
Doctors Reveal That Eating Bell Peppers Frequently Causes..
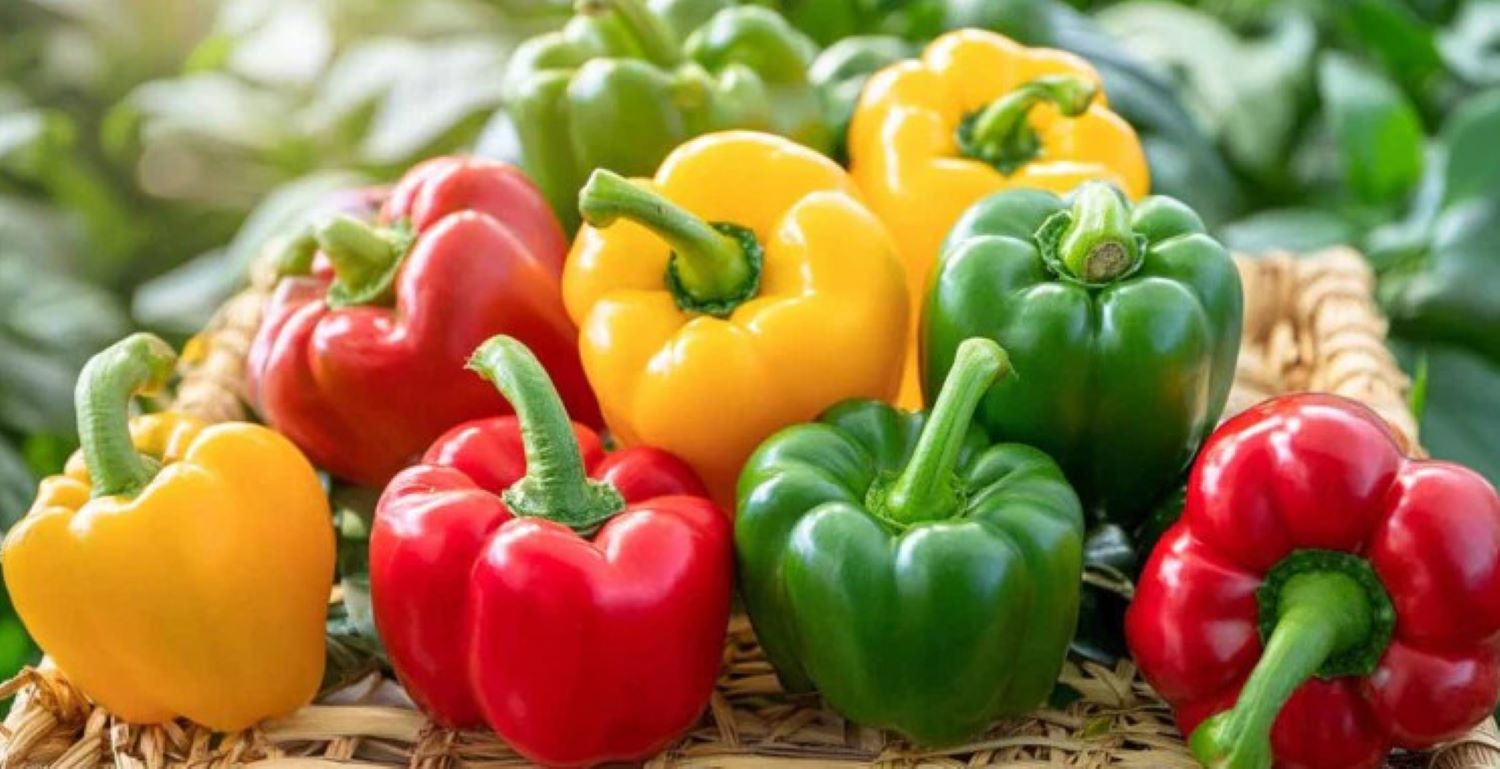

