
Doctors reveal that consuming pumpkin causes in...
🧠 Doctors Reveal: The Side Effects of Eating Pumpkin
Pumpkin is widely recognized as a nutrient-dense food packed with fiber, beta-carotene, potassium, and antioxidants. It supports eye health, immune function, digestion, and heart health when eaten in appropriate amounts.
However, like any food—even healthy ones—overconsumption or improper intake can lead to unwanted side effects. Doctors emphasize that moderation, medical conditions, and individual tolerance all matter.
Here’s what you should know.
⚠️ 1. Can Cause Digestive Problems
Pumpkin is naturally high in dietary fiber. While fiber promotes healthy bowel movements and supports gut bacteria, too much fiber—especially if introduced suddenly—can overwhelm the digestive system.
Possible symptoms:
-
Bloating
-
Gas
-
Abdominal cramps
-
Diarrhea
-
Loose stools
Why this happens:
Excess fiber increases stool bulk and speeds intestinal movement. If your body is not accustomed to high fiber intake, it may respond with irritation or discomfort.
🩺 Tip:
Start with small portions and increase gradually. Drink enough water to help fiber move smoothly through your digestive tract. Sudden large servings of pumpkin soup or puree may be harder on the stomach.
⚠️ 2. May Lower Blood Sugar Too Much
Pumpkin—especially pumpkin seeds and puree—contains compounds that may help regulate blood sugar levels. This is generally beneficial, particularly for people with insulin resistance.
However, for individuals taking:
-
Insulin
-
Oral diabetes medications
large amounts of pumpkin may enhance the glucose-lowering effect and lead to:
-
Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
-
Dizziness
-
Sweating
-
Shakiness
-
Weakness
🩺 Tip:
If you have diabetes or take blood sugar medication, monitor your glucose levels carefully when adding pumpkin to your diet. Consult your doctor before making pumpkin a daily staple.
⚠️ 3. Risk of Allergic Reactions (Rare)
Although uncommon, some people may develop an allergy to pumpkin or pumpkin seeds.
Possible allergic symptoms:
-
Skin rash or itching
-
Hives
-
Nasal congestion
-
Swelling of lips or throat
-
Difficulty breathing (rare but serious)
🩺 Tip:
If you experience any signs of an allergic reaction, stop eating pumpkin immediately and seek medical attention.
⚠️ 4. Can Contribute to Excess Vitamin A Intake
Pumpkin is rich in beta-carotene, which the body converts into vitamin A. Vitamin A is essential for vision, immunity, and skin health.
However, excessive intake—especially when combined with vitamin A supplements or other vitamin A-rich foods—may increase the risk of hypervitaminosis A.
Potential symptoms include:
-
Headaches
-
Nausea
-
Blurred vision
-
Joint pain
-
Fatigue
Adults typically require about 700–900 µg of vitamin A per day. One cup of cooked pumpkin can provide a very high percentage of that requirement.
While beta-carotene is generally safer than preformed vitamin A from supplements, consistently overeating pumpkin alongside supplements may still create imbalance.
🩺 Tip:
If you already take vitamin A supplements, monitor your intake and avoid excessive daily pumpkin consumption.
⚠️ 5. May Interfere With Certain Medications
Pumpkin has mild diuretic (water-releasing) properties due to its potassium content and natural compounds. In moderate amounts, this can support healthy blood pressure.
However, in large quantities, it may:
-
Increase urine output
-
Alter electrolyte balance
-
Interact with blood pressure medications
-
Affect certain heart medications
🩺 Tip:
If you are taking medication for hypertension or heart conditions, speak with your doctor before consuming pumpkin juice, large bowls of pumpkin soup, or pumpkin-based cleanses regularly.
🌿 How Much Pumpkin Is Safe?
For most healthy adults:
✅ Ideal amount: About ½–1 cup (100–200 grams) of cooked pumpkin per day
✅ Best time to eat: During the day, when digestion is more active
✅ Best preparation: Steamed, roasted, or baked
Avoid:
❌ Overeating large portions daily
❌ Deep-fried pumpkin
❌ Excessive added sugar (sweetened condensed milk, syrup, heavy desserts)
Final Medical Perspective
Pumpkin is undeniably nutritious and beneficial when eaten in moderation. It provides antioxidants, fiber, and essential nutrients that support overall health.
However, more is not always better. Excess fiber, potential blood sugar fluctuations, medication interactions, and rare allergic reactions are all possible if intake becomes excessive.
✔ Healthy
✔ Nutrient-rich
✔ Safe in moderate portions
⚠ Overconsumption may cause digestive or metabolic issues
Balance and awareness are key. When eaten thoughtfully as part of a varied diet, pumpkin remains a wholesome and valuable addition to your meals.
News in the same category


