Science Says These Things Are Inherited Straight From Your Mother
When it comes to what makes you you, both parents undeniably leave their mark. Your DNA is a complex blend of genes from your mother and father—but here’s where things get interesting: not all traits are inherited equally. In fact, science shows that many characteristics, from how your brain functions to how your body processes energy, are more likely to come from your mother.
Thanks to the unique way genetics work—especially involving mitochondrial DNA and X chromosomes—mom’s influence often runs deeper than we realize. Below are 16 remarkable traits that research suggests are more commonly inherited from your mother.
1. Mitochondrial DNA: Your Cellular Power Source Comes Only from Mom
Inside nearly every cell in your body are tiny structures called mitochondria, responsible for producing the energy your body needs to function. Without them, life as we know it wouldn’t be possible.
What makes mitochondria unique is that their DNA comes exclusively from your mother. Fathers contribute no mitochondrial DNA at all. This maternal-only inheritance is so reliable that scientists use it to trace maternal ancestry across centuries, offering a direct genetic line through generations of women.
2. Intelligence: Why Mom’s Genes Often Matter More
While intelligence is shaped by both genetics and environment, many genes associated with cognitive ability are found on the X chromosome. Since women carry two X chromosomes and men carry only one, mothers statistically have a stronger genetic influence in this area.
This doesn’t mean intelligence is guaranteed, but studies suggest maternal genes play a significant role in memory, learning capacity, and problem-solving ability.
3. Facial Structure: More Than Just Family Resemblance
If people often say you look like your mother, science may be backing them up. Features such as cheekbone structure, nose shape, jawline, and lips frequently resemble the maternal side more strongly.
While you may still inherit traits from your father, many of the subtle details that define your face often trace back to Mom.
4. Skin Aging: A Glimpse into Your Future
Curious how your skin might age over time? Your mother’s complexion can offer valuable clues. Genetics influence skin elasticity, wrinkle development, and collagen production—traits often inherited maternally.
If your mother aged gracefully, there’s a good chance you inherited some of that same genetic advantage.
5. Sleep Patterns: Night Owl or Early Bird?
Your natural sleep rhythm may not be random. Research suggests that sleep behaviors—such as sleep depth, circadian rhythm, and susceptibility to insomnia—are often linked to maternal genetics.
If you and your mother share similar sleep habits, biology may be the reason.
6. Risk of Certain Diseases: Maternal Health History Matters
Because mitochondrial DNA comes only from mothers, diseases related to cellular energy production are passed exclusively through the maternal line. These include certain neurological and metabolic disorders.
Additionally, studies have found stronger maternal links to conditions such as Type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and some cancers, making your mother’s medical history especially important.
7. Hair Texture and Aging: Curls, Thickness, and Graying
Hair texture—whether straight, wavy, or curly—is influenced by multiple genes, but maternal genetics often tip the scale. Thickness, growth patterns, and even when your hair starts to gray may be more closely tied to your mother’s DNA.
So if your hair mirrors hers, it’s probably not a coincidence.
8. Stress Response: Emotional Wiring from Mom
How you react to stress—calm under pressure or easily overwhelmed—may be partly inherited. Mitochondrial DNA influences neurotransmitter regulation, which affects mood, emotional resilience, and anxiety response.
This could explain why emotional coping styles often resemble those of mothers.
9. Bone Strength: Structural Support from the Maternal Line
Bone density and skeletal strength are partially genetic, and maternal genes play a significant role. If osteoporosis or bone fragility runs in your mother’s family, your own risk may be higher.
This makes nutrition and lifestyle choices especially important as you age.
10. Vocal Traits: Your Mother’s Voice Echoes in Yours
Pitch, tone, cadence, and even speech patterns can be inherited. Research suggests maternal influence often outweighs paternal input when it comes to vocal characteristics.
That familiar rhythm in your speech may sound more like Mom than you realize.
11. Sense of Smell: A Maternal Sensory Gift
Olfactory sensitivity—especially to food and natural scents—can be influenced by maternal genes. If you and your mother share strong reactions to certain smells, genetics may be at play.
This heightened sensitivity may even affect taste preferences and appetite.
12. Metabolism: How Your Body Uses Energy
Metabolic rate, fat storage, and calorie burning efficiency are strongly influenced by maternal genetics. Since mitochondria control energy production, your mother’s DNA largely determines how efficiently your body converts food into fuel.
This can influence weight gain, endurance, and energy levels throughout life.
13. Handedness: Right or Left?
Hand preference is a complex trait influenced by genetics and brain development. Some studies suggest maternal genes may play a stronger role in determining whether you’re right- or left-handed.
Though not fully understood, maternal influence appears significant.
14. Pain Tolerance: Genetic Grit
Pain perception varies widely, and mitochondrial DNA plays a role in how pain signals are processed in the nervous system. This means your tolerance for pain—high or low—may reflect maternal genetic patterns.
It’s one reason pain sensitivity often runs in families.
15. Migraines: A Maternal Legacy
Migraines are far more likely to be inherited through the maternal line. Researchers believe this connection stems from how mitochondrial DNA affects blood flow and nerve signaling in the brain.
If your mother suffers from migraines, your chances are notably higher.
16. Personality Traits: Emotional DNA
While upbringing matters, genetics also shape temperament. Traits such as empathy, emotional sensitivity, introversion, and stress reactivity have been linked to maternal genes.
Some aspects of who you are emotionally may have been present long before your first memories.
Final Thoughts: You May Be More Like Your Mother Than You Think
Even if you inherited your father’s height, laugh, or talents, many of the traits that quietly guide your daily life—from energy levels to emotional responses—likely came from your mother.
Science continues to reveal just how powerful maternal genetics are, reminding us that our connection to Mom goes far deeper than we ever imagined.
News in the same category