What Bell Peppers Can Cause: Benefits & Possible Side Effects
Bell peppers are among the most nutrient-dense vegetables you can eat. They’re colorful, versatile, low in calories, and packed with vitamins and antioxidants. For most people, eating them regularly is a healthy habit.
However, like any food, bell peppers can cause side effects in certain individuals — especially when eaten raw, in large amounts, or if you have specific sensitivities.
Here’s a balanced medical overview.
1️⃣ Mostly Good: High in Vitamins and Antioxidants
Eating bell peppers frequently increases your intake of:
-
Vitamin C
-
Vitamin A (as beta-carotene)
-
Folate
-
Lutein and zeaxanthin
-
Various antioxidants
A single medium red bell pepper contains more vitamin C than an orange. Red and orange varieties are particularly rich in carotenoids that support immune and eye health.
Why this matters:
-
Vitamin C supports immune defense and collagen production.
-
Beta-carotene converts to vitamin A for vision and skin health.
-
Lutein and zeaxanthin help protect against age-related eye damage.
-
Antioxidants reduce oxidative stress in cells.
Result:
Better immune resilience, healthier skin, and stronger antioxidant protection against cellular damage.
2️⃣ Improved Iron Absorption
Bell peppers are excellent sources of vitamin C, which helps your body absorb non-heme iron (plant-based iron).
Why:
Vitamin C converts iron into a form that is easier for the body to absorb.
Result:
-
Especially helpful for vegetarians and vegans
-
Beneficial for mild iron deficiency
-
Supports prevention of iron-deficiency anemia
Pairing peppers with lentils, beans, spinach, or tofu enhances iron uptake significantly.
3️⃣ Better Digestion and Weight Control
Bell peppers are:
-
Low in calories
-
High in water
-
Moderate in fiber
Why:
Fiber promotes bowel regularity, and water content increases fullness without adding many calories.
Result:
-
Improved satiety
-
Better bowel movements
-
Support for weight management
They’re ideal for people aiming to increase vegetable intake without significantly increasing calorie intake.
4️⃣ Possible Digestive Irritation (For Some People)
Some individuals experience:
-
Bloating
-
Gas
-
Stomach discomfort
-
Heartburn
Why this happens:
-
The skin contains cellulose, which can be difficult to digest.
-
Bell peppers are part of the nightshade family (like tomatoes and potatoes).
-
They contain small amounts of naturally occurring alkaloids that sensitive individuals may react to.
If you have:
-
IBS
-
A sensitive gut
-
GERD (acid reflux)
raw bell peppers may trigger symptoms.
What helps:
-
Cooking softens fiber and reduces irritation.
-
Peeling the skin may improve tolerance.
-
Eating smaller portions can reduce symptoms.
5️⃣ Allergic or Sensitivity Reactions (Rare)
True bell pepper allergy is uncommon but possible.
Symptoms may include:
-
Itching
-
Swelling
-
Hives
-
Oral itching (oral allergy syndrome)
Some people with pollen allergies experience cross-reactivity, causing itching in the mouth or throat when eating raw peppers.
Why:
The immune system reacts to specific proteins in the pepper.
If symptoms occur, avoid peppers and consult a healthcare provider.
6️⃣ Medication & Medical Considerations
Bell peppers are generally safe with medications.
✔ They are not high in vitamin K, so they typically do not interfere with blood thinners like leafy greens can.
However, if you:
-
Take multiple medications
-
Have autoimmune conditions
-
Follow a medically restricted diet
consult your healthcare provider before making major dietary changes.
How to Use Bell Peppers Safely and Sensibly
✅ Typical Safe Intake
1–2 medium bell peppers per day is safe and beneficial for most people.
✅ Cook Sometimes
-
Roasting, sautéing, or steaming softens fiber.
-
Cooking reduces digestive irritation.
-
Note: Vitamin C is heat-sensitive, so raw peppers provide the highest vitamin C levels.
✅ Peel If Sensitive
Removing the skin can reduce indigestible fiber and improve tolerance.
✅ Rotate Colors
-
Red & orange: Higher carotenoids and sweeter
-
Yellow: Mild and balanced
-
Green: Less sweet, slightly lower carotenoids but still nutritious
✅ Wash Thoroughly
Bell peppers may carry pesticide residues on the skin. Wash carefully or choose organic if concerned.
✅ Store Properly
Keep in the refrigerator crisper drawer and use within one week for best texture and nutrient content.
Foods to Avoid Pairing (If Sensitive)
⚠ If You Have GERD
Avoid large portions of raw peppers combined with:
-
Tomato-based sauces
-
Spicy foods
-
Fried foods
These combinations may increase reflux symptoms.
⚠ If You Suspect Nightshade Sensitivity
Some people report improvement in arthritis or inflammatory symptoms after removing nightshades (tomatoes, potatoes, eggplant, peppers) during an elimination diet. Consult your doctor before long-term elimination.
⚠ If You Have Oral Allergy Syndrome
Avoid raw peppers and try cooked forms instead.
Great Nutritional Pairings
✔ With iron-rich plant foods → boosts iron absorption
✔ With healthy fats (olive oil, avocado, nuts, cheese) → improves carotenoid absorption
✔ In salads, stir-fries, stuffed peppers, or roasted dishes → versatile and balanced
Why These Effects Happen (Short Science)
-
Vitamin C → Immune support & improved iron absorption
-
Carotenoids → Antioxidant and eye-health support
-
Fiber + water → Satiety and bowel regularity
-
Cellulose & alkaloids → Possible digestive irritation in predisposed individuals
-
Aroma compounds → May trigger histamine-like reactions in very sensitive people
Practical Recommendations (Summary)
✔ Eat them regularly — 1–2 peppers daily is healthy for most people
✔ Combine raw and cooked forms for balance
✔ Peel or cook if you experience bloating or heartburn
✔ Avoid if you have confirmed nightshade allergy
✔ Consult your doctor if you have chronic digestive issues or complex medical conditions
Final Perspective
For the vast majority of people, bell peppers are a powerful, nutrient-rich addition to a balanced diet. They support immune function, digestion, and overall antioxidant protection.
Side effects are usually mild and occur primarily in sensitive individuals. With proper preparation and awareness of your own tolerance, bell peppers can be both safe and highly beneficial.
News in the same category


