Not What You’d Expec

James Webb Space Telescope Reveals Hidden Mid-Infrared Flares from the Milky Way’s Central Black Hole

New Vision Correction Technique Reshapes the Cornea Without Surgery
News Post

Say Goodbye to Varicose Veins Naturally: A Simple Garlic, Onion, and Olive Oil Remedy That May Offer Relief

Why Seniors Are Turning to Honey and Cloves for Everyday Comfort After 60

Can Garlic and Lemon Really Support Better Vision? Kitchen Staples Your Eyes Might Appreciate

Banana Flower: The Underrated Superfood Taking Over in 2025

Fears of a Texas Serial Killer Intensify After Three More Bodies Are Recovered from Houston Bayous

From Casual Drinking to Dependence: A Recovering Alcoholic Reveals Seven Warning Signs of Addiction

Why Americans Were Shocked by the British Way of Washing Dishes

No one told me
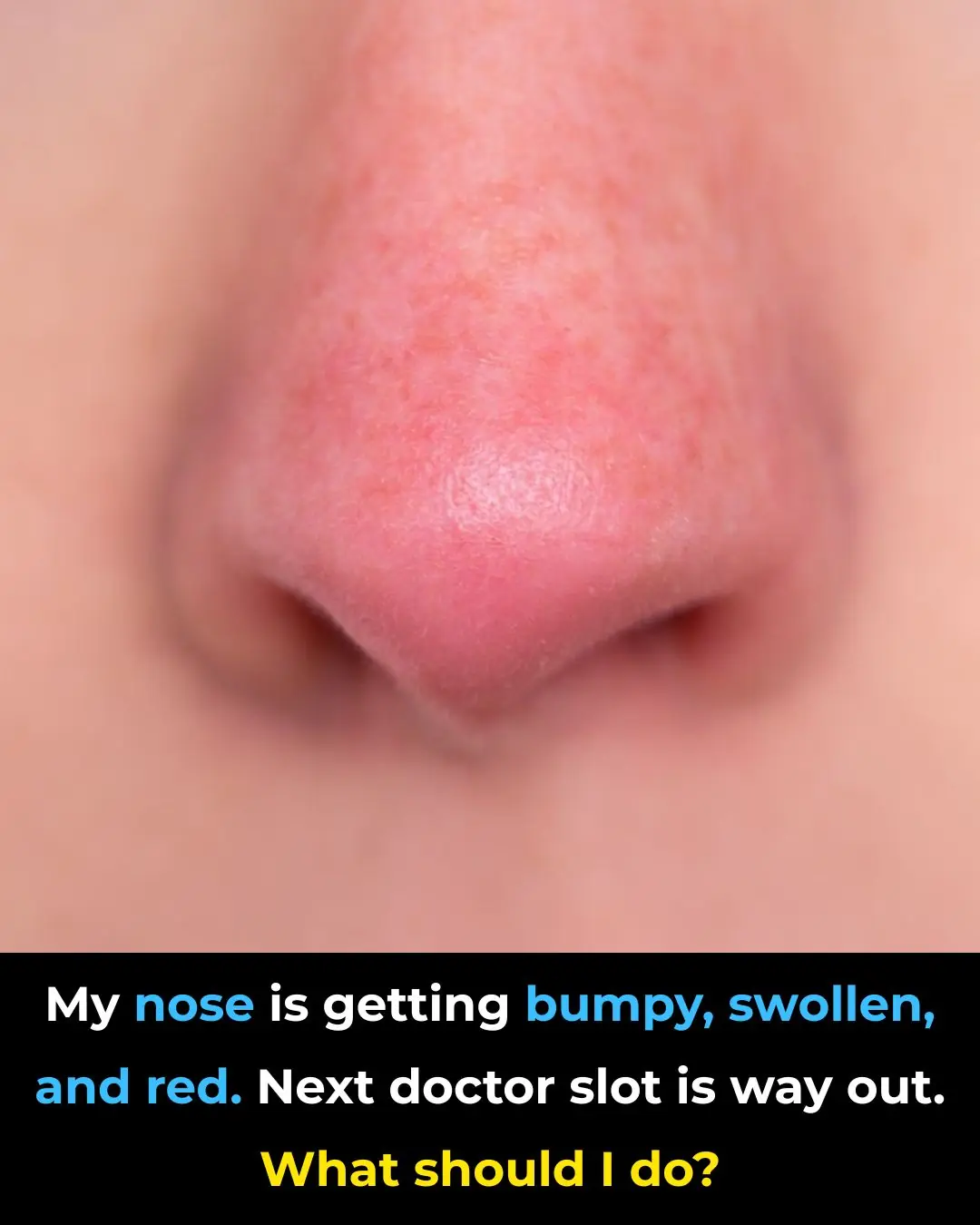
My nose is getting bumpy, swollen, and red. Next doctor slot is way out. What should I do?

