
No Fines, No Enforcement: How Trust Worked During Japan’s Toll System Failure
When Japan’s Toll System Failed, Trust Took Over — and It Worked
For 38 hours, Japan’s electronic toll collection system experienced a nationwide malfunction. Under normal circumstances, such a breakdown could have caused widespread traffic congestion, confusion, and frustration. In many countries, it might even have led to disputes, rule-breaking, or attempts to avoid payment altogether. Yet in Japan, something remarkably different happened.
To prevent massive traffic jams and disruption, officials made an unusual decision: they opened the toll gates. Drivers were allowed to pass freely, with authorities simply asking them to pay the toll later through an online system if they were able to do so. There were no fines, no penalties, and no enforcement measures put in place—only a request based on trust.
What followed surprised many observers.
Once the toll system was fully restored, more than 24,000 drivers voluntarily went online and paid their toll fees, even though they were under no legal obligation to do so. No one was tracking individual vehicles, and there were no consequences for failing to pay. Yet tens of thousands of people chose honesty over convenience.
This quiet moment quickly gained attention as an example of how high levels of social trust can shape behavior. Japan is often described as a “high-trust society,” where citizens generally believe that others will follow shared rules and norms. Sociologists note that such trust does not emerge overnight—it is built through long-standing cultural values, consistent institutions, and a strong sense of social responsibility.
Experts point out that trust-based systems can be surprisingly effective. When people feel respected and trusted by authorities, they are often more willing to act responsibly in return. In contrast, overly punitive systems can sometimes encourage avoidance or resentment rather than cooperation.
The toll system incident also highlights the efficiency of social norms over strict enforcement. Instead of deploying additional staff, issuing citations, or creating legal complications, officials relied on the public’s sense of duty. The result was not chaos, but cooperation.
In a global context where honesty and civic responsibility are frequently questioned, this episode offers a powerful reminder. Trust, when embedded deeply within a society, can function as an invisible infrastructure—one that keeps systems running even when technology fails.
While no society is perfect, Japan’s response to this unexpected breakdown demonstrated how mutual trust between citizens and institutions can lead to outcomes that laws alone cannot guarantee. Sometimes, the most effective solution is not stricter control, but confidence in people’s willingness to do the right thing.
Sources
-
BBC News. Japan’s high-trust society and public responsibility
-
The Japan Times. How social norms shape behavior in Japan
-
OECD. Trust and public governance
-
World Values Survey. Social trust and civic behavior across countries
-
Harvard Business Review. Why trust-based systems outperform control-based systems
News in the same category