Should you eat sprouted potatoes or not?

Doctors reveal that eating onion causes...

Doctors reveal that eating green onions causes …See more

Natural Healing at 60: The Banana Peel, Poleo & Turmeric Drink That Changed My Life

Red Onion Revolution: 3 Irresistible Rituals for Explosive Hair Growth & Thickness

Lemongrass–Guava Leaf Tea: 13 Powerful Benefits You Need to Know

🏠 8 Household Items That Could Be Affecting Your Health (And How to Check Them Safely at Home)
Red Bumps That Look Like Goosebumps
Forget Knee Pain! A Simple Home Remedy with Sea Salt Doctors Don’t Talk About

What Happens After 15 Minutes?

The Surprising Health Benefits of Boiled Eggs
🚨 Recurrent Yeast Infections? STOP Doing These Things Immediately!
Doctors Are Amazed: Two Vegetables That Boost Collagen in the Knees and Relieve Joint Pain

Doctors warn 5 everyday habits are slowly killing your kidneys
9 Powerful Home Remedies to Eliminate Fungal Infections (Daad, Khaj, Khujli) Naturally and Fast

Longevity doctor who ‘reversed his biological age’ shares advice for people over 30

Tea for Swollen Legs: A Natural Remedy for Water Retention and Poor Circulation
News Post

“Do You Even Know What a Piano Is?” He Laughed.

The Child Who Spoke the Truth and the Woman Who Finally Won

I was waiting for the final kick to my ribs. Instead, I heard the sound of a bone breaking.

