
Viral Pneumonia vs. Bacterial Pneumonia: Key Differences
Pneumonia is a serious lung infection that can be caused by viruses or bacteria. While both forms inflame the air sacs (alveoli) and make breathing difficult, viral pneumonia and bacterial pneumonia differ significantly in symptoms, severity, treatment, and recovery time. Knowing the differences can help you seek the right care sooner—and avoid dangerous complications.
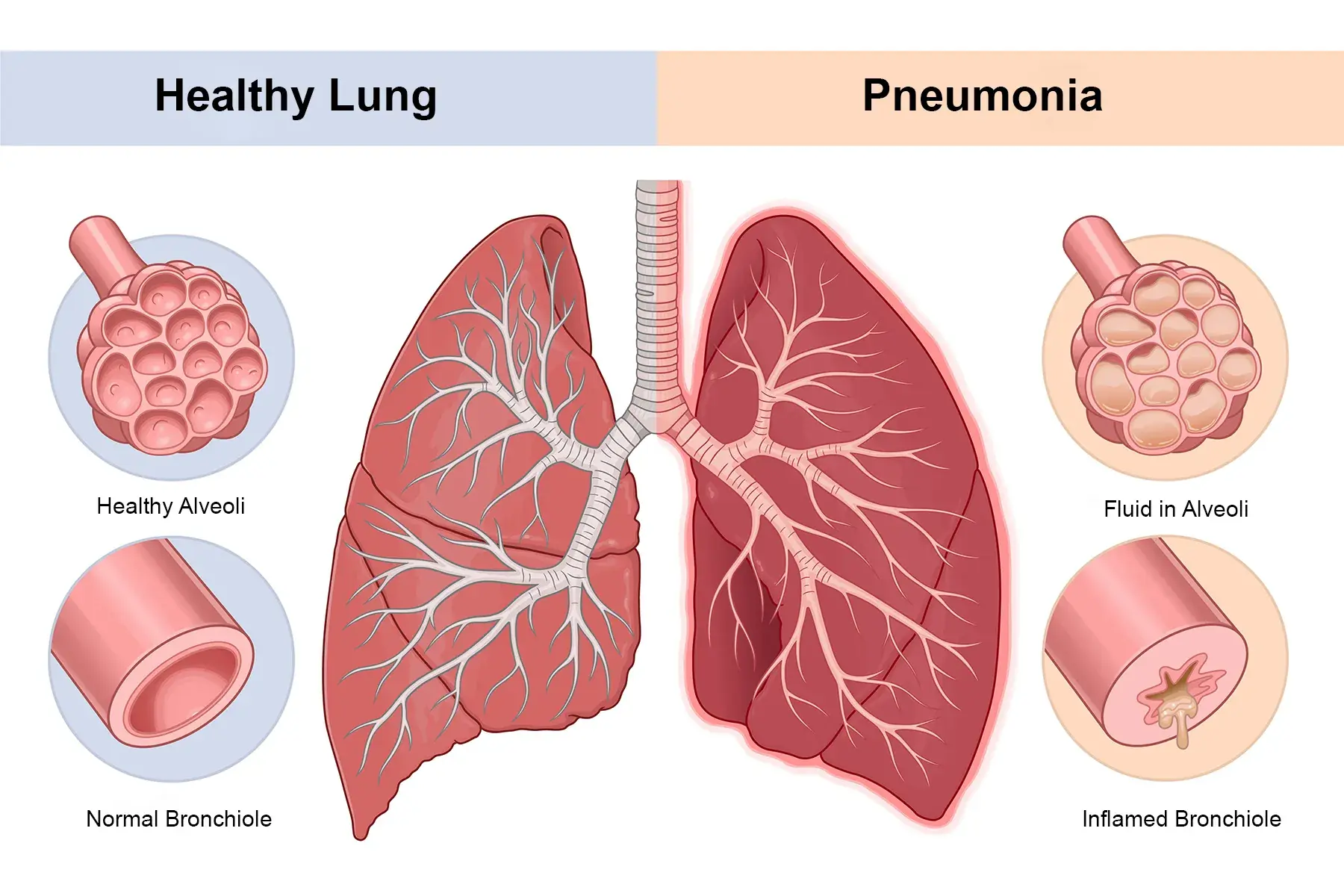
What Is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia occurs when pathogens infect the lungs, causing the air sacs to fill with fluid or pus. This limits oxygen exchange and triggers symptoms ranging from mild cough to life-threatening respiratory distress.
The two most common types are:
-
Viral pneumonia – caused by respiratory viruses
-
Bacterial pneumonia – caused by bacteria
Viral Pneumonia: Overview
Viral pneumonia is often triggered by respiratory viruses and may start like a typical cold or flu before progressing to the lungs.
Common Causes
-
Influenza
-
COVID-19
-
Respiratory Syncytial Virus
Typical Symptoms
-
Dry cough
-
Low-grade fever
-
Fatigue and body aches
-
Shortness of breath (often mild at first)
-
Headache and sore throat
Symptoms tend to develop gradually and may worsen over several days.
Bacterial Pneumonia: Overview
Bacterial pneumonia usually develops suddenly and is often more severe—especially in older adults or those with weakened immunity.
Common Causes
-
Streptococcus pneumoniae (most common)
-
Haemophilus influenzae
-
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Typical Symptoms
-
Sudden high fever (often above 39°C / 102°F)
-
Productive cough with yellow, green, or bloody mucus
-
Chest pain that worsens with breathing or coughing
-
Rapid breathing and heart rate
-
Severe weakness or confusion (especially in elderly patients)
Key Differences at a Glance
| Feature | Viral Pneumonia | Bacterial Pneumonia |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | Gradual | Sudden |
| Fever | Mild to moderate | High, abrupt |
| Cough | Usually dry | Productive (phlegm) |
| Severity | Mild to moderate | Often severe |
| Treatment | Supportive care | Antibiotics required |
| Recovery | Slower but steady | Faster with treatment |
How Doctors Tell the Difference
Accurate diagnosis is crucial because treatments differ.
Diagnostic Tools
-
Physical exam and symptom history
-
Chest X-ray (pattern differences)
-
Blood tests (white blood cell count)
-
Sputum culture
-
Viral testing (flu, COVID-19)
Doctors may initially treat broadly, then adjust once test results return.
Treatment Approaches
Treating Viral Pneumonia
Antibiotics do not work against viruses.
Treatment focuses on:
-
Rest and hydration
-
Fever reducers and pain relievers
-
Antiviral medications (for flu or COVID-19, when appropriate)
-
Oxygen therapy in severe cases
Most healthy adults recover with proper care, but symptoms may linger for weeks.
Treating Bacterial Pneumonia
Prompt antibiotic treatment is essential.
Treatment includes:
-
Targeted antibiotics
-
Fluids and rest
-
Hospitalization for severe cases
-
Oxygen or IV antibiotics if needed
With early treatment, improvement is often seen within 48–72 hours.
Possible Complications (If Untreated)
Both types can lead to serious complications, including:
-
Respiratory failure
-
Sepsis
-
Lung abscess
-
Worsening of chronic conditions (asthma, COPD, heart disease)
Bacterial pneumonia generally carries a higher immediate risk, while viral pneumonia can pave the way for secondary bacterial infections.
Who Is Most at Risk?
-
Adults over 65
-
Children under 5
-
Smokers
-
People with asthma, diabetes, or heart disease
-
Immunocompromised individuals
Vaccination and early treatment are especially important for these groups.
Prevention Tips
-
Get vaccinated (flu, COVID-19, pneumococcal vaccines)
-
Wash hands frequently
-
Avoid smoking
-
Strengthen immunity with sleep and nutrition
-
Seek care early when respiratory symptoms worsen
News in the same category


