
Researchers Create Injectable Hydrogel to Boost Bone Strength
Osteoporosis is often referred to as a “silent disease,” progressing without obvious symptoms until a sudden and severe fracture reveals the underlying damage. Over time, this condition quietly erodes bone strength, leaving patients—especially older individuals—at significant risk.
This disease primarily affects people over the age of 50, with postmenopausal women being particularly vulnerable due to hormonal changes. Globally, osteoporosis is responsible for millions of fractures each year, leading to long-term disability, reduced quality of life, and in severe cases, even death.
The Shortcomings of Current Osteoporosis Treatments
For decades, the standard approach to managing osteoporosis has relied on systemic medications. These include drugs that either promote bone formation or slow down bone resorption. While these treatments can be effective over time, they typically take several months—or even up to a year—to show noticeable improvements in bone density. This delay can be life-threatening for elderly individuals who are at high risk of falls and fractures.
Dominique Pioletti, head of the Laboratory of Biomechanical Orthopedics at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), warns that, “In the absence of effective preventive measures, around 40% of women over age 50 will suffer at least one major osteoporotic fracture; in men, the percentage is about 20%.” These fractures—particularly of the hip or femoral neck—can have devastating consequences. Studies show that nearly 20% of patients die within one year of suffering such a fracture, underscoring the urgent need for faster, more localized treatments.
A Revolutionary Injectable Hydrogel
To tackle this urgent need, researchers at EPFL have developed an innovative injectable hydrogel designed to restore bone strength in specific, weakened areas. This new solution combines hyaluronic acid—a naturally occurring substance in the human body—with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles, which closely mimic the mineral component of bone.
Once injected directly into fragile bone regions, the hydrogel forms a supportive scaffold that encourages rapid bone regeneration. In preclinical trials on mice, the results were remarkable: bone density at the injection site increased by two to three times within just two weeks. This is significantly faster than traditional treatments, which often require months to reach similar results.
Biocompatibility and Precision: Major Advantages
One of the standout features of this hydrogel is its high biocompatibility. It integrates seamlessly with the body’s natural bone tissue, without causing inflammation or rejection. This makes it not only a safe option but also a highly targeted one—delivering treatment exactly where it's needed, rather than throughout the entire skeleton.
Unlike conventional bone cements that are hard, brittle, and sometimes toxic over time, this hydrogel is flexible and injectable. It can adapt to irregularly shaped bone defects, making it ideal for filling complex spaces that other materials can’t reach.
Enhanced Results Through Drug Combination
The research team also explored ways to enhance the hydrogel’s efficacy by combining it with existing osteoporosis medications. They experimented with adding parathyroid hormone, which stimulates bone formation, and also tested loading the hydrogel with zoledronate, a powerful anti-resorptive drug commonly used in osteoporosis treatment.
The results were dramatic: combining the hydrogel with these drugs led to a 4.8-fold increase in bone density at the injection site. “Our findings suggest that injectable hydrogels delivering local anti-catabolic drugs can complement systemic anabolic therapy by rapidly boosting local bone density,” said Pioletti. This dual-approach strategy could provide immediate support to bones at highest risk, while systemic drugs continue to work throughout the rest of the skeleton.
How the Technology Works
The secret behind the hydrogel’s effectiveness lies in its biomimetic design. Hyaluronic acid creates a moist, gel-like environment that attracts water and supports cellular activity. This environment helps bone-forming cells migrate into the area and begin the process of regeneration. Meanwhile, the hydroxyapatite particles not only add structure but also send biochemical signals that encourage the formation of new bone tissue.
Because it mimics the physical and chemical characteristics of natural bone, this hydrogel doesn’t merely patch a weak area—it actually helps rebuild it. Researchers are also exploring its potential applications in other areas, such as cartilage repair and orthopedic implants.
Looking Ahead: Toward Human Trials
So far, the injectable hydrogel has only been tested in animal models. However, the early results have been so promising that researchers are now preparing for human clinical trials. These trials will focus on patients who are at high risk of fractures or those who require extra bone support for medical implants, such as dental anchors or artificial joints.
Régis Gauderon, a scientist at Flowbone—the French startup behind the commercial development of the hydrogel—explained, “The road to getting our product approved and into the clinic is still very long. Fortunately, our motivation is strong and infallible.”
If all goes well, this innovative treatment could offer patients a way to strengthen their bones not in months or years—but in a matter of weeks. This represents a major leap forward in the fight against osteoporosis and opens the door to a new era of fast, localized, and effective bone treatments.
News in the same category