He Went Outside to Stop a Stray. He Found a Baby.
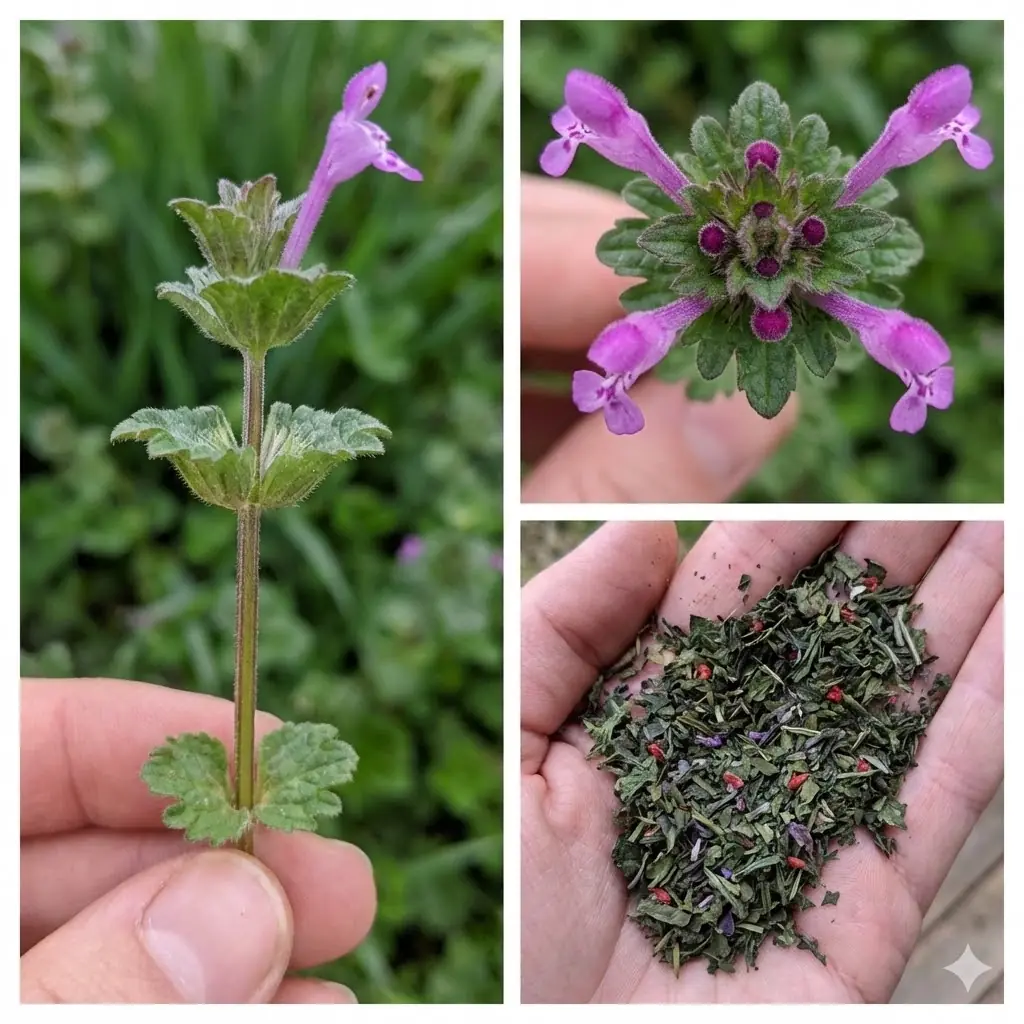