Should you eat sprouted potatoes or not?

Doctors reveal that eating onion causes...

Doctors reveal that eating green onions causes …See more

What Really Happens to Your Body When You Sit Too Much

Natural Healing at 60: The Banana Peel, Poleo & Turmeric Drink That Changed My Life

Red Onion Revolution: 3 Irresistible Rituals for Explosive Hair Growth & Thickness

Lemongrass–Guava Leaf Tea: 13 Powerful Benefits You Need to Know

🏠 8 Household Items That Could Be Affecting Your Health (And How to Check Them Safely at Home)
Red Bumps That Look Like Goosebumps
Forget Knee Pain! A Simple Home Remedy with Sea Salt Doctors Don’t Talk About

What Happens After 15 Minutes?

The Surprising Health Benefits of Boiled Eggs
🚨 Recurrent Yeast Infections? STOP Doing These Things Immediately!
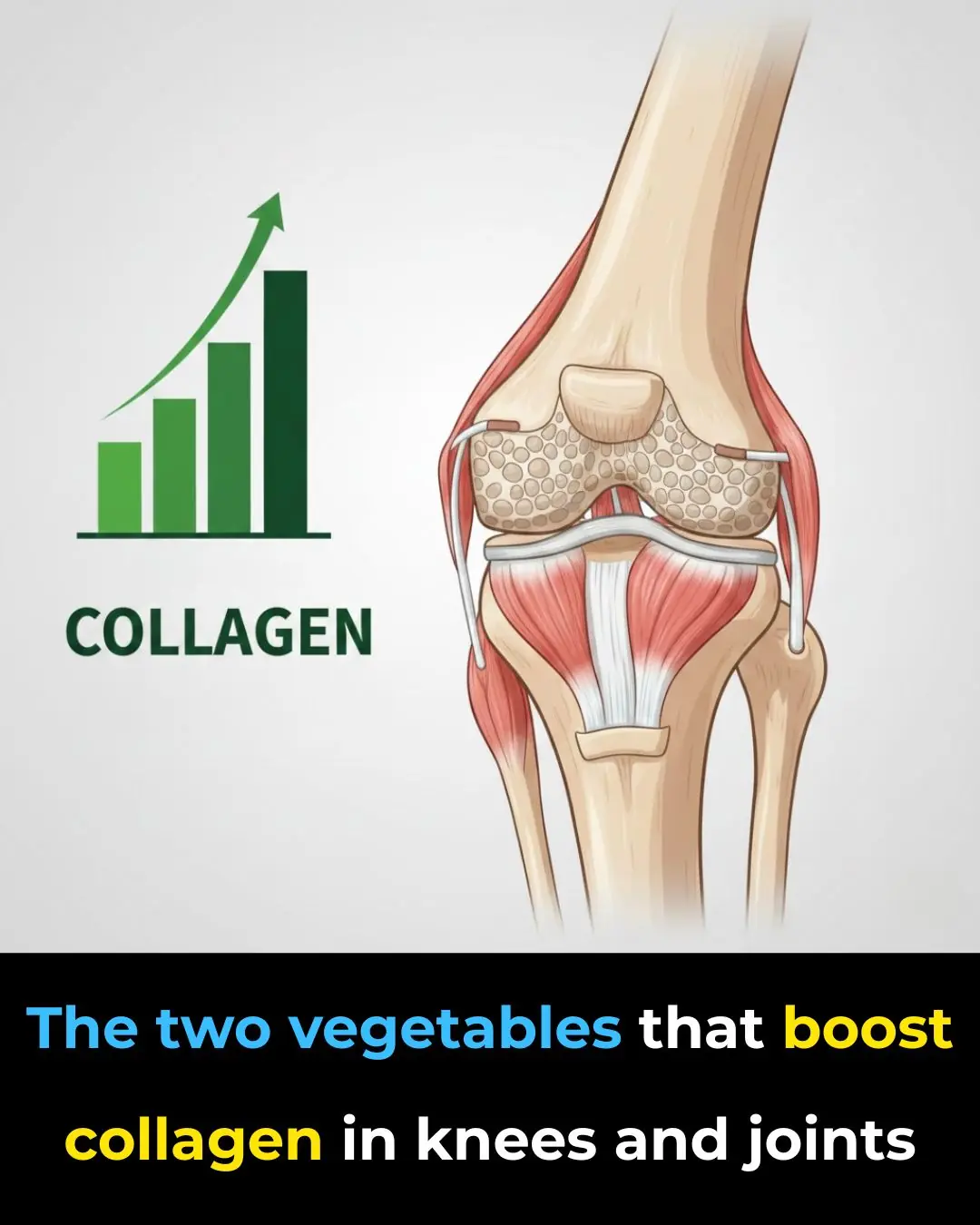
Doctors Are Amazed: Two Vegetables That Boost Collagen in the Knees and Relieve Joint Pain