The Black Diamond Apple: A Rare Gem from the Mountains of Tibet

Marvin Harvin Becomes One of the First Incarcerated Individuals to Graduate from Yale University, Highlighting the Power of Education in Prison Reform

Warren Buffett’s Ice Cream Quote: A Simple Yet Powerful Lesson on Taxes

Why Do Button-Down Shirts Have Loops On the Back

World's Oldest Little Blue Penguin Reaches Remarkable 25 Years in Managed Care

Rare Sighting of Pallas's Cat at 16,400 Feet in the Himalayas Reveals Remarkable Adaptability

Studies Suggest Links Between Swearing, Staying Up Late, and Higher Intelligence
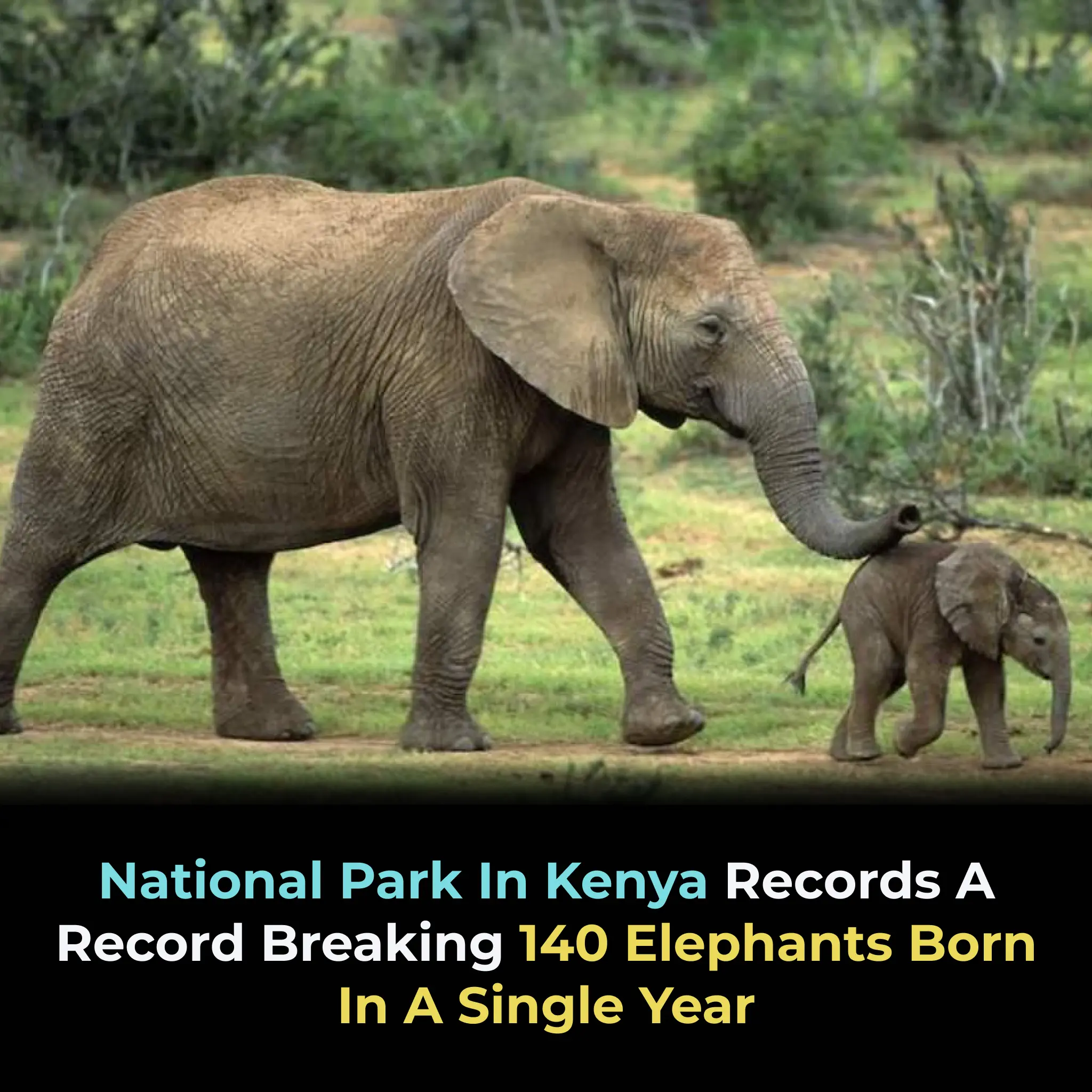