Henbit (Lamium amplexicaule): Identification, Benefits, and Homemade Uses
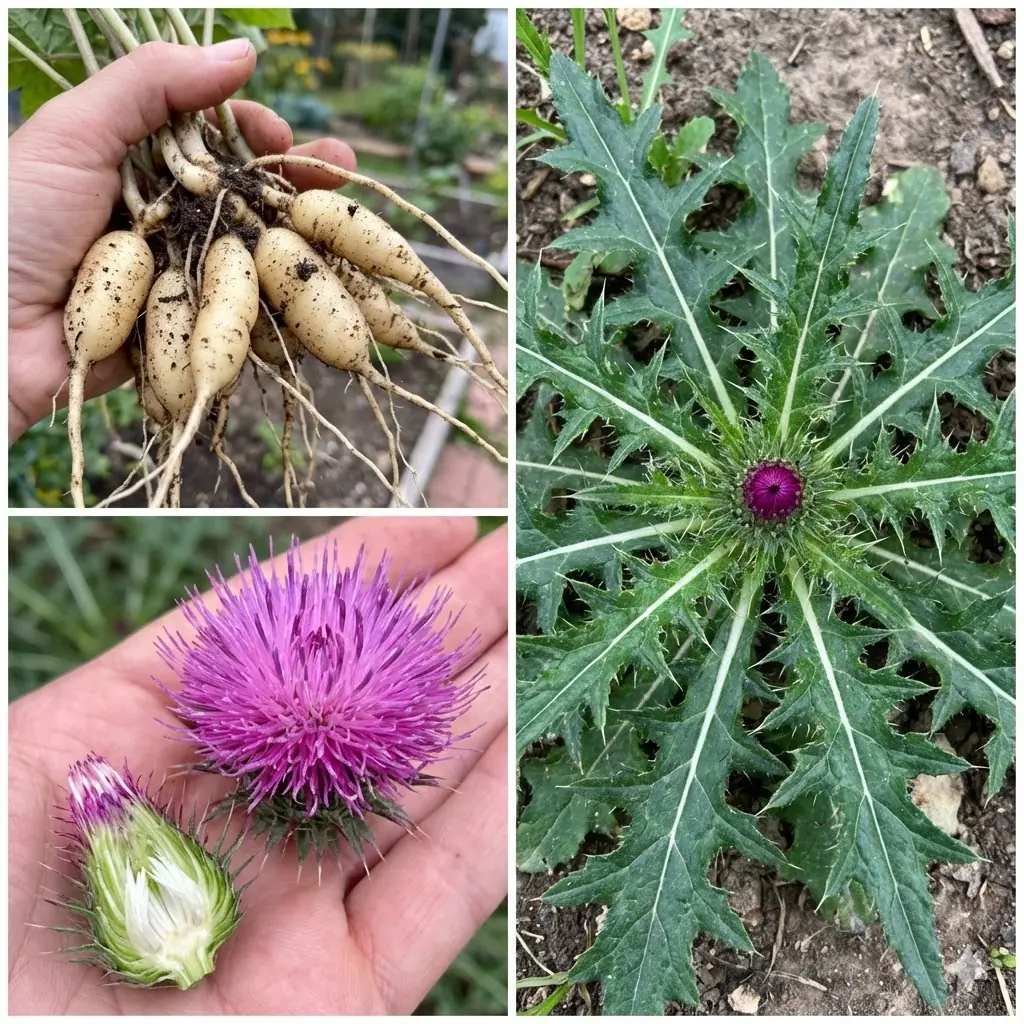