Doctors warn 5 everyday habits are slowly killing your kidneys
9 Powerful Home Remedies to Eliminate Fungal Infections (Daad, Khaj, Khujli) Naturally and Fast

Longevity doctor who ‘reversed his biological age’ shares advice for people over 30

Tea for Swollen Legs: A Natural Remedy for Water Retention and Poor Circulation
News Post

“Do You Even Know What a Piano Is?” He Laughed.

The Child Who Spoke the Truth and the Woman Who Finally Won

I was waiting for the final kick to my ribs. Instead, I heard the sound of a bone breaking.

He Went Outside to Stop a Stray. He Found a Baby.
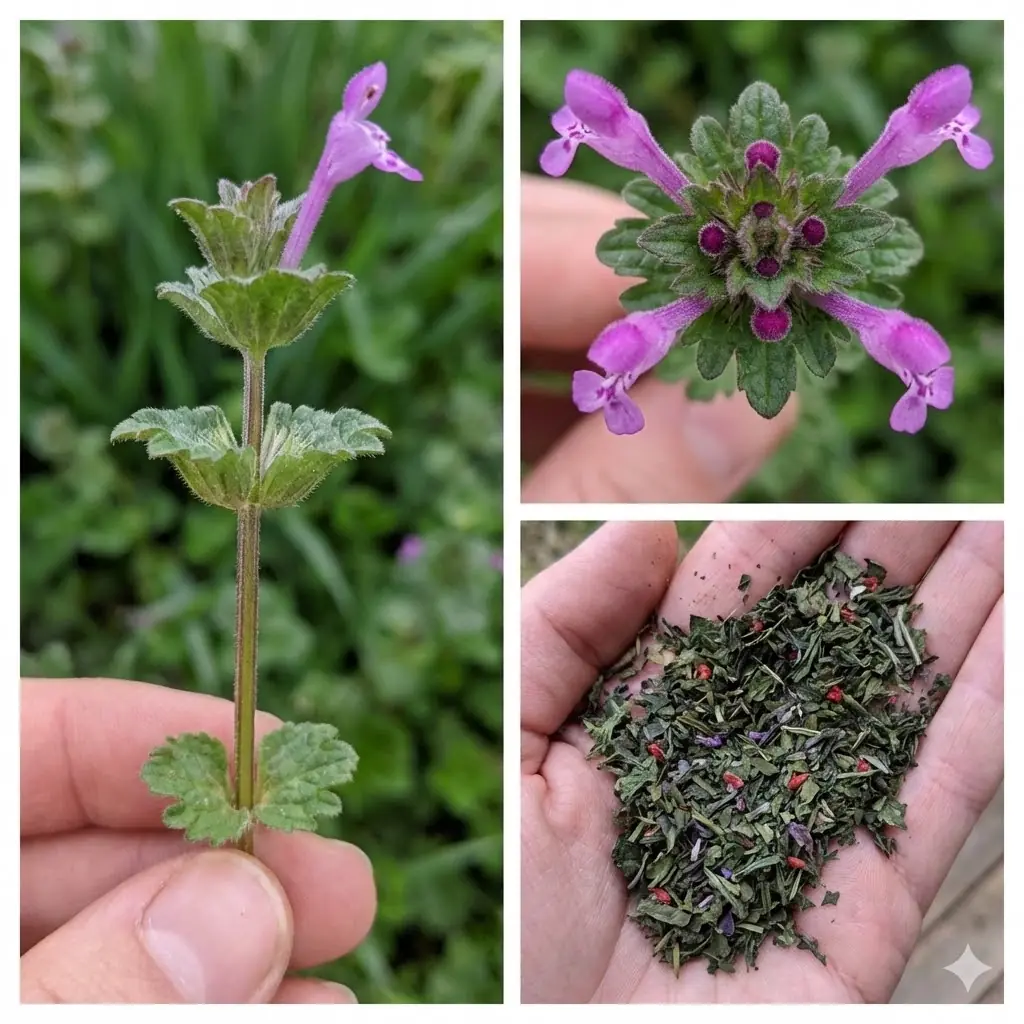