Researchers Find Higher Intelligence Is Correlated With Left-Wing Beliefs and Seems to Be Genetic

Urgent Health Warning Issued After Pigs With ‘Neon Blue’ Flesh Are Discovered in One Specific Part of the Us

'Hostile' comet aimed at Earth could obliterate the world's economy 'overnight' if it hits

Iconic movie sequel delayed until 2027 after online sleuths 'guessed the plot'

Don’t Sleep With Your Pets
The Secret Meaning of the Letter “M” on Your Palm

The Remarkable Journey of Tru Beare, Who Was Born Weighing Only One Pound

If You Have Moles on This Part of Your Body

The Purpose of the Small Pocket in Women’s Underwear

Beware of the Plastic Bottle Scam: A New Car Theft Tactic

Chinese Scientists Say They Created a Cure for Type 1 Diabetes

Rob Gronkowski forgot he invested $69,000 in Apple and ten years later the value has completely changed his net-worth

Scientists discover that powerful side effect of Ozempic could actually reverse aging

Scientists warn ancient Easter Island statues could vanish in a matter of years

NASA astronaut describes exactly what space smells like and it's not what you'd expect

Subtle Signs Your Passed Loved One Is Watching Over You

What Does a Thumb Ring Really Mean
News Post

Parasite Cleanses: Do They Really Improve Your Gut Health — and Are They Safe?

8 Teas to Drink for a Healthier Body and Mind
The Hidden Truth About Tinnitus: Why That Ringing in Your Ears Shouldn’t Be Ignored
Over time, repeated noise trauma damages tiny hair cells inside the cochlea, which cannot regenerate, resulting in permanent hearing changes and tinnitus.

DIY Turmeric & Ginger Shots to Fight Inflammation, Boost Immunity & Soothe Your Gut

Coconut water: Is It Good for You, Nutrition, Benefits, Side Effects (Science Based)