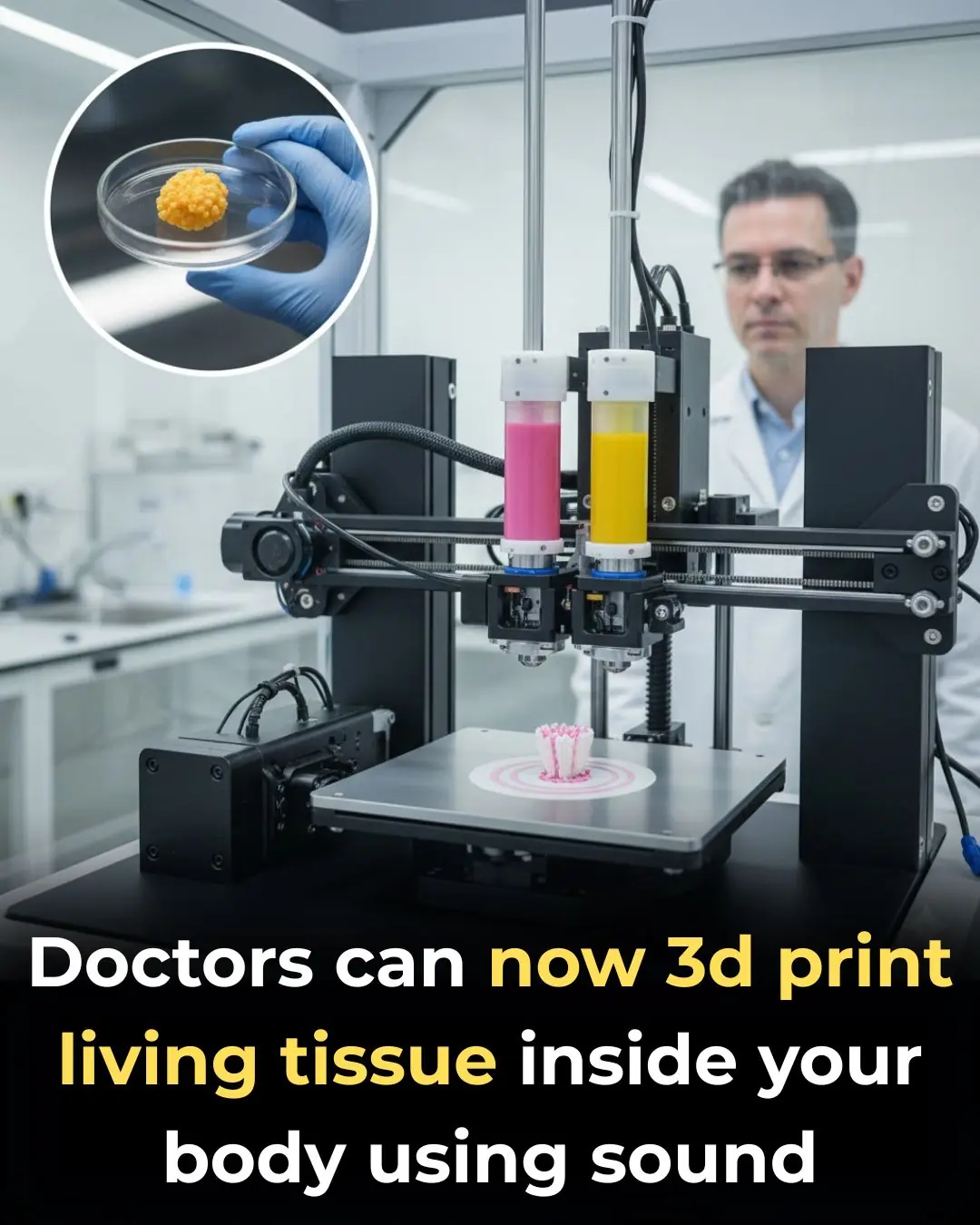
Medicine Breaks New Ground as Ultrasound Builds Tissue Without Surgery