Henbit (Lamium amplexicaule): Identification, Benefits, and Homemade Uses
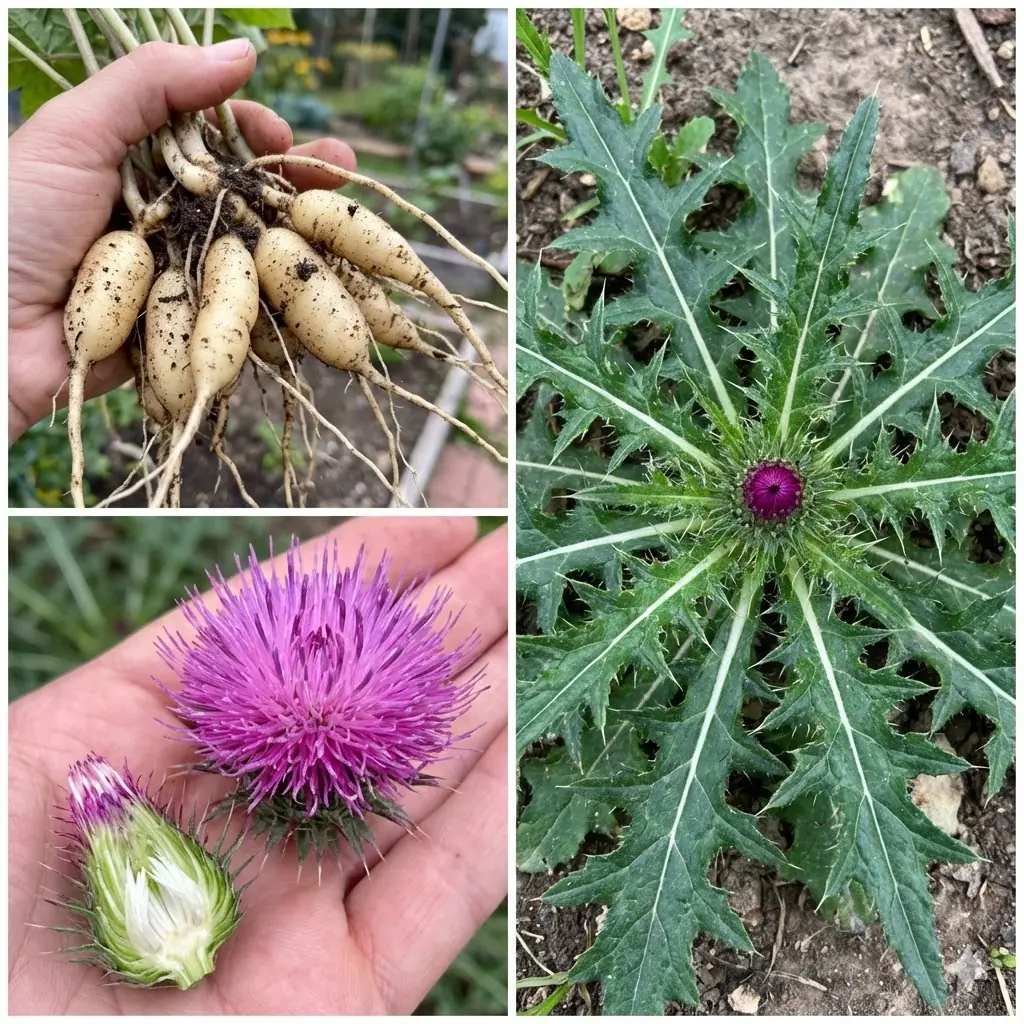