Kenya Records Historic Elephant Baby Boom in National Park: 140 Calves Born in One Year

Photograper Captures A Once-In-A-Lifetime Shot Of A ‘Horizontal Rainbow’ That Filled The Whole Sky

Afghan Men Detained for Dressing Like "Peaky Blinders" Characters, Authorities Claim Promotion of Foreign Culture

Austrian Man Arrested for Manslaughter After Leaving Girlfriend to Freeze on Grossglockner Peak

Midea Group Unveils MIRO U: A Revolutionary Six-Armed Super Humanoid Robot for Factory Automation

A Touch of Viking Brilliance: Moss-Carpeted Homes in Norway

China Conducts World’s First Wireless Train Convoy Trial, Moving Nearly 40,000 Tons of Cargo
Gene-Edited Immune Cells Reverse Aggressive Blood Cancers in World-First Human Trial

Dutch Artist Berndnaut Smilde Creates Fleeting Indoor Clouds to Explore Transience and Atmosphere

Starlings Obscure the Sky Over Rome: A Dystopian Viral Photo

Sperm Donor with Rare Gene Mutation Leads to Urgent Screening Across 14 Countries

Cockroach Milk: A Potential Future Superfood with Remarkable Nutritional Value
News Post

Tamarind: The Tangy Superfruit Your Body Will Thank You For

Why Your Legs Show Signs of Aging First — and 3 Drinks That Can Help Keep Them Strong
Intensive Gum Disease Treatment Slows Artery Thickening, Benefiting Heart and Brain Health

The #1 Food Proven to Support Kidney Cleansing and Protection

High Olive Oil Intake Linked to Significantly Lower Risk of HER2-Negative Breast Cancer

Tight Junction Proteins and Permeability Improved by Roasted Garlic in Mice with Induced Colitis
Randomized Controlled Trial Confirms NEM® Efficacy and Safety in Reducing Osteoarthritis Pain and Stiffness

Whole Fish Trumps Pills: Study Finds Whole-Food Factors, Not Isolated Omega-3s, Lower Autism Risk

Dark chocolate and tea found to significantly lower blood pressure

Burglar Uncovers Shocking Crime During Robbery, Turns Himself In and Exposes Serious Offense

The Black Diamond Apple: A Rare Gem from the Mountains of Tibet

The Power of Pine Needles: 30 Benefits and Homemade Uses

Marvin Harvin Becomes One of the First Incarcerated Individuals to Graduate from Yale University, Highlighting the Power of Education in Prison Reform

The Hidden Power of Pistachio Shells: Benefits and Clever Homemade Uses

Warren Buffett’s Ice Cream Quote: A Simple Yet Powerful Lesson on Taxes

Papaya Seeds: A Powerful Remedy for Liver Health and How to Use Them as a Pepper Substitute

30 Amazing Benefits of Lactuca serriola (Wild Lettuce)

Why Do Button-Down Shirts Have Loops On the Back

World's Oldest Little Blue Penguin Reaches Remarkable 25 Years in Managed Care