
'Hostile' comet aimed at Earth could obliterate the world's economy 'overnight' if it hits
NASA has recently provided a much-anticipated update on the 3I/ATLAS comet — an interstellar visitor that some have sensationally described as a “hostile alien object” currently speeding through space toward our solar system. The phrase alone has stirred up equal parts fascination and fear, as pop culture has shown us countless times what happens when foreign cosmic bodies make contact with Earth. Even if it isn’t extraterrestrial beings stepping out of a spacecraft, the environmental and planetary effects of such an impact could still be catastrophic on a scale humanity has never faced.
The 3I/ATLAS comet first came onto astronomers’ radars on July 1, 2025. Early tracking revealed that it was racing at an astonishing 209,000 kilometers per hour — making it the fastest interstellar object ever detected. That jaw-dropping speed alone has already set 3I/ATLAS apart from more familiar comets and asteroids that occasionally pass near Earth.
Could It Actually Strike Earth?
According to NASA, October 29, 2025, will mark the comet’s closest approach to the Sun, an event that will allow scientists to collect more precise data about its orbit. Initial size estimates made by the Vera C. Rubin Observatory suggested that 3I/ATLAS could be as large as seven miles across — significantly bigger than the so-called “city-killer” asteroids that routinely make headlines. More refined observations from the Hubble Space Telescope have since adjusted its estimated size to somewhere between 1,000 feet and 3.5 miles in diameter. While that may be smaller than initially feared, the potential destructive power of an object of that size colliding with Earth remains beyond comprehension.
For perspective, even a much smaller meteorite has been enough to cause panic in the past. Just earlier this year, when a cherry tomato-sized fragment older than our planet itself came crashing through the roof of a home in Georgia, the incident dominated headlines. If such a tiny rock can cause alarm, the thought of something thousands of feet wide entering our atmosphere is nothing short of terrifying.
Scientific and Public Reactions
Some astronomers remain confident that 3I/ATLAS will do what most comets tend to do — pass through the solar system, perhaps offering a spectacular celestial display, before disappearing again into deep space. But others are less optimistic. In fact, a study published in July 2025 by Harvard University titled “Is the Interstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Alien Technology?” raised eyebrows across the scientific community. The paper analyzed the comet’s unusual trajectory and motion patterns, questioning whether they could be the result of artificial design rather than natural physics. It warned that “the consequences, should the hypothesis turn out to be correct, could potentially be dire for humanity, and would possibly require defensive measures to be undertaken.” Even more ominously, the authors added that such measures might ultimately “prove futile.”
Though the idea of alien technology masquerading as a comet may sound like science fiction, the study underscores just how little we truly know about objects arriving from beyond our solar system. The mystery has only fueled speculation online, where conspiracy theories about an alien “doomsday probe” now trend alongside jokes and memes.
The Economic Fallout Scenario
Even if 3I/ATLAS does not strike Earth directly, the very thought of it has prompted discussions far beyond planetary defense. When asked about the potential economic implications of such an impact, AI chatbot ChatGPT bluntly replied: “If 3I/ATLAS were to literally land on Earth in one piece, we’d have much bigger problems than market crashes — think extinction-level event.”
The reasoning is chillingly simple. A direct collision with an object in this size range could cause global climate disruption, trigger mass extinctions, collapse critical infrastructure, and essentially erase the concept of a functioning global economy. The asteroid that wiped out the dinosaurs 65 million years ago was roughly in the same league, and we all know how that ended.
But what if humanity somehow managed to “soft land” the comet instead of suffering its devastating impact? In that scenario, the consequences could still be world-changing — just in a very different way. Scientists estimate that comets like 3I/ATLAS could contain millions or even billions of tons of valuable resources, including water, gold, platinum, and iron. Paradoxically, bringing that treasure trove safely to Earth would likely crash commodity markets overnight.