Clean Arteries: 10 Foods to Eat Daily
10 Warning Signs of Parasites in Your Body

Diet and Uric Acid: Foods to Avoid for Gout Prevention
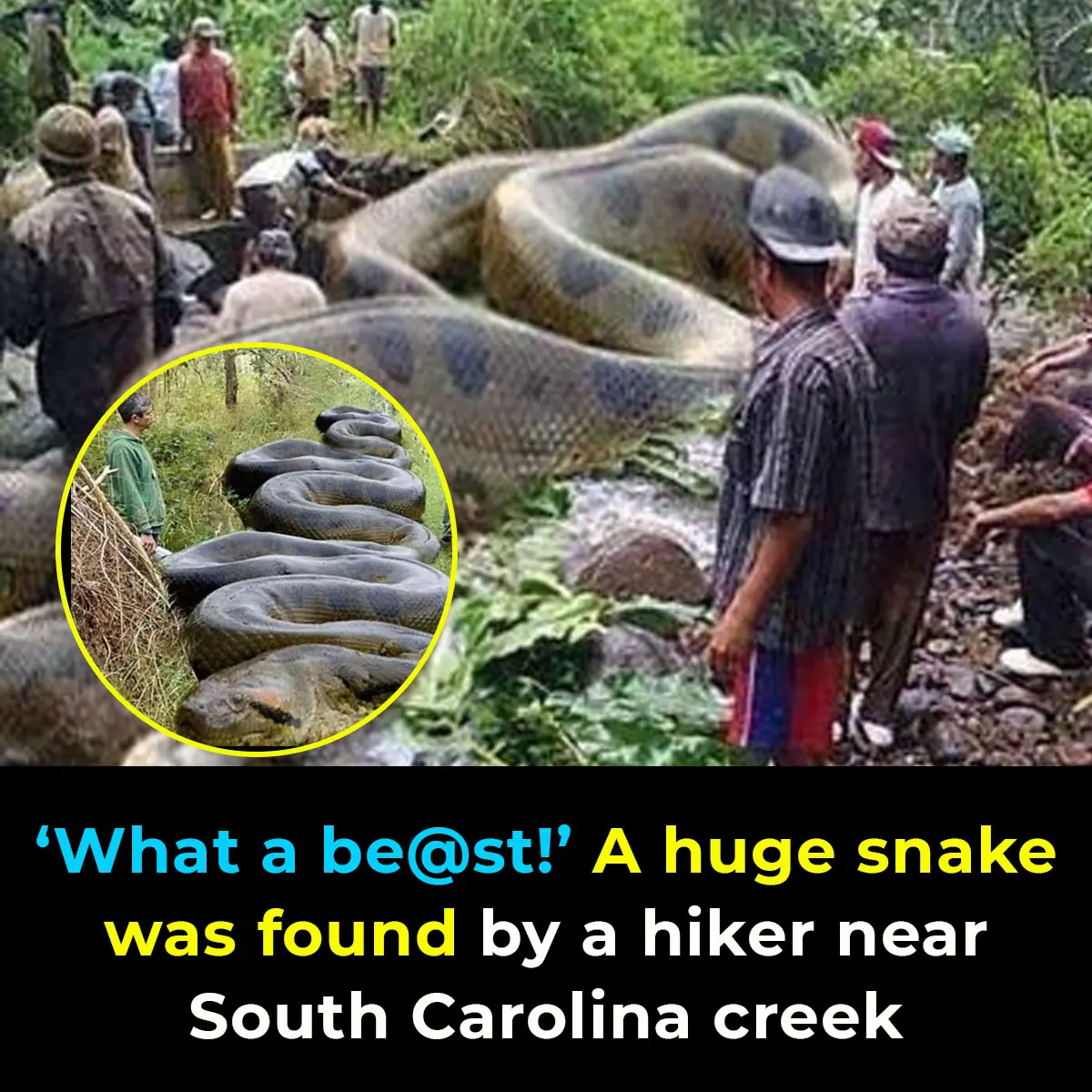