12 Benefits of Bull Thistle Root and How to Use It Naturally
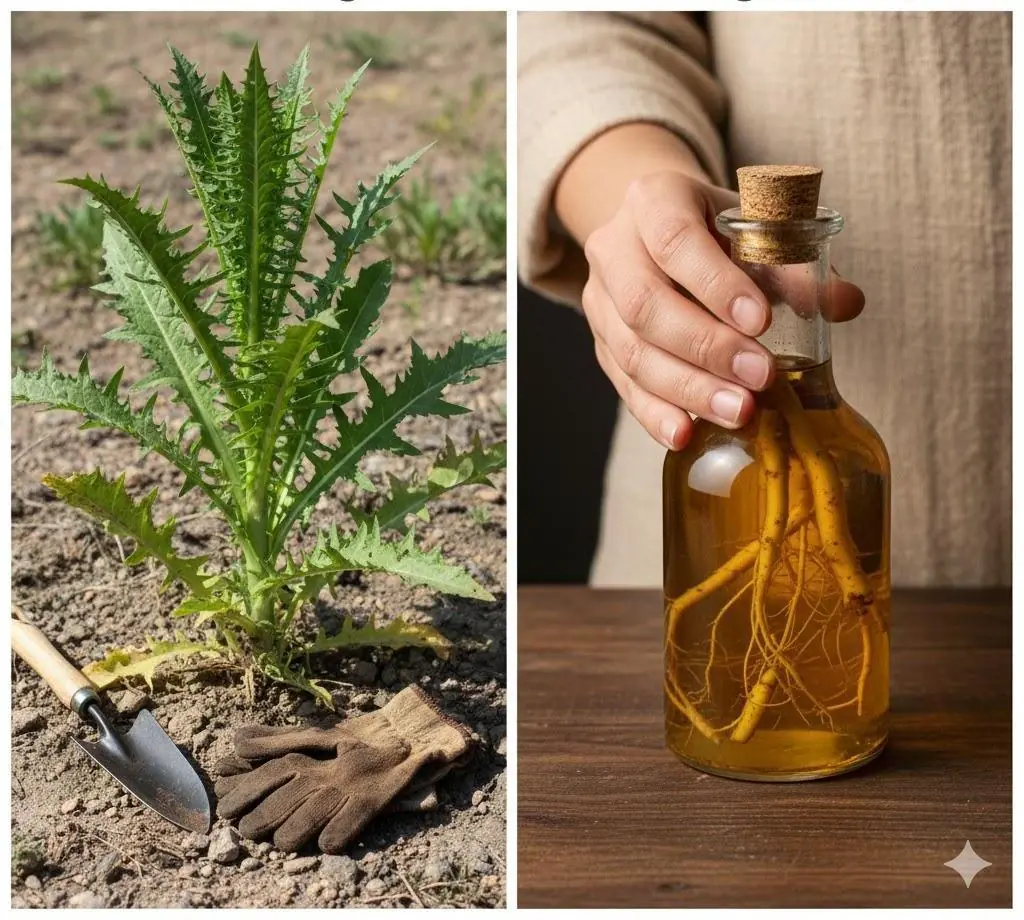