Any impact from 3I/ATLAS could have dire consequences (NASA)
If gold and platinum suddenly became abundant, their prices would plummet. Mining, refining, and shipping industries could collapse under the weight of oversupply. Economies that depend heavily on resource exports would face devastation, leading to global ripple effects. As ChatGPT noted, this would spark “stock market crashes, currency instability, trade imbalances, unemployment spikes” — essentially a “resource glut-induced depression.”
Two Types of Doom
In the end, humanity faces a strange choice of nightmares. On one hand, a catastrophic collision could obliterate life on Earth entirely, an extinction-level event that would wipe human civilization off the map. On the other hand, an impossibly safe landing of the comet would likely destabilize financial systems and lead to a worldwide economic meltdown. One scenario erases us physically, the other destabilizes everything we know socially and economically.
Whether 3I/ATLAS proves to be nothing more than another comet passing quietly through our solar system or something far more ominous, its arrival has already succeeded in capturing global attention. In a world where scientific discovery often feels routine, this alien visitor has rekindled a profound sense of awe — and anxiety — about our fragile place in the universe.
News in the same category


Researchers Find Higher Intelligence Is Correlated With Left-Wing Beliefs and Seems to Be Genetic

Urgent Health Warning Issued After Pigs With ‘Neon Blue’ Flesh Are Discovered in One Specific Part of the Us

Iconic movie sequel delayed until 2027 after online sleuths 'guessed the plot'

Don’t Sleep With Your Pets
The Secret Meaning of the Letter “M” on Your Palm

The Remarkable Journey of Tru Beare, Who Was Born Weighing Only One Pound
Researchers Create Injectable Hydrogel to Boost Bone Strength

If You Have Moles on This Part of Your Body

The Purpose of the Small Pocket in Women’s Underwear

Beware of the Plastic Bottle Scam: A New Car Theft Tactic

Chinese Scientists Say They Created a Cure for Type 1 Diabetes

Rob Gronkowski forgot he invested $69,000 in Apple and ten years later the value has completely changed his net-worth

Scientists discover that powerful side effect of Ozempic could actually reverse aging

Scientists warn ancient Easter Island statues could vanish in a matter of years

NASA astronaut describes exactly what space smells like and it's not what you'd expect

Subtle Signs Your Passed Loved One Is Watching Over You

What Does a Thumb Ring Really Mean
News Post

Parasite Cleanses: Do They Really Improve Your Gut Health — and Are They Safe?

8 Teas to Drink for a Healthier Body and Mind
The Hidden Truth About Tinnitus: Why That Ringing in Your Ears Shouldn’t Be Ignored
Over time, repeated noise trauma damages tiny hair cells inside the cochlea, which cannot regenerate, resulting in permanent hearing changes and tinnitus.

DIY Turmeric & Ginger Shots to Fight Inflammation, Boost Immunity & Soothe Your Gut

Coconut water: Is It Good for You, Nutrition, Benefits, Side Effects (Science Based)