A Heartbreaking Survival Trick: How a Stray Cat Learned to Hide His Pain

Bears Turn Honey Theft Into a Surprising Taste Test in Turkey

Scientists Say Your Butt Shape May Say More About Your Health Than You Think
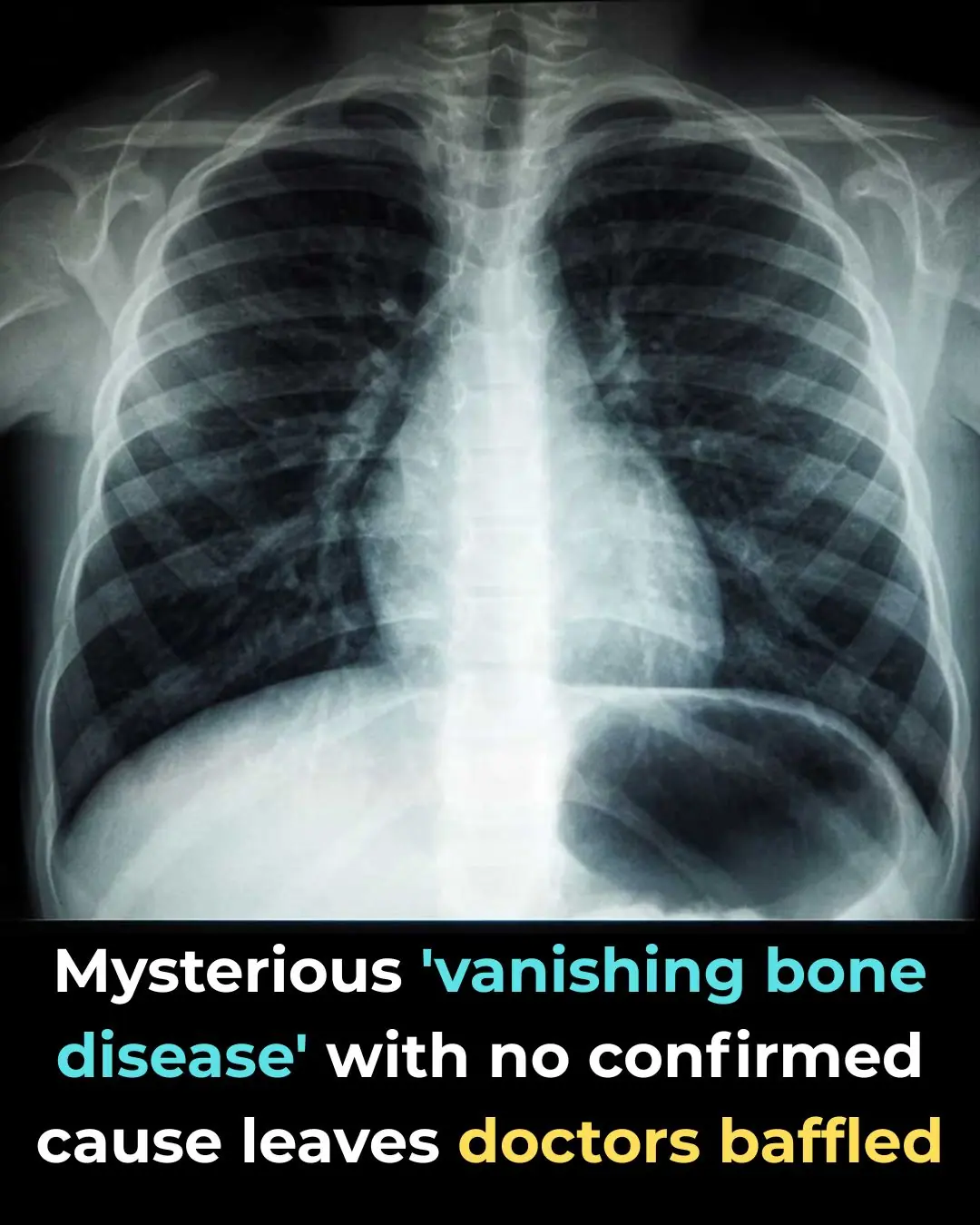
The Rare Condition That Makes Human Bones Slowly Vanish

A Hidden Consequence of Tick Bites You Should Know About

Smoking, Obesity, and Hypertension: The Leading Risk Factors for Kidney Cancer

When Blue Wings Return: A Second Chance for the Spix’s Macaw

Three Friends, One Hive, and a Very Bad Idea

Measles Cases Hit 30-Year High in the US, Raising Urgent Public Health Concerns

Why Skipping Housework on New Year’s Day Might Bring You Good Luck

Millie Bobby Brown’s Reaction to Eleven’s Ending Goes Viral After Stranger Things Finale

Baby Name Expert Predicts the Most Popular Naming Trends for 2026

This “Easy” Puzzle for Kids Is Completely Stumping Adults

Beavers Build a Dam in the Czech Republic, Solving a Years-Long Environmental Problem

Social Media Users Agree on the Most Painful Physical Experience — and It’s Not What You’d Expec

James Webb Space Telescope Reveals Hidden Mid-Infrared Flares from the Milky Way’s Central Black Hole