Wild Lettuce Root – Benefits, Uses, and Natural Pain Relief Properties
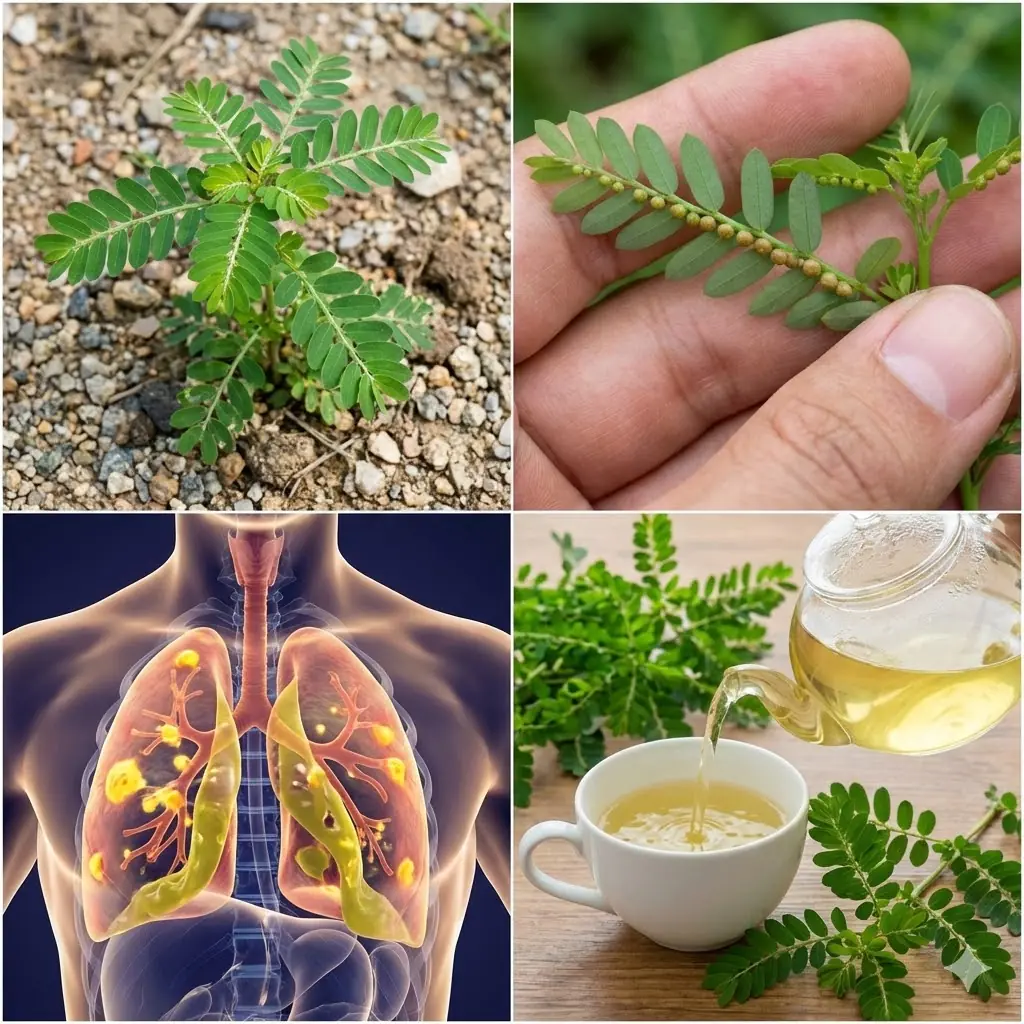