Can You Spot It? The Viral “Sniper Vision” Challenge That’s Testing Human Perception

Most Doctors Won’t Tell You, But This Can Cut Heart Attack & Stroke Risk By 80%

The Best Proven Ways to Heal Scars Naturally (Evidence Based)

How Japan Preserves Nature by Relocating Trees Instead of Cutting Them Down
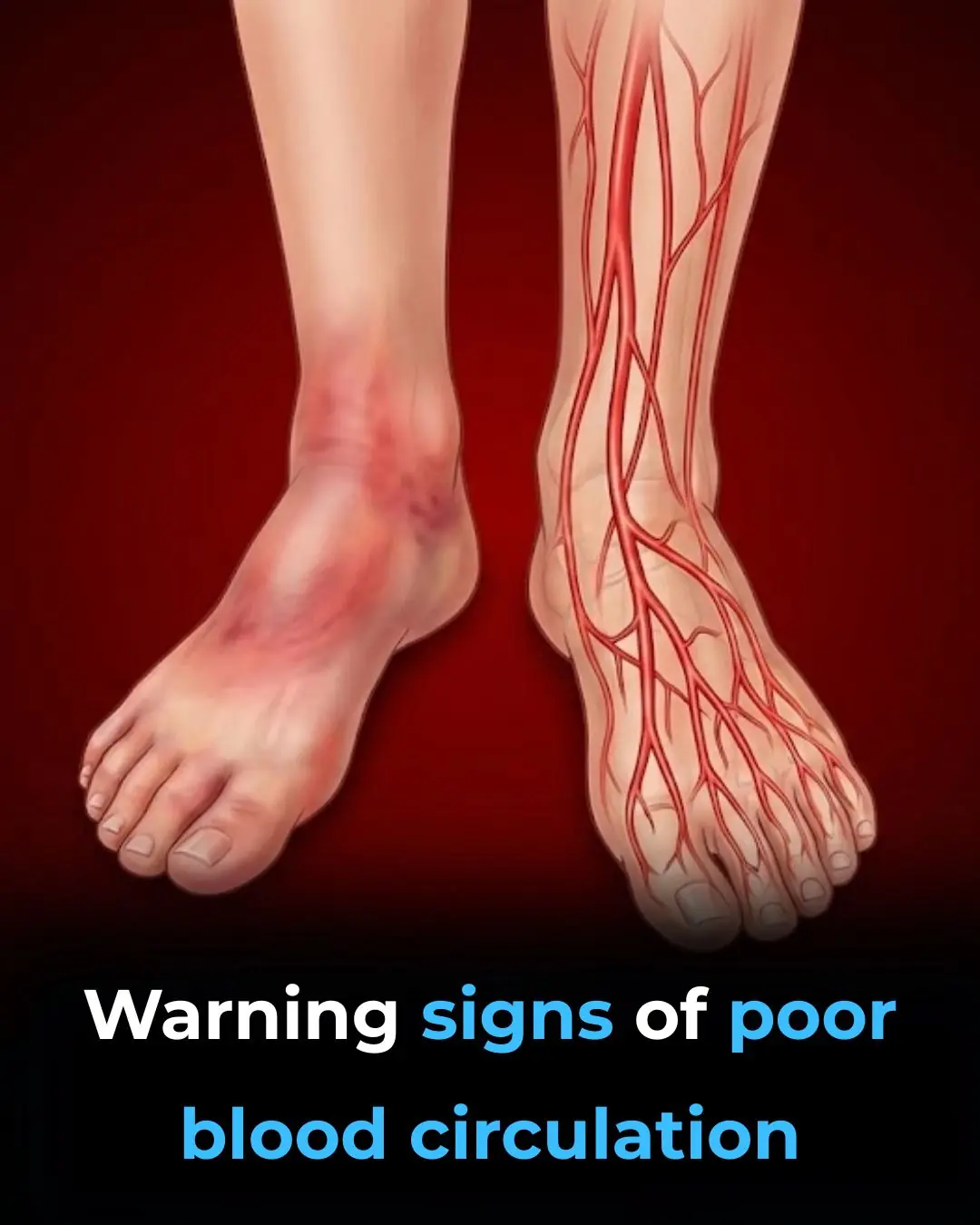
16 Warning Signs of Poor Blood Circulation and How to Treat It
The Best Home Remedies For Getting Rid of Ear Infection

A Simple Act of Kindness That Turned a Lifelong Dream into Reality

Soap Left on Plates? British Dishwashing Method Sparks International Debate

A Hero on Four Paws: How a Cat’s Instincts Saved a Baby from an Alligator

Florida’s Trooper’s Law: A Landmark Step Toward Protecting Pets During Natural Disasters