12 Benefits of Bull Thistle Root and How to Use It Naturally
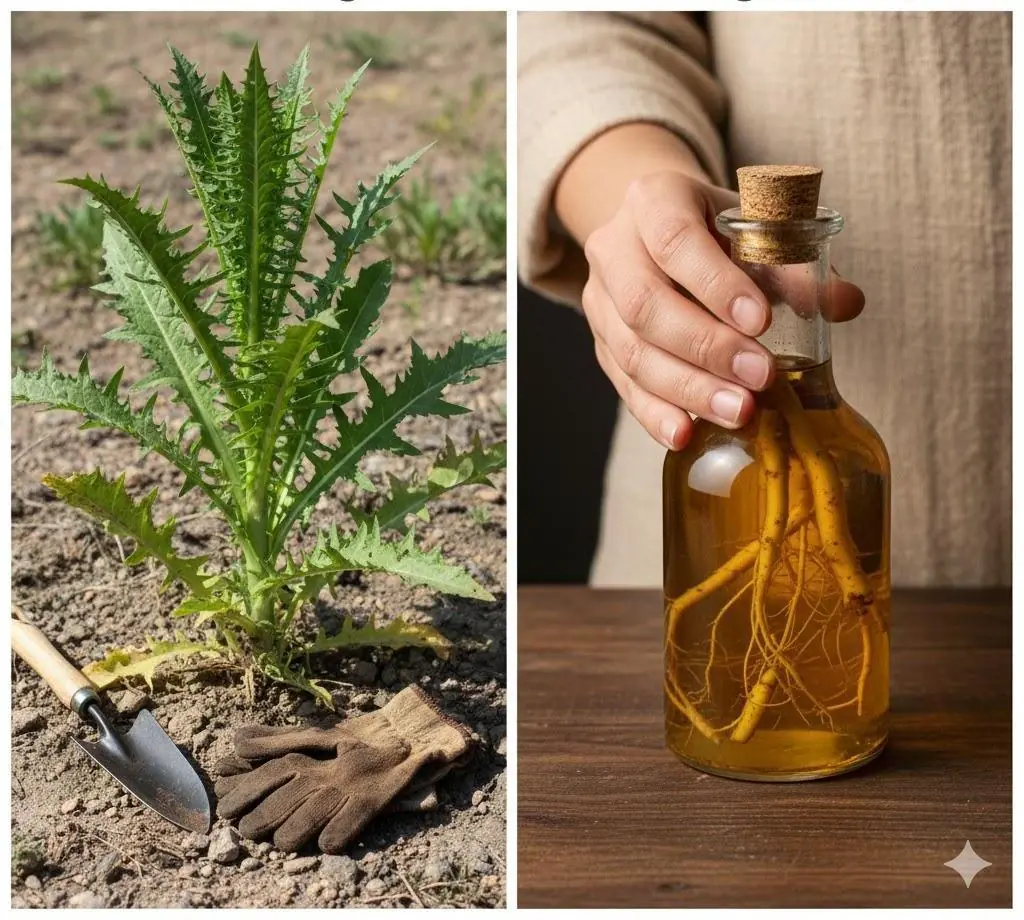

Wild Lettuce Root – Benefits, Uses, and Natural Pain Relief Properties
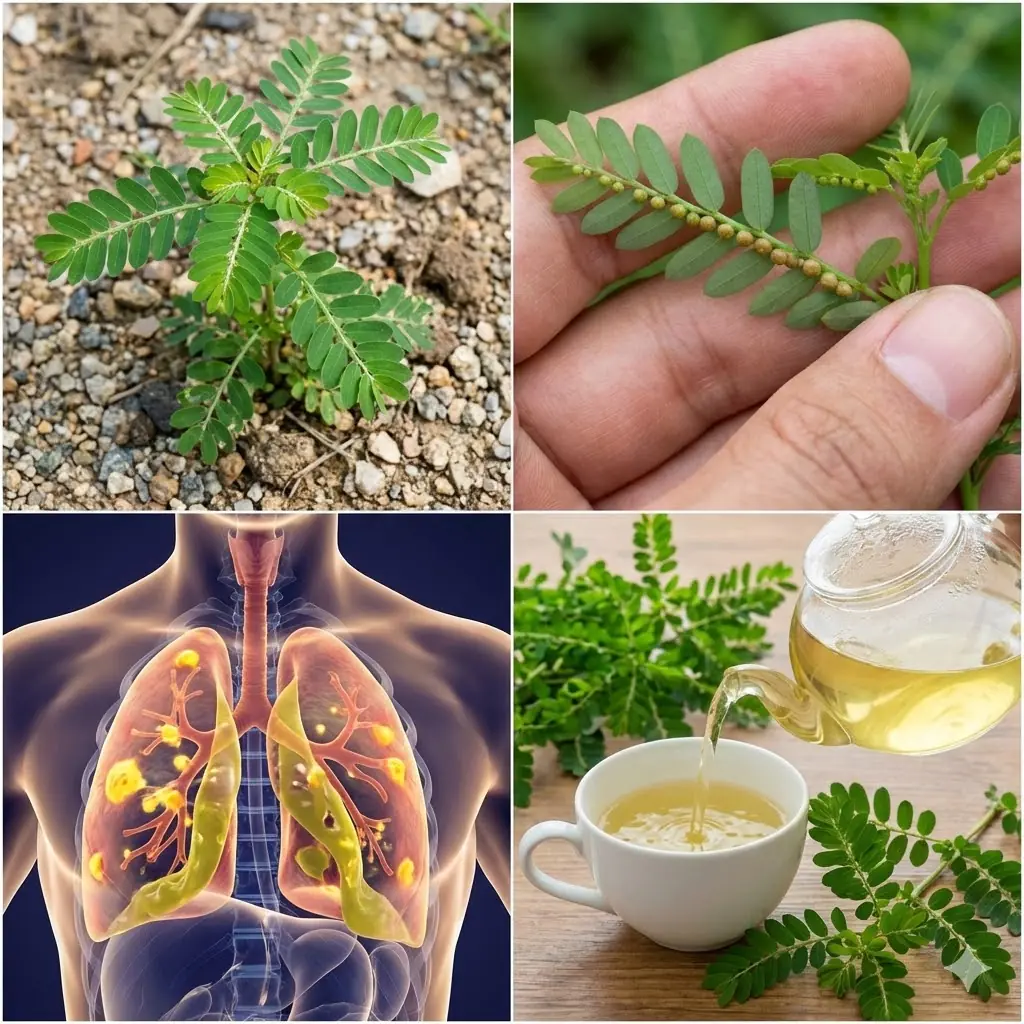