Chanca Piedra Tea: Benefits, Uses, and How to Prepare Stone Breaker Tea Naturally
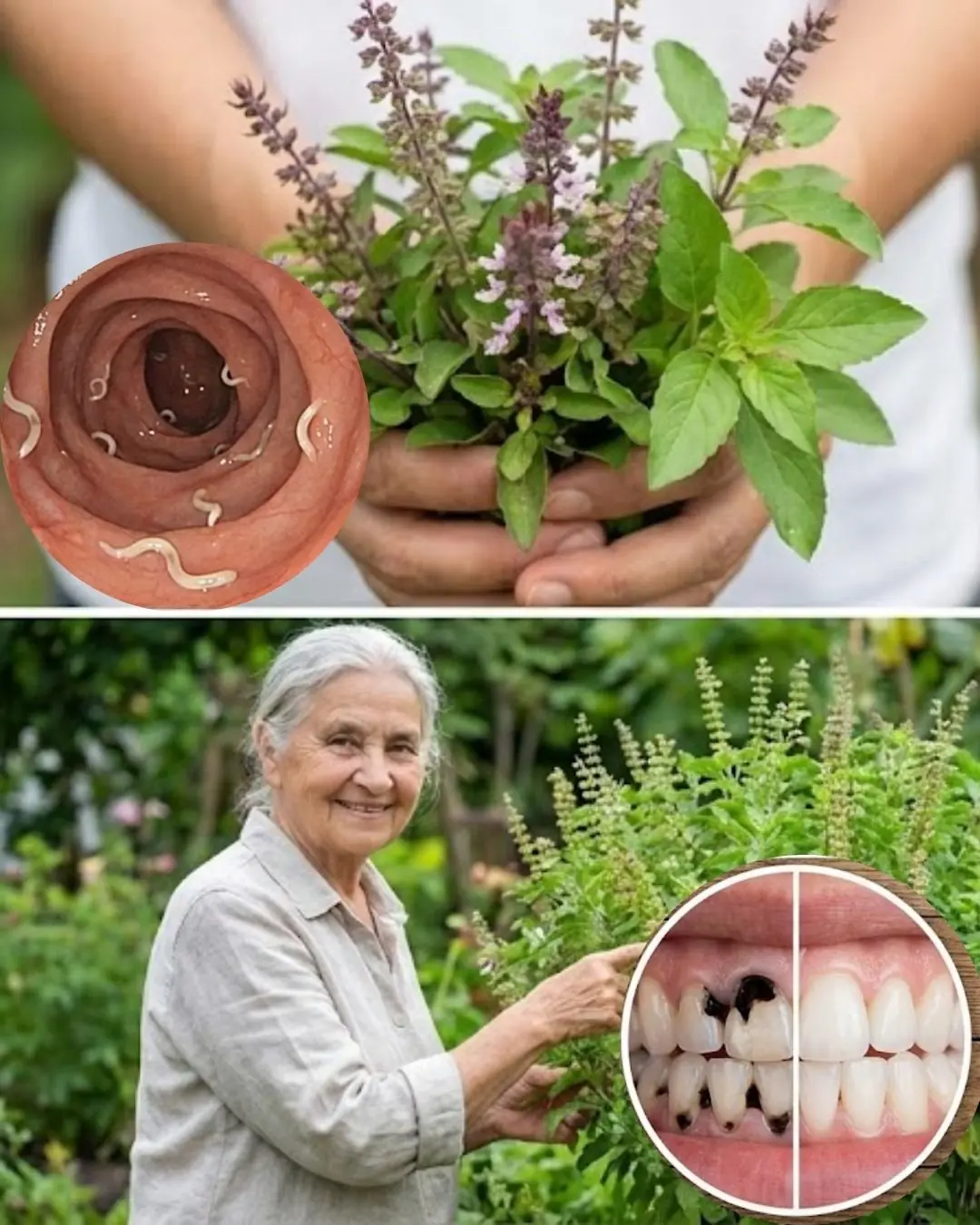

Tulsi Oral Health Benefits: Natural Protection Against Cavities, Gum Issues & Bad Breath

Unlock Crystal-Clear Vision with Cuban Oregano: Natural Eye Remedies That Transform Your Sight

They Threw Trash at the Orphan Girl in the Gym. Then Her Father Walked In, and Nobody Laughed Again.

Doctors Reveal That Eating Bell Peppers Frequently Causes..

Should you eat sprouted potatoes or not?

Doctors reveal that eating onion causes...

Doctors reveal that eating green onions causes …See more

What Really Happens to Your Body When You Sit Too Much

Teen Slaps Girl at Skate Park—Her Dad Was Right There

Player Hits Cheerleader During Game—Then Learns Who Her Dad Is