Clean Arteries: 10 Foods to Eat Daily
10 Warning Signs of Parasites in Your Body

Diet and Uric Acid: Foods to Avoid for Gout Prevention

Hiker Encounters Massive Snake Camouflaged Along South Carolina Creek

8 Foods That Help Eliminate Cancer Cells

David Quammen, the COVID Predictor Warns of New Pandemic Threats
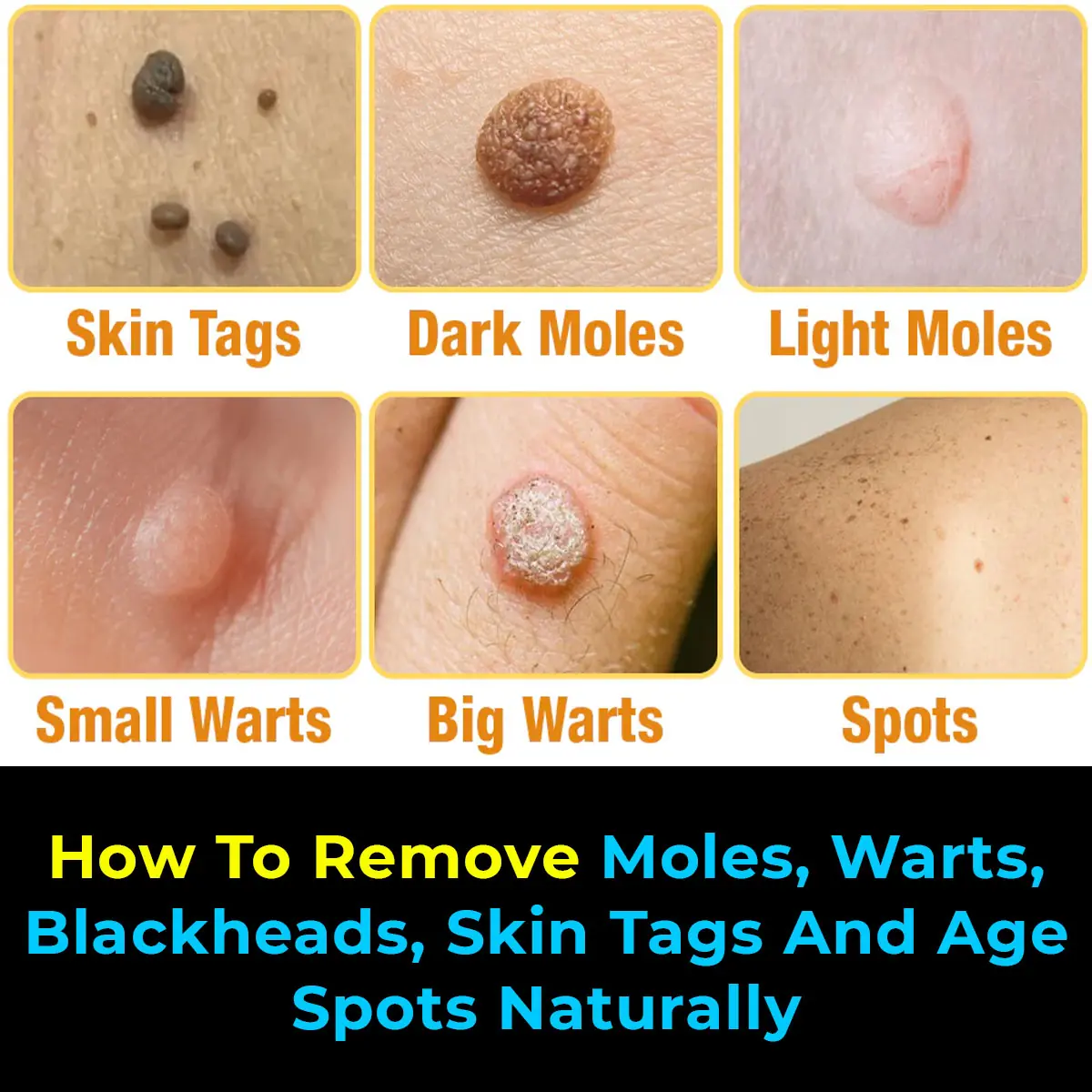
Natural Remedies to Address Skin Tags, Warts, and Blackheads

Tips for Selecting Fresh Pork at the Market

The Deficiency of These Vitamins Contributes to Panic Attacks

Researchers Find Higher Intelligence Is Correlated With Left-Wing Beliefs and Seems to Be Genetic

Urgent Health Warning Issued After Pigs With ‘Neon Blue’ Flesh Are Discovered in One Specific Part of the Us