Hiker Encounters Massive Snake Camouflaged Along South Carolina Creek

8 Foods That Help Eliminate Cancer Cells

David Quammen, the COVID Predictor Warns of New Pandemic Threats
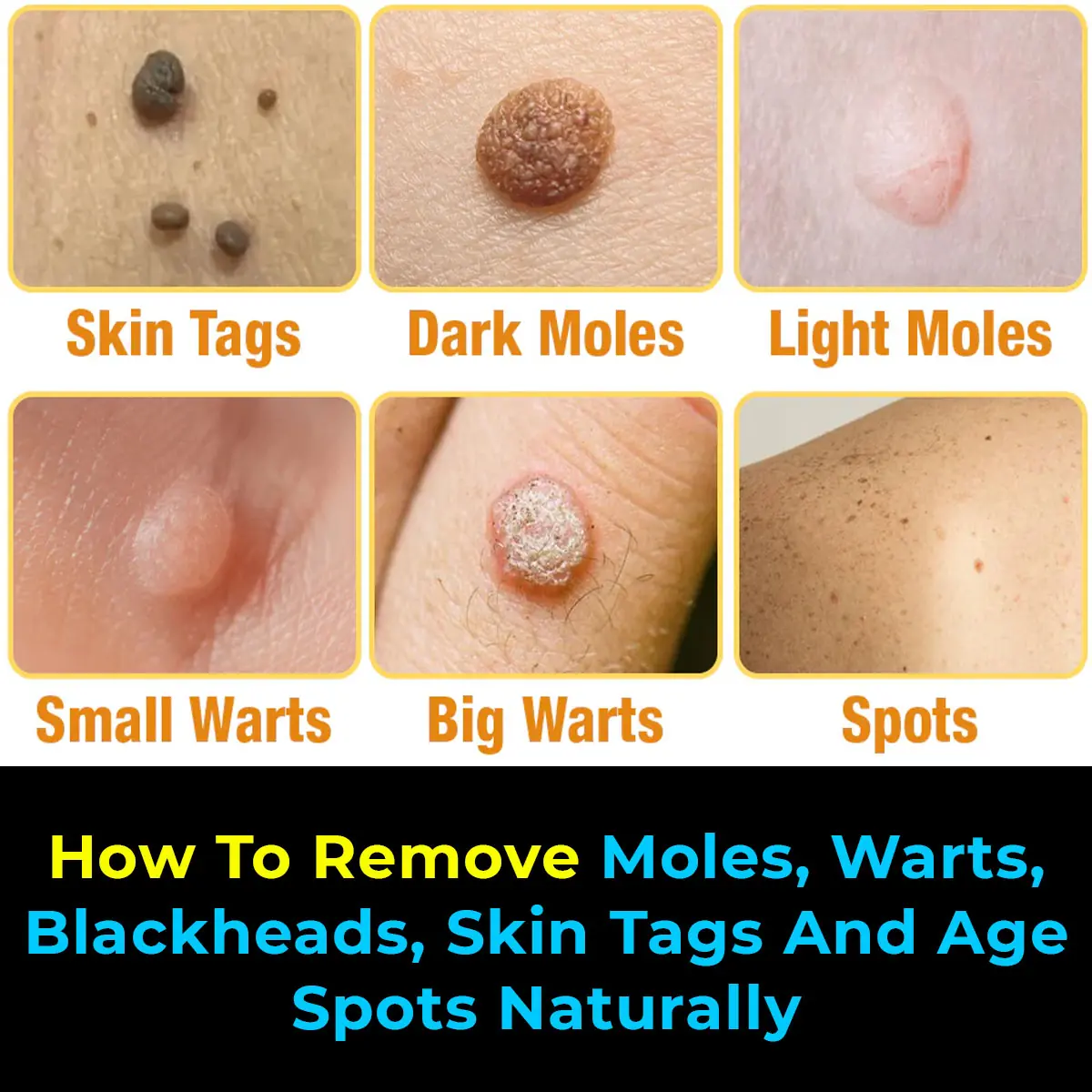
Natural Remedies to Address Skin Tags, Warts, and Blackheads

Tips for Selecting Fresh Pork at the Market

The Deficiency of These Vitamins Contributes to Panic Attacks

Researchers Find Higher Intelligence Is Correlated With Left-Wing Beliefs and Seems to Be Genetic

Urgent Health Warning Issued After Pigs With ‘Neon Blue’ Flesh Are Discovered in One Specific Part of the Us

25-Year-Old Groom Dies from Acute Liver Failure After Eating Chicken – Doctors Warn of One Critical Danger!
Doctors caution people with pre-existing liver conditions, weakened immune systems, or chronic illnesses to exercise extra care when handling poultry and other high-risk.
What Your Legs Can’t Say, Your Vagina Can — The Truth About the Female Body Most People Don’t Know
9 Areas Where Itching Could Signal Malignant Tumors — #7 Happens Most Often

The World’s Deadliest Food Kills 200 People Every Year — Yet 500 Million Still Eat It
Despite its deadly reputation, millions of people continue to eat this every day without issue.