Chanca Piedra Tea: Benefits, Uses, and How to Prepare Stone Breaker Tea Naturally
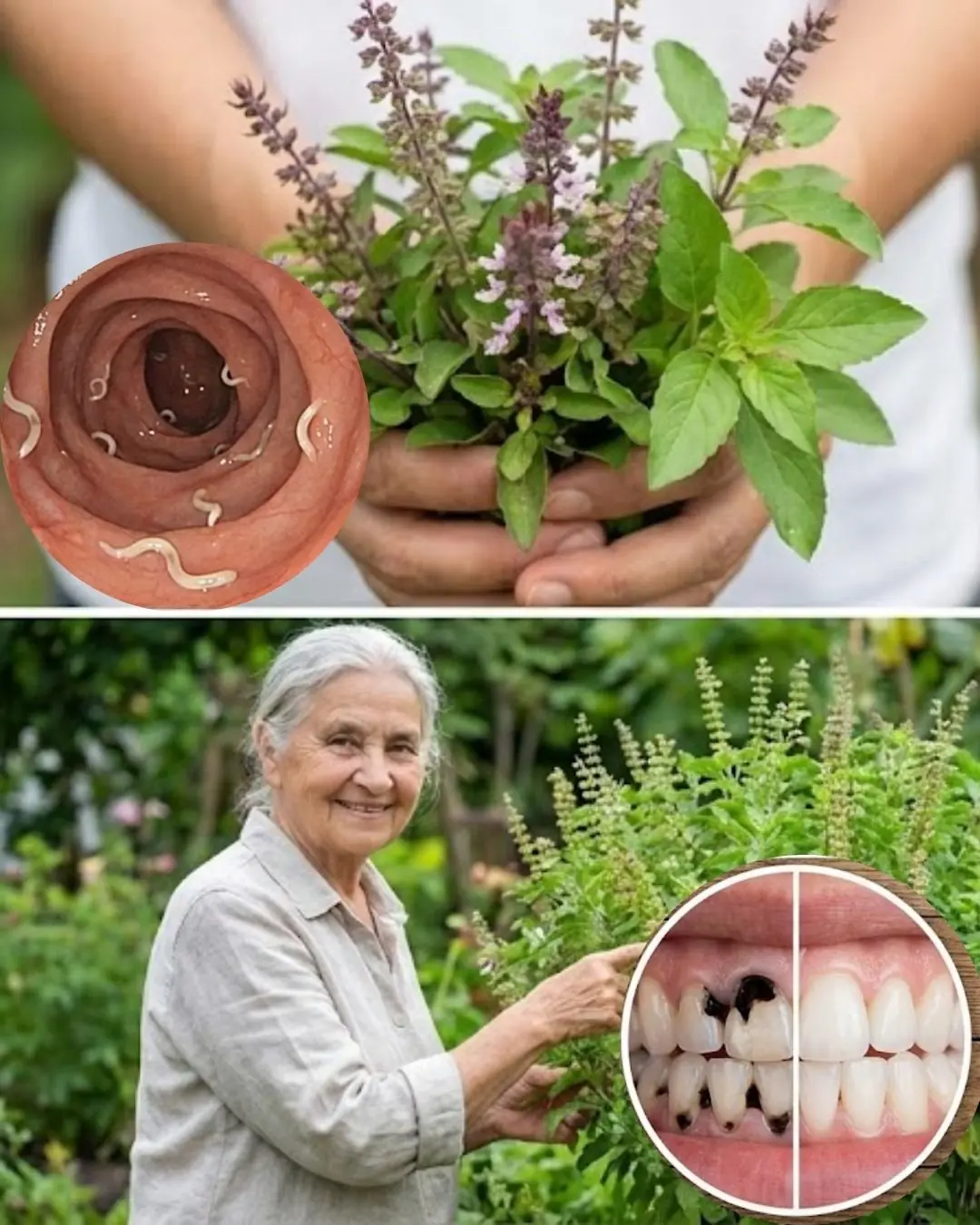

Tulsi Oral Health Benefits: Natural Protection Against Cavities, Gum Issues & Bad Breath

Unlock Crystal-Clear Vision with Cuban Oregano: Natural Eye Remedies That Transform Your Sight

They Threw Trash at the Orphan Girl in the Gym. Then Her Father Walked In, and Nobody Laughed Again.

Doctors reveal that consuming pumpkin causes in...

Should you eat sprouted potatoes or not?

Doctors reveal that eating onion causes...

Doctors reveal that eating green onions causes …See more

What Really Happens to Your Body When You Sit Too Much

Teen Slaps Girl at Skate Park—Her Dad Was Right There

Player Hits Cheerleader During Game—Then Learns Who Her Dad Is