25-Year-Old Groom Dies from Acute Liver Failure After Eating Chicken – Doctors Warn of One Critical Danger!
Doctors caution people with pre-existing liver conditions, weakened immune systems, or chronic illnesses to exercise extra care when handling poultry and other high-risk.
What Your Legs Can’t Say, Your Vagina Can — The Truth About the Female Body Most People Don’t Know
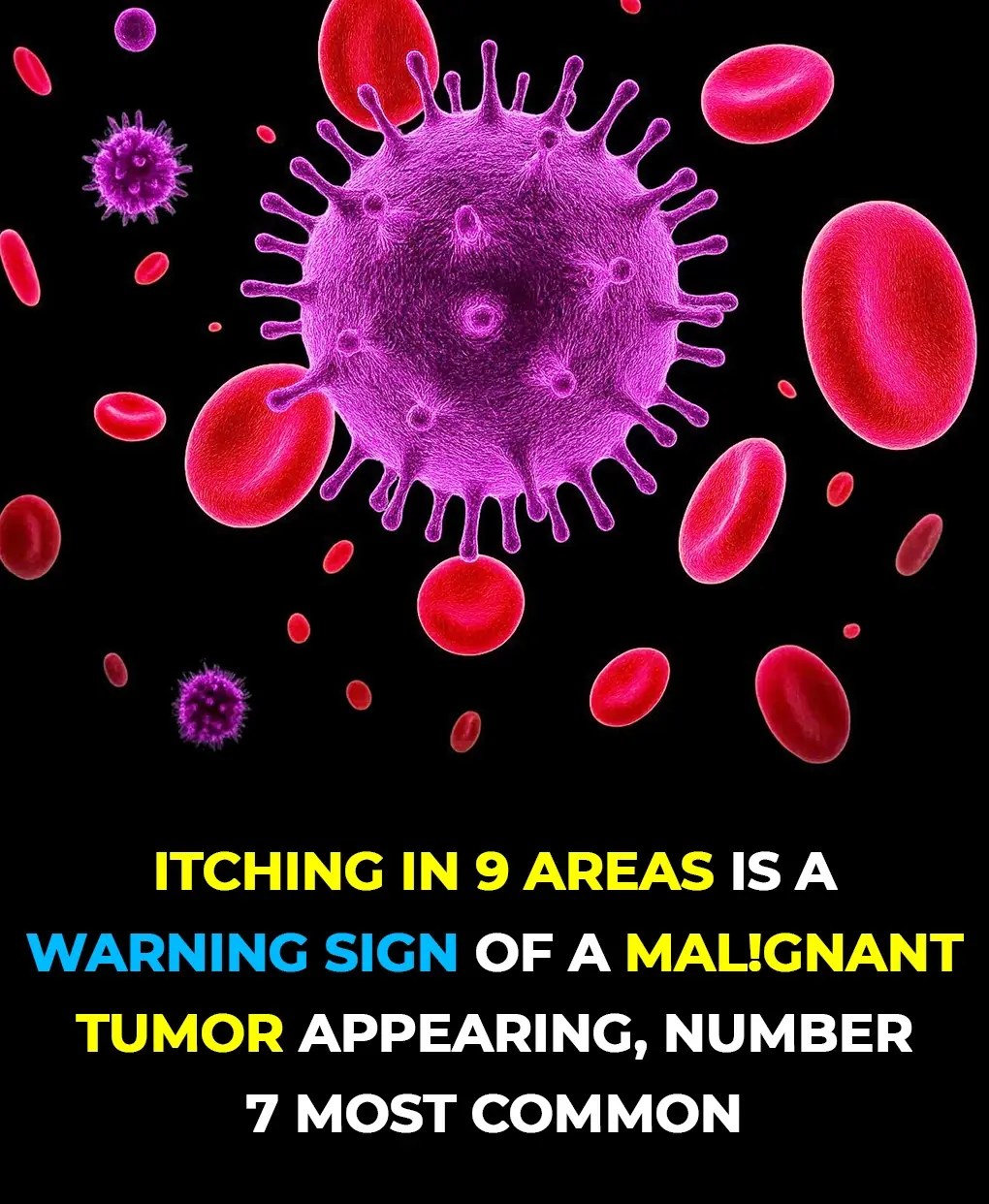
9 Areas Where Itching Could Signal Malignant Tumors — #7 Happens Most Often

The World’s Deadliest Food Kills 200 People Every Year — Yet 500 Million Still Eat It
Despite its deadly reputation, millions of people continue to eat this every day without issue.