12 Bizarre Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency You Need to Know
8 warning signs of colon cancer you should never ignore
The daily drink that helps clear blocked arteries naturally

This old school home remedy will soothe your back, joints & knee pain in just 7 days!

Sleep Apnea: Symptoms, Risks, and Treatment Solutions

Allergic Rhinitis: What Triggers It and How to Manage It

COPD Exacerbation: Symptoms That Indicate a Flare-Up

Bile Reflux vs. Acid Reflux: Key Differences You Need to Know

Ulcerative Colitis vs. Crohn’s Disease: What Makes Them Different

How to lower blood sugar without giving up carbs

Top 8 warning signs of ovarian cancer women absolutely need to know
Don’t Ignore These Warning Signs of Vitamin B12 Deficiency!
Why you keep waking up with dry mouth—and what it may be telling you

Here’s What Eating Blueberries Every Day Does to Your Body, Says a Registered Dietitian
How To Get Rid Of Eczema: 13 Natural Remedies Backed By Research
Scientists Explain The Effects of Eating Too Much Sugar

Top 10 Functional Foods In The World Which Fight Cancer Cells
90% of diabetes cases could end if you STOP these foods
News Post

Put a few ice cubes in the washing machine with your wrinkled clothes and do this, and you'll see an unexpected miracle.

A 2013 study conducted by researchers

Experienced tofu makers share tips on how to distinguish between clean tofu and tofu containing gypsum.

Don't put the purchased sấu fruit in the refrigerator right away: Follow this one extra step, and the sấu fruit will stay fresh and delicious for a whole year, retaining its original flavor.

How Retired Buses in France Are Becoming Mobile Book Rooms for Thoughtful Travel

How Turkey’s ‘Micro Animal Closets’ Are Offering Care to Stray Animals in Urban Parks

How Portugal Is Turning Urban Parking Towers into Night Shelters for the Homeless

How Retroftted City Buses Are Providing Warmth and Rest for the Homeless in Canada

People with heart problems should avoid these 4 things to reduce stimulation to the heart

12 Bizarre Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency You Need to Know

8 warning signs of colon cancer you should never ignore

The daily drink that helps clear blocked arteries naturally

This old school home remedy will soothe your back, joints & knee pain in just 7 days!

Sleep Apnea: Symptoms, Risks, and Treatment Solutions

Always the Strong One: The Emotional Cost of Holding Everything Together
A New Cancer Vaccine Shows Long-Lasting Protection in Preclinical Studies

Allergic Rhinitis: What Triggers It and How to Manage It

COPD Exacerbation: Symptoms That Indicate a Flare-Up