New Vision Correction Technique Reshapes the Cornea Without Surgery
News Post
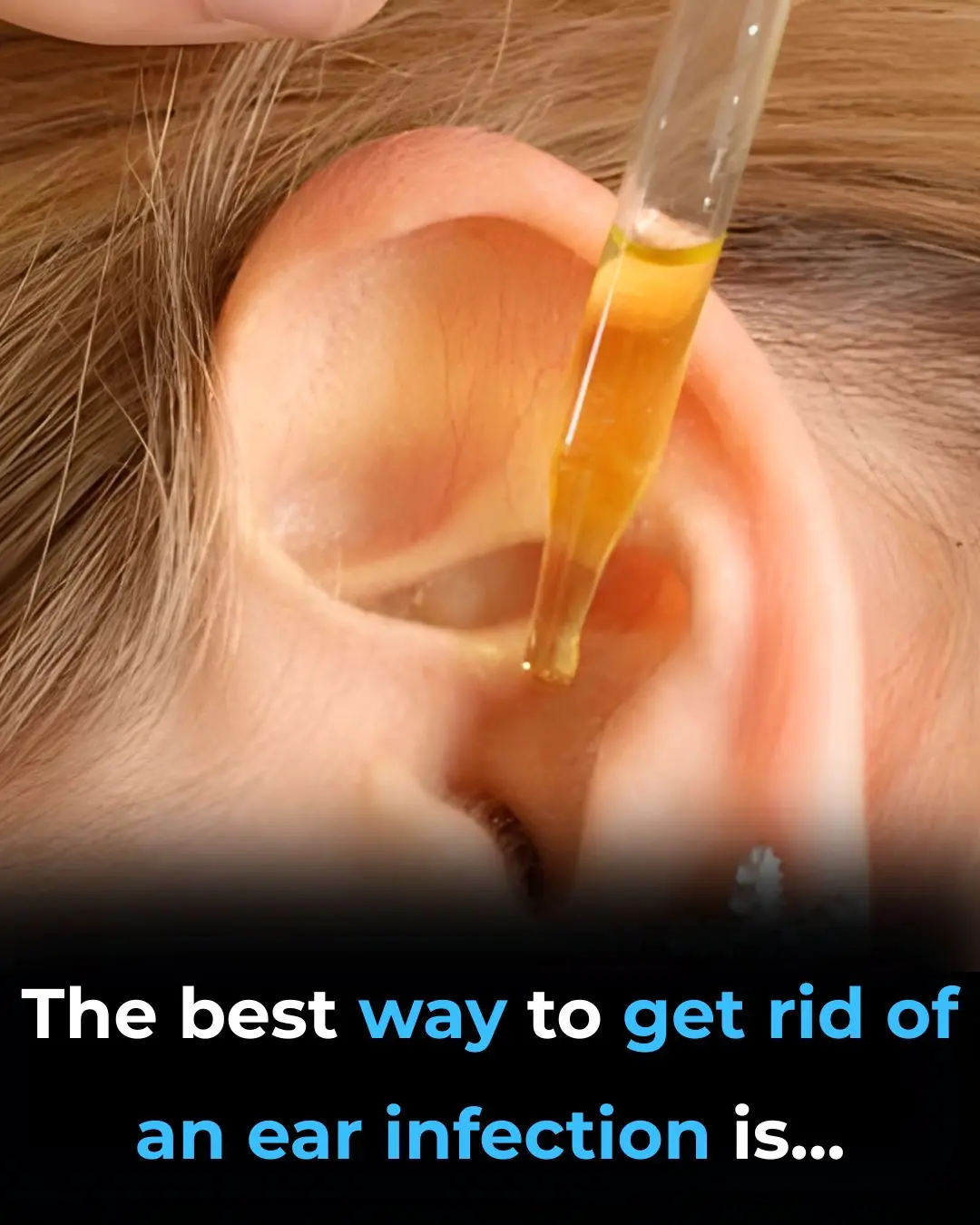
The Best Home Remedies For Getting Rid of Ear Infection

A Simple Act of Kindness That Turned a Lifelong Dream into Reality

Soap Left on Plates? British Dishwashing Method Sparks International Debate

A Hero on Four Paws: How a Cat’s Instincts Saved a Baby from an Alligator

Florida’s Trooper’s Law: A Landmark Step Toward Protecting Pets During Natural Disasters

An 11,000-Year-Old Indigenous Settlement in Saskatchewan Is Transforming Our Understanding of North America’s Ancient Past

Never realized this

When Speed Saves Lives: The Lamborghini Mission That Delivered Hope

Daily Step Counts Combined With Genetic Risk Can Better Predict Type 2 Diabetes

Gestational Diabetes Rates Surge Across the United States

Why Does Lung Cancer Affect Non-Smokers? A Hidden Culprit in the Kitchen That Many People Overlook

Love, Sacrifice, and the Healing Power of Commitment 💖🩺

Figo’s Bravery: A Testament to the Selflessness of Dogs 🐕💛

Braving the Storm: A Mail Carrier’s Act of Compassion ❄️💙

Belgian Prodigy Earns PhD in Quantum Physics at Just 15 🌟⚛️
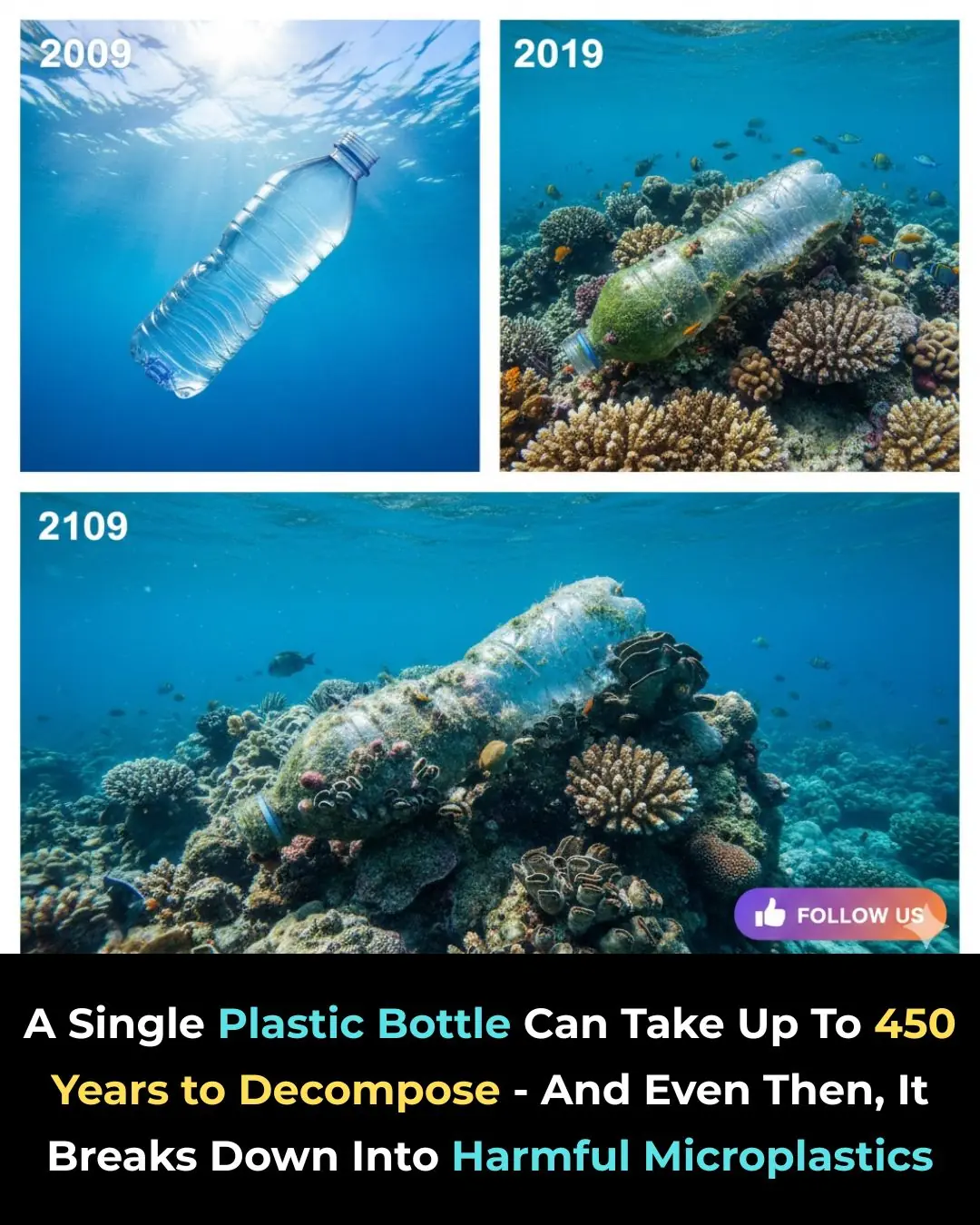
One Plastic Bottle. One Huge Problem. 🌍♻️

A Major Shake‑Up in the EV World: BYD Surpasses Tesla 🚗⚡🔋🌍

MS Treatment Costs in the United States Surge by 125% Over Two Decades

Cold air pours in under the garage door and the repair company can’t come until after New Year. What can I do now?
